Do-it-yourself water-heated floor on the ground. Recommendations for the installation of a water heated floor on the ground Installation of warm water floors on the ground
Floors on the ground are arranged in individual residential buildings, baths and utility rooms for all types of foundations, with the exception of columnar ones. On any soil, you can make a dry and warm floor. It is a reliable, practical and durable design.
Modern owners of private houses prefer to heat the premises through the floor. The best option for such heating is floors mounted directly on the ground. If we consider them in a section, then this is a layer cake, consisting of several layers. The bottom layer is the primer, and the top coat is the top coat. The layers are arranged in a certain sequence, each with its own purpose, thickness and function.
The main disadvantage of floors on the ground is the high financial costs and the time required for their manufacture. Requirements are also imposed on the soil: it should not be too loose, the standing groundwater should not be closer than 5–6 m.
The layered construction of a warm floor on the ground should provide sound and heat insulation, prevent the penetration of groundwater, not accumulate water vapor in the floor layers and create comfortable conditions for residents.
concrete floors
Concrete floors on the ground do not provide for a basement and space under the floor for its ventilation.
Important! When laying concrete floors on the ground with a close standing of groundwater, it should be borne in mind that their level can change within a short time. This must be taken into account when laying layers.

The classic floor on any soil consists of 10 layers:
Layers that protect against groundwater and distribute the load
- Cushion made of compacted clay. It is necessary to stop the rise of groundwater. If, after removing the layer of soil, you reach the clay, then it must be properly prepared. A layer of clay cuts off the penetration of groundwater upwards.
- Sand pillow. Its purpose is also to prevent the ingress of groundwater and equalize the load on the ground. Sand weakens the capillary rise of water and evenly distributes the pressure of the floor layers lying above it on the ground. Any sand will do.
- Large rubble. This is a kind of drainage, its purpose is to make the foundation strong, to distribute the load. It generally does not allow water to flow upwards due to the capillary property. Crushed stone is used fractions - 40–60 mm.
The first three layers should be placed in this order, each with a thickness of 10 cm in a compacted state. Layers must be rammed.
Advice. By hand it is difficult to compact a thick layer of sand or clay, therefore, when filling such a layer, thinner layers (10–15 cm) must be successively added and compacted.

- Waterproofing layer (roofing material or polyethylene film). It is placed directly on the crushed stone, and it serves both to protect the crushed stone from the flow of concrete solution into it from above, and as an obstacle to the penetration of water vapor into concrete layer from below. The film is laid with a whole sleeve (without cutting) with an overlap, wound onto the walls, gluing the places of overlaps with adhesive tape.
- Rough coupler 80 mm and thicker. For it, washed sand and fine gravel (10–20 mm) should be taken. Steel fiber is added to the solution or reinforcement is used. For the screed to be ready for the next stages of work, it needs to withstand a certain time.
- Waterproofing layer (coated waterproofing, roll or film). If the first layers are laid correctly and efficiently, roofing material without powder in 1-2 layers or a film with a thickness of at least 120 microns can be used for waterproofing. The waterproofing layer must be monolithic. If roofing material is used, the overlaps are smeared with bituminous mastic, the overlaps of the plastic film are glued with adhesive tape.
- Insulation. You can insulate the floor with expanded clay, extruded polystyrene foam, polystyrene foam. The thickness of polystyrene plates and foam sheets depends on climatic conditions, but not less than 5 cm. Expanded clay is covered with a layer of 15 cm.
- Waterproofing. On expanded clay or other insulation, it is recommended to lay waterproofing. This will protect the insulation from moisture from the upper layers and improve its thermal insulation properties. At this stage, a thick polyethylene film is used, which is laid in a continuous layer.
- The screed is clean. It can accommodate floor heating heaters (water heating circuits, cable mats or heating cable). A layer of finishing screed is poured 50 mm or more. It is reinforced using composite or steel reinforcement, fiber is added to the solution.
- Finish coating. If all layers are made in the specified order, any coating can be laid.
Pros and cons of concrete floors on the ground
Advantages
- Reliably protect the room from the cold. No matter what the weather is outside, the soil will always be warm.
- Any insulation and waterproofing materials are applicable, as well as any coatings for finishing the floor.
- The main load is distributed over the ground, no need to do additional calculations. If a heavy load is expected, you just need to increase the thickness of the three lower layers.
- It is possible to organize the heating of the house through the floor, which will quickly heat up and evenly distribute heat, preventing drafts.
- Protect the house from mold, reproduction of microorganisms.

disadvantages
- It is required to take into account the location of the groundwater level.
- They can significantly reduce the height of the room with certain design features of the house.
- The technology is not applicable for pile and column foundations.
- If a system malfunctions, its repair and dismantling is a very time-consuming and financial undertaking.
- The installation of floors is a lengthy and complex procedure in terms of volume of work, as well as costly in finance, it is best to perform such work during the construction of a house.

How to make a concrete floor on the ground yourself
It is best to remove the soil and fill in the first three layers immediately after the construction of the foundation of the house. First, calculations are made to what depth the soil needs to be removed. The level of the finished floor is taken as the zero mark. Add up the dimensions for the thickness of each layer, for example:
- laminate + substrate -1.5 cm;
- screed + waterproofing - 6 cm;
- thermal insulation + waterproofing - 6–11 cm;
- concrete screed 8–10 cm;
- crushed stone, sand, clay - 15 + 15 + 10 cm;
The total value is 61.5 cm. If the layers are thicker, the soil will have to be removed for great depth. Add 5 cm to the resulting depth.
A hole is dug over the entire area of \u200b\u200bthe building to the calculated depth and the soil is removed. For the convenience of subsequent work on the walls of the foundation along the entire perimeter, the levels of the floor layers are marked. This will make it easier to align them. The soil does not necessarily contain clay, for clarity, we give the procedure for working on soil that does not have a layer of clay.
Floors on the ground: preparation and pouring
Clay.
Any clay is poured with a layer thickness of at least 10 cm. It is leveled and watered abundantly with a weak liquid glass(solution of 1 part glass in 4 parts water). The wet layer is tamped with a piece of timber 200x200mmx1.5 m. On a large area, you can use a vibrotamping or vibrocompacting machine by renting it. If, as a result of compaction, the layer turned out to be thinner, the clay is poured and compacted again.
Advice: a durable rammer can be made from a channel cut (20x30 cm) by welding a piece to it metal pipe in which to pour sand for weighting.

Clay is one of the layers of the concrete floor
The leveled compacted clay layer is poured with milk from cement (2 kg of cement is stirred into 10 liters of water) so that there are no puddles, and left for a day so that the process of chemical interaction of cement with liquid glass is completed completely. Walking on it at this time is not recommended.
Sand
Trying not to walk on the prepared clay layer, they pour sand on 15 cm. You can walk on it. It is leveled and also compacted to the appropriate mark on the wall of the foundation of the house.

rubble
It is covered with sand and also carefully compacted with a rammer. Especially carefully align the rubble in the corners, tamping it tightly. The result should be a flat horizontal surface.

Polyethylene film
Uncut sleeves are laid with an overlap of 10–15 cm, led onto the walls by 3–5 cm. The overlaps are carefully glued with adhesive tape. It is recommended to move in shoes with soft soles, trying not to damage the film with sharp edges of pieces of rubble. Although experts say that this is just a technological technique, the film also performs its waterproofing functions.

Rough coupler
For it, you can order ready-made "skinny" concrete or make a solution yourself by mixing M500 cement with crushed stone and sand in a volume ratio of 1: 4: 3. Metal fiber is also added to the mixture in the amount of 1–1.5 kg per 1 m 3 of the solution. The solution can be poured, aligning with beacons or marks on the walls of the foundation. It should be borne in mind that the even horizontal surface of the rough screed will simplify the further stages of the floor installation.

After two days, the concrete is ironed with a mixture (10: 1) of water with liquid glass and dry cement. They do it this way: with a roller or spray gun, moisten the entire surface of the screed with a solution, then sprinkle it with a thin layer of dry cement and rub it with a grater into the concrete. This technique will increase the strength of concrete by an order of magnitude and increase its resistance to water. The screed needs at least 1.5 months to fully mature, but subsequent work can be carried out after 1-2 weeks.
Waterproofing
The prepared rough screed is covered with liquid bitumen (primer), especially carefully smearing the corners and capturing 5 cm of the walls. On such a bitumen-treated base, strips of roofing material are glued with an overlap of 10 cm and a 5 cm overhang of the walls. In places of overlap, the strips are heated with a hairdryer or coated with bituminous mastic.

The strips of the second layer are placed offset by half the strip in the same way. Ruberoid is especially carefully glued in the corners of the room. When performing this type of work, it is recommended to move on the floor in shoes with soft soles.
thermal insulation
The purpose of laying this layer is clear. best material in this case there will be plates of extruded polystyrene foam (EPS). A 5 cm thick sheet of this heat insulator replaces expanded clay, poured with a layer of 70 cm in its effectiveness. The material practically does not absorb water and is characterized by high compressive strength.
In order for XPS sheets to serve more efficiently, they are recommended to be laid in 2 layers, each of them 3 cm thick, shifting the joints by 1/3 or ½ sheets. This will completely eliminate cold bridges and improve the thermal insulation properties of the insulation. The joints of the XPS boards in each layer should be glued with special adhesive tape.

If expanded clay or mineral wool is used as a heater, an additional layer will be required. waterproofing material, for example, a plastic film to protect the insulation from the moisture of the finishing screed.
Finishing screed
Along the perimeter of the room, a damper tape 1.5–2.0 cm is fixed to the walls for the entire height of the screed. End damper tape fixed on the insulation boards. The screed is reinforced with a 3 mm masonry mesh with a mesh size of 100x100. If it is planned to install a warm electric floor, a reflective waterproofing material is placed on the XPS sheets. When installing water heating circuits, the thickness of the screed will be needed more, the water heating pipes must be in the thickness of the screed.
The reinforcing mesh is positioned in such a way that it is in the screed and does not protrude onto its surface. To do this, use coasters, pieces of wooden bars, metal profiles or, for example, corks from plastic bottles. The combination of reinforcement and leveling beacons is a rather complicated task, therefore it is recommended to pour the screed according to the mark on the walls, and then pour a self-leveling self-leveling floor over it with a thin layer.

For screed, ready-made dry mixes are used or a solution is prepared from washed river sand and cement in a ratio of 3: 1. The work is done quickly. The screed will be hardened for 4-5 days, and its final readiness will be in a month. The use of ready-made mixtures with special additives will accelerate the maturation of the screed. Its readiness is checked with a paper napkin, laid on the floor and covered with a sheet of polyethylene. If the napkin remains dry in a day, the screed is ready for applying a self-leveling mixture and installing top coats.
Wooden floor on the ground on logs
In private houses, wooden floors are most often made. There are several reasons for this:
- in frame houses the wooden floor is an extension general design building;
- wood is a natural material that is safe for the health and life of the residents of the house. Some types of wood have a beneficial effect on health;
- the tree is easy to process and lay even for a beginner in construction work;
- wood treatment with antiseptics significantly increases its service life;
- floors are easy to repair and open if necessary.
The device of a wooden floor on the ground in a private house on the ground floor is quite feasible with your own hands. The floor can be insulated, communications can be hidden under it, basement. It is laid on logs, which can be mounted when tying the strip foundation.

As a log, logs sawn into two halves, bars with an aspect ratio of 1: 1.5, double thick boards of wood are used conifers. If the logs were not mounted when tying the foundation, they can be placed on prepared soil or on brick posts on a concrete base.
Logs are placed at a distance, which is determined by the thickness of the floorboard. So, if the board is 50 mm, the logs are set after 100 cm, if the board is 35 mm, the logs are set after 60 cm. The first and last logs are installed at a distance of 20 cm from the wall, the rest are placed between them. If the distance between the lags is somewhat greater than required, then the number of lags is increased, and the extreme ones are not shifted. If the room is rectangular, the logs are laid along a long wall. For a square room, there is not much difference.
Installing a lag on the ground (cold floor without underground)
Work is performed in the following order:
- They calculate to what depth to take out the soil, based on the thickness of the log, layers of sand, crushed stone, clay or expanded clay.
- They remove the completely fertile layer of the earth and dig deeper, based on the estimated depth. The remaining soil is well leveled and compacted over the entire area of \u200b\u200bthe future floor. Compaction should be done with a rammer. On large areas, you can use a vibrator to compact the soil.
- Pour any sand with a layer of 15 cm or more and the same layer of rubble (or construction debris) and rammed. If the house is on clay soil, pour and ram a layer of clay, and then successively sand and gravel on it. If the soil is sandy, then you can fill up a layer of calcined sand or slag ventilated for at least a year. You can pour a layer of expanded clay. The thickness of all layers of the fill should be approximately three times the height of the lag. All layers are carefully leveled and rammed.
- On lined upper layer(sand, slag or expanded clay) install logs treated with an antiseptic, they are sunk into the bedding and well rammed around. The upper level of the lag should be located so that the floor boards are in desired position. Logs are attached to the foundation or lower crown.
- Floor boards are mounted along the lags.

Logs on brick columns (warm floor with underground)
Usually logs are installed on posts stacked in 2 bricks (25x25 cm).
- The fertile soil is removed, the remaining soil is leveled and rammed.
- Carry out the marking of the locations of the columns under the logs (in the event that the logs are not installed when tying the foundation). The height of the columns depends on which part of the wall the logs will rest on. This can be a beam of the first row or a grillage (a roofing-covered beam of the foundation binding).
- The cords are pulled so that they are located above the center of all the planned posts, and from the cords at an equal distance, pegs are driven into the ground to the width of the brick posts (25 cm in each direction).

Bases for posts
In marked places, pits are dug 40x40 cm in size and 15–25 cm deep on rocky or sandy soil and up to 45 cm on clay and loose soils. A layer of sand 10 cm and a layer of crushed stone of a large fraction of 10 cm are successively poured into deep pits and rammed.
Advice: If the groundwater level is close, the pits can be filled with a layer of clay 20–25 cm and compacted (this is a clay castle).
- The bottom of the pits is covered with plastic wrap or roofing material.
- The concrete base under the brick columns is poured so that it protrudes 5 cm above the level of the compacted soil. To do this, install the formwork from the boards (about 5 cm high above the ground) and the reinforcement in the pits. As reinforcement, you can use a wire or a mesh with cells of 10x10 cm.
- Concrete is poured (cement: sand: crushed stone (fr. 5–10 mm) = 1: 3: 2–3 and water to a thick consistency) and left for several days to mature.

Making columns
- A roofing material is laid on a concrete base in 1–2 layers so that it protrudes 1–2 cm beyond the edges.
- Brick columns of 2 bricks are laid out strictly vertically (on a plumb line) on the roofing material so that the last layer of bricks is perpendicular to the direction of the log. To obtain a solution, cement M100 and sand are mixed in a volume ratio of 1: 3 and water is added by eye.
- A roofing material is placed on the column and a lining made of plywood treated with an antiseptic or OSB boards square shape so that it protrudes 2 cm beyond their edges.
Installation and alignment of the lag
Logs are installed on these linings. Leveling the lag is a long and painstaking job. For this, linings are used or part of the support is cut off. As a result, all lags should be at the same level.

Having aligned, they are attached to the posts with corners, and to the elements of the walls or foundation - with special fastening systems used for the construction frame houses. Holes are pre-drilled in concrete and dowels are inserted.
Floor installation

The last stage of the process - installation of the floor
- For a floor with insulation, bars of 30x50 or 50x50 mm are attached to the bottom of the log, on which a draft floor is laid from a thin unedged board 20 mm thick.
- A vapor barrier (vapor barrier membrane) is laid on the subfloor.
- A soft insulation (mineral wool) is placed on the membrane, so that its sheets fit snugly between the lags and tightly adjoin one another, not reaching about 2 cm to the top of the lag.
- Floor boards are laid along the logs.
Do-it-yourself floors on the ground
When planning to make a warm floor in the house on the ground, it is advisable to make the structure in two stages: first, pour a rough screed onto the lower layers, and only after it has matured, lay all the other layers on it.
The fact is that the soil and, accordingly, all layers above it can sag. Even if the soil is compacted, even if it is rammed, there will be movements. He lay simply, without load. If you lay a warm floor cake on top, and it weighs a lot, drawdowns will begin, cracks will appear. It can even break the elements of the warm floor. Then all the money will be thrown to the wind. That is why experts advise first to make a rough floor according to all the rules, and then lay a water floor on top. So much more reliable.
Yes, many have a warm floor on the ground without a screed, and nothing sags. But not for everyone and not always. So think carefully. A warm concrete floor on the ground will be more reliable with a rough screed. If you still decide to do without this layer, install at least two reinforcing frames: the first under the heat insulator, and the second in the screed. Then, with careful ramming, everything can stand well.
First of all, we determine the level to which you need to remove the soil. The soil must be removed. If a layer of humus or plant remains do not remove, they will begin to decompose and "smell". Therefore, you will make a draft floor or not, but you need to remove all unnecessary. Moreover, the fertile layer is usually the loosest, and it will definitely settle and can pull all the layers lying above with it. The rocks lying below are denser, firstly because they experience heavy loads, and secondly, because living beings and microorganisms live there less.
For the whole cake of a warm floor on the ground, it can take from 20 cm or more (in some regions - much more). Therefore, you need to start marking with zero level- where you will have a finishing floor. Mark it, and then consider how deep you need to go. It is advisable to mark the level of each layer: then it will be easier to navigate.

The correct design of a warm floor on the ground is as follows:
- Take off fertile soil remove all rubbish and stones. Level and compact the remaining soil. This must be done very carefully, and verified by the level. This is the basis for all subsequent materials.
- A layer of compacted sand (level). Any sand is taken for filling. The main thing is to compact it well and level it again.
- A layer of expanded clay or crushed stone (preferably crushed stone due to lower thermal conductivity). Fraction - small or medium. We compact for a long time and persistently until it becomes almost a monolith.
- Pre-stretch. There are two options here:
- Spill crushed stone and sand with a liquid solution (sand + cement in a ratio of 2: 1).
- Fill in the black screed. The desired thickness of this layer is 5-7cm. And for reliability, lay a reinforcing mesh made of metal wire 3 mm, with a cell of 10 * 10 cm. Such a subfloor is more reliable. It will withstand heavy loads.
- After everything has set and the concrete has hardened, a layer of waterproofing is laid. If the primer is dry, this is usually a polyethylene film, preferably 200 mn in two coats.
- Styrofoam plates (glue the joints with adhesive tape so that the solution does not leak).
- A layer of metallized waterproofing (not foil, but metallized).
- Underfloor heating fixing system and heating tubes, cables, etc.
- Underfloor heating screed, preferably reinforced.

The thickness of all layers of the underfloor heating cake on the ground depends on the region: the colder, the more. In the south, it can be 2-5 cm, but the further north, the more massive layers are required. Each of them is well compacted and leveled. You can use manual rammers, but mechanical ones are much more effective.
Particular attention should be paid to the heat insulator. It is recommended to use expanded polystyrene in plates, its density is not lower than 35 kg / m 3. For the northern regions, it can be 10 cm or more. If the thickness of the thermal insulation is large (extruded polystyrene foam), it is advisable to use two layers of boards. And lay them so that the seams of the lower layer overlap with the slab lying on top. Glue the joints of each layer with tape.
To protect against dampness, do not forget to carry out waterproofing work with the foundation before starting all work. It is also important not to forget to isolate the foundation from the entire underfloor heating structure. It is necessary to put the same polystyrene foam in plates along the perimeter. In general, the idea behind hydro and thermal insulation is this: to reduce heat loss, you need to isolate your floor from everything except indoor air. Then the heating will be economical, and the rooms will be warm.

Choice of thermal insulation key moment in the organization of a warm floor
Process technology at high groundwater levels
If the groundwater is high, the correct sequence of layers is not everything. You need to get the water out somehow.
If the depth of laying the underfloor heating layers turned out to be lower than the level of soil water, drainage is necessary. For him, at least 30 cm lower required level making a drainage system. It is advisable to pour river sand, but such volumes cost a lot, so you can use other rocks, but not peat or black soil. As an option - excavated soil mixed with crushed stone.

When laying thermal insulation boards their joints need to be glued with adhesive tape - so the solution will not flow into the gap
The selected material is poured in layers of 10 cm, each of which is compacted and spilled with water. Layers are usually made three, but more can be. On compacted sand or soil with crushed stone, we lay a layer of geotextile. This modern material, which will pass water down and will not mix different materials. It is not damaged by insects and animals, has high tensile strength. Also, geotextiles additionally equalize the mechanical loads that the floor will experience.
At the same stage, you need to take care of both the hydro and thermal insulation of the floor from the foundation. Can be used for this purpose bituminous mastic or other modern and reliable waterproofing materials and impregnations. And the thermal insulation is standard: the inner perimeter of the foundation is covered with expanded polystyrene plates.
Then there are layers of sand and gravel, and they are poured rough screed. Spilling with a liquid cement-sand composition in this case is undesirable. A rough screed is needed for reliability. After it dries, a layer of waterproofing should be applied. With a high level of groundwater, it is better to use not polyethylene, but welded waterproofing or polymer membranes. They are more reliable, although they are more expensive.

Further, all layers, as previously recommended: a heat insulator, a metal-coated hydrobarrier, and fasteners with (or, for example). All this is covered with a metal reinforcing mesh and filled with another layer of mortar. And then - depending on the one used.
Results
Warm floor in the house on the ground - quite complex structure. In order for it to be reliable, a rough screed is needed. If for some reason it is not possible to make a screed, you can, in extreme cases, get by with tamping the layers.
Any owner of a private house faced the problem of heating. Especially important element heating are the floors. The right floors do not let dampness into the house and keep it warm for a long time. IN Lately floors on the ground are rapidly gaining popularity.
They are effective because they are practical, reliable and relatively inexpensive. If a basement is not planned during construction, then on the ground in a private house - one of the best options thermal insulation.
Such a design is built directly on the ground, taking into account all its irregularities and will help prevent cold from entering from its surface. This option is far from the easiest, but it can be implemented independently, without hiring workers or equipment.
Such floors have nothing to do with baking. They are called "pies" due to the fact that their thermal insulation has many layers and in appearance they slightly resemble a layer cake. If you still decide to build, then keep in mind that underfloor heating on the ground requires some measurements.
For example, ground water should not be too high, because this will make your "pie" float. You should also make sure that the soil is strong enough, because the whole structure can simply settle. It should also be remembered that the “pie” reduces the height of the room, and the dismantling of such a structure is a difficult matter, so everything must be done correctly the first time.

Foundation preparation
The device of your structure includes several layers, and therefore several stages too.
Don't move on to the next step until you've completed the previous one.
The first thing we must do is to prepare the base directly on the ground itself. For this you need:
- remove the layer of earth. This must be done without fail, because the fertile layer is usually loose, and the remains of vegetation can then begin to rot and decompose - this will cause bad smell, and it will be impossible to stay in the room. The floor cake requires about 20 centimeters, or even more (depending on the region).
Tip: measure each level and calculate how deep you need to remove the soil. Leave marks on each of the levels to make it easier to navigate;
- remove all rubbish and stones. This is also very important, because one unnoticed pebble can cause unevenness;
- the remaining clean soil is leveled and compacted. This must be done very evenly - along the level.
Separating layer
To prevent anything from moving apart, the foundation of the pit must be lined with geotextiles or dornite. It is better to choose the first, because it also protects against the germination of weeds.
The correct underfloor heating cake must be separated from the parts of the foundation and the basement (the lower part of the building wall lying on the foundation) with a special layer. It is strictly forbidden to rest the plate on the protruding parts of the structure.
The correct floor should be made in the form of a floating screed.
Underlayment
Further, some variation is allowed. To floors on the ground proper pie not settled, there are several options for laying. The underlying layer must be selected taking into account the height of the groundwater, the expected loads, the same looseness of the soil, and so on.
Most often, a concrete layer is used - this is the most reliable and proven option. But there are cases when it is impossible to use concrete, then the following materials can be used:
- sand. It is used exclusively on dry soils to avoid water absorption through small holes in the sand. It is noteworthy that such a process can occur even in cases where dew forms on the surface. It will also be more difficult with sand because it needs to be perfectly evenly compacted, again, this must be done with the help of a level;
- rubble. Crushed stone works well at high groundwater levels. In a layer of crushed stone, capillary absorption is completely impossible. Laying should also occur evenly;
- natural soil. It is used quite rarely and is, most often, coarse sand or gravelly soil (soil with a grain content larger than 2 mm, but less than 50 mm). It will fit if neither groundwater nor special looseness of the soil is observed.
- expanded clay. Also suitable.

Mineral wool boards will be an excellent insulation ( thermal insulation material which is made from mineral wool and synthetic binder). They have high density are quite strong and long lasting. Such plates are laid in two layers, they can be vulnerable to moisture, so they need to be treated with a water-repellent substance.
Footing
Whatever bonding material you use, you will still need a footing. You will need skinny concrete mix B 7.5. We remind you that lean concrete is concrete in which the content of cement and water is reduced, and the content of filler is increased.
Such material is much “weaker” than its “fat” counterpart, but at the same time cheaper. In our case, it is impractical to use a stronger concrete composition.

The footing is not reinforced, but must be separated from the basement or parts of the foundation. For this, pieces of foam or a special tape are suitable.
If you want to further reduce the cost of the floor cake on the ground, then you can use the saturation of the upper layers of crushed stone with cement milk. The resulting crust should be perfectly even, and its depth should be several centimeters. This trick will help make a waterproof concrete crust.
Waterproofing and insulation
Finally, we got to waterproofing and insulation. At this stage, it is necessary to isolate from moisture. We will do this through waterproofing film or special membrane. Lay the film overlapping, and seal the gaps at the joints with construction tape.
The first thing you need to put is waterproofing material, and not thermal insulation.
As a heater, use a layer of expanded polystyrene foam or dense polystyrene. You can also use special plates, but we advise you to do this only if the load on the surface of the structure is large.
You can choose the thickness of the layer yourself, depending on the climatic conditions of the region, usually it is from 5 to 20 centimeters. Joints and cracks fill with construction foam.

On top of the resulting "sandwich" lay another layer of waterproofing material or just roofing material. This is optional, but if you live in a humid region with high groundwater, it's best to play it safe.
damper layer
Lay a damper tape over the walls, which will be slightly higher than the planned thickness of the screed. This is necessary in order to isolate the future screed from the bearing elements of the foundation or basement.
We remind you: the floor on the ground of the cake is strictly forbidden to be rigidly connected with the elements of the base.
Instead of tape, you can use strips of polystyrene foam, which also needs to be laid a little higher. Excess pieces can then be cut off.

floating screed
Such a screed performs several functions at once: it produces thermal insulation and sound insulation at the same time. The design feature of this screed is that the solution is placed on the surface of the insulation, and not on the base.
Well, or on a layer of roofing felt, if you covered the insulation with it from above. Here's what to look out for:
- it is desirable to do everything at once. IN large rooms this will not be possible, so separate the finished and unfinished sections with partitions. This will create an expansion joint and help the screed to subsequently take on completely;
- if possible, pour over plaster beacons;
- the thickness of the screed should not exceed 20 centimeters, the minimum should not be less than 5. Be guided by the expected operational loads and the type of future flooring.
Reinforcement of the floor on the ground
Reinforcement - milestone which will help strengthen concrete screed. The metal mesh will also serve to fix the pipes on it.
The reinforcing mesh should be a wire with square cells with a thickness of 5 to 10 centimeters. Depending on the design features thickness may vary.
The grid laying is as follows:
- a protective layer extends from below - polymer material. The thickness of this layer should not exceed 1.5 - 3 centimeters.
- grid installation;
- installation of special beacons (in small rooms it is not necessary);
- pouring the mixture.
Walking on a non-hardened mixture is not advisable; it is better to install special paths along which you will move. Even when the mixture is taken, it is better to continue walking along these paths anyway, metal meshes have a much lower density and can bend under the weight of a person.

Stiffening ribs under partitions
In order for the cake of a warm water floor to hold better, it must be strengthened. This is done by stiffening ribs. To create them, it is laid under the partitions - a material that consists entirely of closed small cells.
The material must be laid intermittently, and the resulting voids should be used for laying the reinforcement. Thus, it should turn out that the entire structure is evenly reinforced with reinforcing bars.
Underfloor heating contours
For even greater savings in a warm floor on the ground, you can install it, this will allow you to create a literally warm floor. The reinforced mesh has just the right dimensions for placing a heating pipe on it.
To connect to the collectors, pipes are brought out near the walls. The walls must be pasted over with a protective tape. As for all other communications, they need a similar system.

After the final filling of the "pie" everything will be ready. Then you are free to do the floor the way you want. This design is just one of options, if you wish, you can modify or any of its elements. It all depends on your finances and construction conditions.
Video: underfloor heating cake on the ground
IN last years many people leave noisy metropolitan areas, erecting private houses outside the city. Houses built from natural materials are especially popular. After concrete walls apartment life in wooden house seems like heaven. Due to the availability of materials, the construction of such houses is much cheaper, and the healthy microclimate created natural material makes it easier to breathe.
But what to do if a wooden house has already been built, and underfoot instead of the usual concrete base- dirt floor? In this case, it is advisable to install underfloor heating, laid in a concrete screed, and powered by a boiler. And as finish coat in a wooden house, use laminate or porcelain stoneware tiles, since these materials are the best conductors of heat. In this way, it will be possible to make your home warm and cozy, as close as possible to the comfort of a city apartment.
Features of a warm floor on the ground
In a wooden private house, alternative heating systems are increasingly being used, which include underfloor heating, laid under the laminate.
Moreover, it is water systems that are most popular, allowing significant savings on energy consumption.
Having equipped a dry warm water floor under a laminate on the ground in a wooden private house, you can significantly reduce the cost of building a foundation, and put the house into operation faster, providing high level comfort.
It is very important that such heating has a high degree of durability. And therefore the only way its installation is the installation of system pipes in a concrete screed.
Despite the apparent complexity of the work on the organization of such heating, it is quite possible to organize it independently, carrying out work in several stages.

When arranging heating on the ground in the house, it is necessary to achieve the following results:

Underfloor heating cake on the ground
Comply with everything necessary requirements and to ensure the rational use of the "warm water floor" system in the house, powered by a boiler, helps a special multi-layer structure, laid under the laminate. So what layers does the pie of the system, equipped on the ground, and working from a common heating boiler, consist of?
Before proceeding to direct work in the house associated with laying layers on the dirt floor, it is necessary on the surface of the walls around the entire perimeter of the room in log house draw a control line. This stage is necessary in order to adjust each layer of the cake.
Only after that you can proceed to the next stages of work, which ultimately allows you to get a dry and warm floor.
Underfloor heating cake on the ground
Laying an insulating pad
The organization of heating in the form of a water heated floor on the ground, powered by a boiler, requires preliminary insulation - pillows. And its first layer should be dry river sand of a large fraction.
It is poured onto the waterproofing covering the soil floor with a layer equal to 15 cm, after which it is carefully compacted in a wet way. If the sand is not compacted, then in the future the soil may subside.
If groundwater is located close, then first the earthen floors must be provided with a drainage system.
The next step will be laying a pillow of large gravel or expanded clay. Moreover, it is preferable to use crushed stone, since it has a very low degree of thermal conductivity, which means it will more effectively retain heat inside the cake.
It should be borne in mind that the thickness of the pillow for the “warm floor” system, together with sand, should not exceed 30 cm.
Pouring a rough screed
To increase the strength of the structure, before proceeding with the pouring of the rough screed, it is necessary to lay a reinforcing mesh. Also when installing a water floor heating in a wooden house must be guided general requirements to the length of the pipeline in the circuit: it should not exceed 100 m. Therefore, if the area of \u200b\u200bthe room is large, the floor must be divided into sections, laying a damper tape around their perimeter.

The thickness of the rough screed should be 10-15 cm. It is possible to eliminate cracking of the rough screed when arranging heating on the ground under the laminate if it is wetted daily with water, covered in this form with plastic wrap. Such manipulations must be carried out within a week.
Laying waterproofing
To obtain a dry warm floor, a waterproofing layer is laid on its rough surface, which can be an ordinary polyethylene film with a thickness of 250 microns or more. However, PVC membranes will handle this function more effectively. It should be noted that along the perimeter of the entire room it is necessary to make an allowance for the walls equal to 15 cm, fixing it with construction tape. They also glue all the joints of the film. Excess waterproofing is removed after all work is completed.

Laying thermal insulation
To get a dry and warm floor in a private house allows laying a heat-insulating layer. This minimizes heat loss. Styrofoam or extruded polystyrene plates with a thickness of 5 cm to 10 cm can be laid as thermal insulation. The latter option is preferable.
Insulation of the base before laying pipes
Laying water circuits and finishing screed
It is necessary to lay a reinforcing mesh on the heat-insulating layer, which in this case will perform two functions:

The contours of the warm floor on the ground, laid under the laminate, may consist of various pipes. But the most popular are pipes made of metal-plastic and cross-linked polyethylene. Underfloor heating circuits are laid with a snake or snail, observing a certain step between the turns of the system.

Regardless of the method of laying the circuits and their number, they are all connected to a collector, which is installed on the wall in close proximity to the floor. Next, the system is pressure tested and tested for thermal stability.
For cooking cement-sand mixture used cement brand M100. And the mixture itself is prepared by mixing with sand in proportions of 1: 3. The drying time of the finished floor is about 28 days, after which it will be possible to lay the laminate. You can reduce the waiting time if you use the dry method of laying the mixture.
When installing several water circuits laid under the laminate, it is necessary to use expansion joints created by separating sections of the room with a damper tape.
How to install a heating boiler
The most important stage in the organization of heating in a private house is the installation of a boiler. certain power, which should be determined based on the total power of all circuits of a warm water floor and a margin equal to 15-20%.
The circulation of the coolant in the system is carried out using a pump, which can be included in the boiler package or purchased separately. If the area of the house exceeds 150 m², additional pumping equipment is installed in manifold cabinets.
It should be noted that when installing several floor heating circuits, it is advisable to install two collectors - one for the supply of coolant, and the other for its intake.
At the same time, shut-off valves must be installed at each outlet from the collector, which will allow disconnecting individual circuits from the system.
To eliminate the need to drain the coolant from the system during the repair work, shut-off valves are installed at the inlet and outlet of the boiler.
When the "warm water floor" system under the laminate is fully assembled and connected to the collector, all that remains is to connect the collector pipes to the pipes of the heating boiler.
The piping of the heating boiler must be carried out in accordance with the drawing, and the pipelines must be connected using factory parts.
Video: Tying a wall-mounted boiler
 Balabol, balabolit, blah blah - etymology Balabol which means
Balabol, balabolit, blah blah - etymology Balabol which means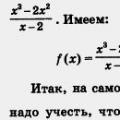 Aperture: what is it and why is it important for a smartphone?
Aperture: what is it and why is it important for a smartphone?