The first wake-up calls: signs of cerebral atherosclerosis. What is blockage of cerebral vessels Blockage of the vessel lumen by a foreign body
Pain in the lower extremities when walking or physical activity (running, cycling) is not only the result of muscle strain, but it may also indicate that there is a blockage of blood vessels in the legs, both arteries and veins. Intermittent claudication is the main early symptom of gradual occlusion of the leg arteries, most often caused by atherosclerosis. A more severe manifestation of this disease is the appearance of non-healing ulcers or, in extreme cases, gangrene. Blockage of the arterial bed of the lower extremities can occur acutely, the cause of which is the complete and sudden occlusion of the lumen of the vessel by a detached thrombus.
Thrombus formation can occur in both superficial and deep veins of the lower extremities. Thrombosis in the first is not as dangerous because it rarely leads to pulmonary embolism, unlike the second situation. It is worth understanding the causes and consequences of pathologies.
Blood coagulation is a very important physiological process for the human body, in which platelets, fibrin and other components stick together to form a clot (thrombus). This reaction allows you to stop bleeding in case of damage to the skin or internal organs. The clot forms a protective film that saves the body from heavy bleeding. In the absence of this reaction to damage, any minor cut can end in failure.
There are two types of thrombi. Some are formed in the zone of fast blood flow (arteries), initially consist of platelets, have a gray color. Others arise in vessels with relatively slow blood flow (veins), are red in color, and appear as a result of fibrin sticking to red blood cells.
Clot formation can occur directly within the vessel when there is no "open" injury (blood is not in contact with the environment). This situation is called pathological thrombosis.
In veins, this happens more often than in arteries, since blood flows more slowly there. Other mechanisms for the development of venous thrombosis: damage to the endothelium (the inner layer of the vessel wall), hypercoagulability (increased blood clotting).
In the arterial bed of the lower extremities, blood clots most often come from the higher parts of the systemic circulation. This situation is called thromboembolism, which means that the clot did not form in the area of the blockage of the vessel, but moved there from the heart, abdominal aorta, iliac artery. Therefore, arterial embolism in the legs often occurs against the background of cardiac arrhythmias, aneurysms, atherosclerotic lesions of vessels located above the femoral artery (thrombotic masses form on the atherosclerotic plaque, which can come off, after which they move to the periphery with the blood flow).
Research method |
How is it carried out |
Ultrasonic |
Sound waves are used to see how blood moves through the arteries. |
Arteriography |
One of the methods of contrast radiography, in which contrast (a substance that does not transmit x-rays) is first introduced into the vascular bed. After that, a picture is taken of the necessary area of \u200b\u200bthe leg, where the obstruction to the movement of blood is supposed to be. This method is used in the case of severe stenosis, when there is a serious blockage of the vessels in the legs, the treatment of which requires only surgical intervention. |
How are pathologies of the vessels of the legs treated?
If you notice the first signs of a blood clot, you can prevent a catastrophe. What are the symptoms if a blood clot is in the arm, leg, head, heart? What are the signs of education that has come off? What is a thrombus and what substances are involved in its formation? 

Efficiency, intellectual potential and mental abilities of a person largely depend on the saturation of the cerebral vessels with useful nutrients and oxygen, which the human brain receives through the blood vessels. Healthy vessels have elasticity and good blood flow to brain regions.
If there is a blockage of blood vessels caused by adverse factors, a pathology occurs in which the throughput of blood vessels decreases, thereby reducing the supply of nutrients necessary for the normal functioning of the brain.
In humans, blood vessels are made up of three layers, each of which performs specific functions.
The inner layer consists of epithelial cells, which ensure the free passage of blood inside the vessel. The middle layer consists of elastic cells and muscle fibers that do not allow blood to spread outside the vessel. The third layer, the outer layer, is responsible for separating the vessels from the surrounding tissues.
Blockage of cerebral vessels occurs due to accumulation in the inner layer plaque cholesterol, their number gradually increases and begins to interfere with the free passage of blood flow, blood circulation decreases, and the vessel loses its elastic mobility due to a decrease in the elasticity of the inner layer, which contributes to the destruction of the integrity of the blood vessel and the formation of blood clots.
Prolonged blockage of cerebral vessels can cause the development of discirculatory encephalopathy, or lead to inadequate blood supply, which is fraught with hemorrhages or stroke.
There are more and more people diagnosed with blockage of cerebral vessels every year, the causes of the manifestation of this disease are the use of fatty foods, the abuse of nicotine alcohol and malnutrition. The accumulation of cholesterol plaques or atherosclerosis affects the largest vessels responsible for the blood supply to the brain.
Also, chronic arterial hypertension leads to deformation and blockage of cerebral vessels. In many cases, these are the two main factors in the narrowing of cerebral vessels.
Symptoms of blockage of blood vessels in the brain
The disease proceeds according to two scenarios, acute, which includes the occurrence of a stroke, which, without timely assistance, leads to the death of the patient, and according to the scenario of the chronic course of the disease, which lasts for several years. A person can get used to the symptoms of the chronic form and eventually stop noticing them.
The chronic course of the disease of blockage of cerebral vessels has three stages:
- At the first, a decrease in the elasticity of the walls of blood vessels begins, which causes headaches, irritability appears, concentration of attention decreases and fatigue increases.
- In the second stage, the symptoms of the disease intensify, often accompanied by tinnitus and sleep disturbance or insomnia. All together, this leads to memory impairment, to the appearance of fainting, prolonged migraines, to a violation of the musculoskeletal system, and false urge to urinate is possible. Sometimes a patient with blockage of cerebral vessels has visual impairment and sensitivity in the extremities.
- The third stage is the most distinct in terms of symptoms, during its development it becomes difficult for the patient to move, coordination of movements is lost and mental ability is inhibited. Due to violations of brain activity in a person, uncontrolled acts of urination and defecation can occur.
In the third stage, the patient needs constant help, as he almost completely loses his ability to work and cannot control his actions. Often failure to provide assistance at this stage of the disease leads to immobility of the patient.
Diagnosis of the disease
Diagnosis of the disease must be made in several directions. A neurologist conducts an examination of neurological symptoms, assessing the degree of mental activity of the patient and reflexes. To assess the severity of the disease and the accuracy of the diagnosis, the doctor needs the help of relatives who observe the patient's behavior at home.
ECG and computed tomography of the brain, along with dopplerography and computed angiography, are among the most important tools in the detection of the disease. They allow you to find out the speed of blood flow, the presence of blood clots, aneurysms and atherosclerotic plaques in the vessels.
Methods of treatment of blockage of blood vessels in the brain
In the treatment of blockage of cerebral vessels, one must proceed from the clinical picture (stage of the disease). The acute form of the disease requires the immediate intervention of specialists and the appointment of medications that reduce or eliminate the symptoms of the disease. With this form it is possible rapid blockage of blood vessels, which will lead to irreversible consequences in the human brain.
Identification of the disease in the chronic stage requires the appointment of therapy and complex treatment by cardiologists, therapists, angio-neurologists. At this stage, the cure of the patient depends on the observance of all procedures by the patient himself and on the correctly selected drug therapy. In particularly difficult cases, drug treatment can last a lifetime.
In the absence of a positive effect after taking medication, it is necessary surgical intervention. The goal of surgery is to restore healthy blood flow to the vessel, for this, bypass surgery or endarterectomy is performed.
During shunting, a special stent is inserted into the patient's vessel, which opens the normal flow of blood into the vessels of the brain. And with endarterectomy, atherosclerotic plaques are removed.
Disease prevention
To prevent blockage of cerebral vessels, a healthy diet is recommended; foods high in fat and salt should be excluded from your daily diet. Eat vegetables and fruits more often, because the acids contained in them contribute to the breakdown of fats. Provide your body with constant physical activity, stop smoking, and reduce the consumption of strong alcohol. And also avoid stress or reduce their impact on your nervous system.
What is a blockage of cerebral vessels, everyone needs to know its symptoms in order to identify the first signs of a developing disease. After all, a good blood supply allows the body to maintain normal capacity, which provides soft tissues with nutrients, oxygen, vitamins and microelements. Since the coordinated work of all internal organs and systems depends on the state of the brain, a full-fledged human life is ensured.
Causes
There are a number
causes of cerebral vascular obstruction.
Everyday factors that damage the circulatory system are:
- Inactivity - a sedentary lifestyle leads to the development of abnormalities in the functioning of blood flow;
- The intake of a large amount of unhealthy junk food into the body - foods containing the wrong carbohydrates and fats, leading to the deposition and accumulation of toxins, plaques, which lead to clogging of the lumen of blood vessels;
- Bad habits - alcohol abuse, smoking, drug use;
- Non-compliance with the drinking regime - an increase in blood viscosity with a violation of its current;
- Prolonged stressful conditions.
The most common causes of blockage of the venous and arterial channels of the brain tissue include:
- Heredity - a genetic predisposition, which is the risk of developing a certain disease of the blood circulation system;
- Disorder of metabolic processes;
- Pathologies associated with coagulation, thrombophlebitis;
- The period of pregnancy, during which complications of various kinds arise, as well as the bearing of a child causes an increase in the level of coagulation indicators;
- Crash syndrome - the release of a large amount of toxic decay products of soft tissues, leading to thickening of the blood and increased clotting activity;
- Some types of diseases: autoimmune, atherosclerotic changes in the vessels of the brain, blood poisoning, diabetes;
- Post-traumatic complications, causing clogging of the lumen of the veins and arteries with fat particles;
- The use of medications, the side effect of which is thrombosis;
- Injury to the cranium, bruises of soft tissues.
Also, the processes of blockage of cerebral vessels are caused by air entering during medical procedures: a dropper, poor-quality injection.

Symptoms
Clogged vessels of the central nervous system, in the initial period of the development of the disease, may not show any serious symptoms. A person faced with such a problem is most often accompanied by pathological conditions:
- Dizziness, tendency to faint;
- Pain, often - migraine;
- Sleep disturbance, distraction;
- Fast fatiguability;
- Decreased memory;
- Feeling of numbness of the limbs;
- Deterioration of coordination of movements;
- Mood swings.
A painful condition, without proper medical therapy, leads to the appearance of:
- Noise in the ears;
- Prolonged headaches;
- visual disturbance;
- Weakening of mental abilities;
- Pathology of urinary excretory function;
- Dyslexia of motor coordination.
The lack of timely treatment leads to paralysis, often ending in the death of the patient.
Diagnostics
The development of medicine and the experience of a qualified diagnostician make it possible to make the most accurate assessment of the state of the vascular system of brain tissues, the main arteries that feed them, using:
- Ultrasound. It includes: duplex scanning of the cervical and intracerebral canals, dopplerography - the study of fluid movement in large channels, echotomography - examination of deep internal tissues, transcranial dopplerography - examination of the blood flow of intracranial vessels;
- Computed tomography - an X-ray examination technique for assessing the state of the structural elements of the brain, detecting the location and size of the pathology;
- Magnetic resonance imaging - a full-scale analysis of the structure of brain tissues, blood vessels, allows you to identify the presence of deviations from the norm, leading to abnormal changes;
- Angiography is a method of X-ray examination, which makes it possible to judge the quality of the blood filling of the vascular system, the time and sequence of its filling, as well as the places of changes in blood flow that have arisen due to narrowing or blockage of the canal lumen;
- Electroencephalography - allows you to check the functional side of the circulatory system in the brain tissues, as well as the activity of the transmission of nerve impulses;
- Rheoencephalography - helps to analyze the state of the vascular network, their elasticity, fullness and patency;
- Neurosonography is a technique for assessing the state of the brain and its structure in young patients, until a large fontanel is closed on the child’s head, through which the vascular network is examined with an ultrasound machine.
Treatment: medication, folk remedies
If the diagnosis is an embolism, this means that the patient has clogged cerebral vessels, what to do with such a conclusion - immediately begin treatment. Complex therapy can be prescribed by a neuropathologist, a general practitioner and a cardiologist. Treat:
- With the help of medicines;
- With the use of folk remedies;
- Correction of lifestyle and nutrition system;
- In particularly severe cases, surgery may be undertaken. The operation allows you to restore normal blood flow, with laser excision of the pathology of the vessel.
Drug treatment primarily consists of a list of necessary drugs to eliminate concomitant conditions and adjust blood flow through the arteries and veins. The main list of medicines includes:
- Statins - to lower cholesterol levels;
- Fibrates - regulate the process of formation of atherosclerotic deposits;
- Expanding the vascular network of the circulatory system of the brain;
- Improving blood flow;
- Strengthening the immune system.
Depending on the severity of the condition, the doctor individually selects the dose and period of use of the drug.
If we are talking about folk remedies, then their main goal is to cleanse, strengthen and support the proper functioning of the circulatory system. Traditional methods will only complement the main therapy. when blocking the vessels of the brain, the treatment most often used is: garlic, hawthorn, immortelle, rose hips, walnuts.
The doctor also supplements therapeutic measures with a special diet, which excludes: fatty, smoked, fried, heavily salted, sweet foods. The emphasis is on the use of vegetables, fruits, seafood.
Consequences
The problems of clogged cerebral vessels, which have arisen at any age, carry a huge threat to health and normal life. The name of the disease - embolism is associated with a number of quite serious pathologies. One of the consequences is occlusion or restriction of the patency of blood vessels with overlapping of its lumen, leading to the development of atherosclerosis, strokes, ischemia, gangrene of the organ, necrotic processes in tissues and other irreversible changes in the brain.
The cost of treating cerebral vascular obstruction is quite high. At the Burdenko Research Institute, it starts from 10,000 rubles, so everyone should think about the fact that prevention in the form of a healthy lifestyle and proper nutrition is much more effective than expensive and lengthy treatment.
Video
Blockage of cerebral vessels, the symptoms of which are specific, is carefully studied by modern medicine. The functionality of any living organism directly depends on blood circulation and the functioning of the nervous system. Violation of blood flow in the organs leads to malfunctions in their work. The most dangerous is the violation of blood flow in the arteries of the brain, which is responsible for the human central nervous system. Blockage of cerebral vessels leads to oxygen starvation of brain tissues, accumulation of decay products. The consequences of such a failure in work can be different, up to a fatal outcome. Therefore, it is necessary to know the main symptoms of this disease.
Why does pathology occur?
An embolism of the cerebral vessels is a sudden blockage of them. This pathology is often the source of ischemic stroke. At the beginning, signs of embolism of the arteries of the brain may not appear or be insignificant. As a result, this leads to cerebral hemorrhage, and then to death.

The causes of embolism of the cerebral arteries are different. The main cause of blockage of blood vessels in the brain is a blood clot. It has various sizes and can settle in any blood vessels of the human body. Blockage of cerebral vessels can be caused by one or more blood clots. Embolism of cerebral vessels is divided into the following types:
- Air (presence of air in the blood stream).
- Gas (presence of gas in the blood stream).
- Fat (accumulation of fatty droplets in the blood).
- Cellular (accumulation of foreign cells in the blood).
- Mechanical (foreign body entering the bloodstream).
- Microbial (accumulation of settling microbes in vessels).
The principles of treatment of cerebral embolism differ depending on its type and cause. A common cause of clogged arteries is their trauma. It doesn't have to be a head injury. Physiological childbirth is as much a cause of vascular embolism as an accident or surgery. All causes of cerebral embolism can be divided into 2 main groups.
Heart related:
- heart rhythm disturbances;
- trichinosis;
- surgical operations on the heart;
- installed prosthetic heart valve;
- bacterial endocarditis.
Not related to the heart:
- pulmonary vein thrombosis;
- any surgical intervention;
- malignant neoplasms;
- purulent process in the tissues of the lungs;
- head injury;
- any injury, including vascular damage;
- natural childbirth and by caesarean section.
In most patients aged 20-50 years, it is impossible to determine the cause of an embolic stroke. It is believed that cerebral embolism can occur suddenly in people with an elevated level of platelets in the blood against the background of the appearance of metastases of malignant tumors or chronic brain diseases. This is also facilitated by long-term use of contraceptives in women, because they cause blood clotting with an increase in the number of platelets in it. Sometimes it is difficult to recognize valvular stenosis or some forms of arrhythmias (arrhythmia syndrome) on examination.
And this could alert the workers of medical institutions, and against this background, the necessary measures would be taken to prevent possible embolism.
An embolus, like a thrombus, has its own dimensions. In turn, the place where it is located affects the nature of the resulting heart attack. So, for example, a small embolus can lead to blockage of the vascular capillaries of the brain, which contributes to the formation of a non-serious focus of stroke. An embolus with a size of 3 mm will already be considered large. A formation of this size can stop blood flow in the middle artery of the brain. This leads to extensive damage to brain tissue.
Symptoms of blockage of the arteries and veins of the brain
The clinical picture of embolism of the lumen of blood vessels in the brain is different. It depends on the location of the embolus, its size and the volume of brain tissue affected as a result.
A hallmark of cerebral thrombosis is the occurrence of disturbances at rest. The first signal is a severe headache, confusion. Appears:
- dizziness;
- dyspnea;
- feeling very tired;
- sometimes - a strong cough with sputum;
- hemoptysis.
The person is conscious, but looks sleepy, inhibited, does not react to what is happening around him. Often there is muscle weakness, speech and swallowing reflex is disturbed, there is a loss of coordination of movements and balance. With severe cerebral lesions - loss of consciousness, paralysis of half of the body, convulsions, epileptic seizures. Complete discoordination indicates blockage of the anterior cerebral artery.
With a blockage of such a large vessel as the basin of the middle cerebral artery, the following symptoms are noted:
- Distortion of the face with partial or complete loss of speech.
- Paralysis of the whole arm or hand.
- Complete inability to see the left visual fields.
With an embolism of the upper part of the main artery, the patient notes the inability to look up, involuntary drooping of the upper eyelid of both eyes, a feeling of severe weakness and drowsiness.
Blockage of the arteries by a fat embolus is manifested mainly by severe agitation, disorientation and mental disorders, impaired consciousness (from its stupefaction to coma).
Thromboembolism of the cerebral vessels in young people often manifests itself after a lot of physical exertion or in severe stressful situations. The patient needs urgent treatment.
The worsening of the prognosis is possible in the presence of the following risk factors:
- Elderly age.
- Male.
- The appearance of seizures.
- development of paralysis.
- The presence of a large intracranial hemorrhage.
How to treat the disease
Diagnosis of the disease begins with the collection of anamnesis (lifestyle, presence of diseases, medication, patient complaints) and examination by a doctor. If there is a suspicion of vascular occlusion in the head, research methods such as computed tomography or MRI are prescribed. The second option is preferable, because it provides information about the state of the vessels even in the absence of blood flow in them. They also prescribe blood and urine tests, ECG, ultrasound and transcranial dopplerography. If necessary, a lumbar puncture is done to detect red blood cells in the CSF. After the examination, treatment is prescribed.
The patient should be given first aid for signs of embolism of the arteries of the brain. It is necessary to call an ambulance team, lay the patient down and provide him with a state of rest. When the tongue is retracted, it is required to turn the person's head to one side. When convulsions occur, do not restrain the patient's body, do not insert foreign objects into the mouth. It is necessary, if possible, to free the patient from restrictive clothing, remove hard objects that he can hit, and provide access to fresh air.
At the end of the seizure, turn the patient on his side and clean the oral cavity with a clean towel.
Further treatment is provided by medical personnel. The patient is transported to a medical institution in the intensive care unit for intensive care. Then the patient undergoes treatment in the neurology department and rehabilitation. After discharge from the hospital, the person remains on the dispensary record, periodically visits the doctor and fulfills his appointments.
Methods for the prevention of cerebral embolism:
- To prevent the development of this disease, experts recommend treating existing cardiovascular diseases, monitoring the state of the blood (the number of its elements).
- It is also necessary to lead an active lifestyle, observe the basics of proper nutrition, undergo medical examinations, regardless of the presence of complaints, with a preventive purpose.
Often thromboembolic obstruction of the arteries and veins of the brain ends in death. Therefore, it is very important to listen to your body, monitor its performance and help recovery by conducting timely treatment.
Thromboembolism, or blockage of cerebral vessels, leads to the cessation of blood supply in the basin of the blocked vessel. This develops local ischemia: a lack of oxygen and nutrients. This condition leads to tissue death. For the brain, blockage of blood vessels is complicated by ischemic stroke and cerebral infarction.
Thromboembolism is not an independent disease, but acts as an acute pathological condition that can result in the death of the patient.
The cause of the blockage is a blood clot that has come off the vessel wall and got into free swimming. Having reached the artery, suitable in diameter, the clot clogs the vessel and blocks the blood flow.
There are factors that can lead to the development of a blood clot:
- Sedentary lifestyle and overweight.
- Arterial hypertension.
- Heart failure, ischemic heart disease.
- Varicose disease.
- Long-term use of drugs that increase blood viscosity.
Cardiac arrhythmia, such as atrial fibrillation or paroxysmal tachycardia, can provoke a thrombus to detach from the wall.

Symptoms
Symptoms of blockage of cerebral vessels consist of cerebral and focal neurological symptoms.
Cerebral symptoms develop due to lack of oxygen and reduced supply of nutrients. Signs:
- stun;
- drowsiness, which is replaced by excitement;
- short-term loss of consciousness;
- severe headache accompanied by nausea and vomiting;
- dizziness, eye pain;
- less convulsions;
- autonomic disorders: darkening of the eyes, goosebumps, sweating, trembling of the fingers and extremities, dry mouth, pain in the heart and palpitations.
Focal neurological symptoms depend on the artery and pool where the blockage occurred.
What happens if the blood flow in the area of the internal carotid artery is clogged:
- Paralysis or paresis on one side of the body or one limb.
- Speech is detuned according to the type of motor aphasia: the decay of the grammar of oral speech.
- Monocular blindness: Vision is lost in only one eye on the side of the blockage.
Blockage of the choroidal artery:
- Paresis or paralysis on the opposite side of the blockage. For example, if the occlusion occurs on the left, the right side of the body is paralyzed.
- Violation of sensitivity on the opposite side.
- Speech disorder.
- Violation of vision and orientation in space. Often there is hemianopsia - simultaneous blindness in both eyes.
Blockage of the anterior cerebral artery:
- Increased muscle tone on the opposite side of the occlusion.
- Paralysis of the lower limbs.
- Activation of the grasping reflex.
- With damage to the caudate nucleus, the facial muscles, muscles of the arm and tongue on the opposite side are weakened.
- Speech is upset: the intelligible pronunciation of hard and soft sounds is disturbed.
Occlusion of the anterior cerebral artery can sometimes be asymptomatic due to the fact that it has collateral blood flow.
Blockage of the middle cerebral artery:
- Weakening of muscle strength or its complete loss on the opposite side.
- Contralateral sensory disturbance.
- Bilateral blindness.
- If the dominant hemisphere is affected (for a right-handed person it is the left one, and vice versa), speech disorders develop, if the non-dominant one, the purposefulness of movements and tactile perception of familiar objects are disturbed. With the defeat of the non-dominant hemisphere, anosognosia (lack of criticism of one's illness) and asomatognosia (the perception of one's own body scheme is disturbed) also develops.
Blockage of the posterior cerebral artery:
- Violated sensitivity and muscle strength on the opposite side of the occlusion.
- Memory is impaired: patients forget the events that preceded the blockage of the vessel.
- Speech is upset, mostly oral, without violations of the letter.
- Ataxia is the inconsistency of the muscles of different parts of the body.
If the vessel is clogged in the cervical spine:
- Unilateral muscle imbalance.
- Contralateral weakening of muscle strength.
- Violation of sensitivity on the opposite side of the occlusion.
- Ipsilateral (on the side of the blockage) paresis of facial muscles.
- Dizziness, vomiting, nausea.
- Involuntary contraction of the palate.
- Oscillopsia is a perceptual disorder, an illusion in which the patient feels that impending objects are moving in space.
- Isolation syndrome is a condition in which the patient does not respond to external stimuli, including words. Accompanied by a speech disorder. Patients retain the ability to transmit elementary information with the help of eye movements.

Consequences
Blockage of blood vessels in the brain can lead to:
- Movement disorders. For example, with damage to the cranial nerves, swallowing may be upset, after which the patient is connected to a probe through which he eats.
- Speech disorders.
- Decrease in cognitive and intellectual properties. The emotional sphere is also disturbed: the patient may become irritable and unbalanced.
Diagnosis and treatment
When diagnosing, an objective examination of the patient is taken into account, of particular interest is the neurological history (state of consciousness, balance, safety of movements, visual accuracy, sensitivity, presence of convulsions). Instrumental research methods: magnetic resonance and computed tomography. They help to determine the localization of ischemia.
Treatment of blockage of cerebral vessels begins with the patient's hospitalization in the intensive care unit. Already during transportation, the first procedures are performed: they examine the patient and plan treatment.
In resuscitation and intensive care, breathing and cardiovascular activity, water and electrolyte balance and hemodynamics are supported. From drug therapy, anticoagulants and antiplatelet agents are urgently introduced. These drugs prevent blood clotting and thin existing blood clots, such as Clopidogrel, Aspirin or Heparin.
Blood vessels in the human body are the most important link in maintaining the vital activity of all internal organs. It is through them that blood flows with the necessary energy substrates to the cells of the body, which take part in the necessary biochemical processes. But due to many external and internal factors, the lumen of the vessel can be obliterated (clogged) from the inside, as a result of which the corresponding organs do not receive proper nutrition, and the cells can die, leading to the loss of their functions by the organ.
Let's consider for what reasons and with what the human vessels - arteries and veins - are usually “clogged”.
Why does vascular blockage occur?
Obliteration of the vascular lumen can occur as in arterial, as well as in venous bed. The mechanisms that contribute to blockage of an artery or vein include two main ones: formation and formation:

- Blood clots can clog both types of vessels - veins and arteries, but initially form mainly in the veins.
- Atherosclerotic plaques, in turn, "grow" only on the walls of the arteries. However, like blood clots, when detached, they can migrate through the bloodstream.
- In many cases, when it comes to vascular occlusion of “serious” localizations (occlusion of the vessels of the heart, brain), the genesis is mixed - atherothrombotic. The atherosclerotic plaque does not allow the “microthrombus” to pass through, and the atherothrombotic substrate grows from the two components like a snowball.
- In relatively rare cases, blockage of blood vessels can occur through other mechanisms - fat, body tissues, microbes. About it - .
The first group of causes in most cases (except for local thrombosis of the veins of the legs) includes thromboembolic conditions, that is, the formation of a thrombus in the lumen of the vessel and its further migration through the bloodstream. The system of the pulmonary artery, coronary arteries (own vessels of the heart), arteries of the brain, veins of the lower extremities, as well as arteries of the mesentery in the abdominal cavity, which supply blood to the small and large intestines, are mainly affected. Most often, thrombi form in the lumen of the deep and superficial veins of the lower leg and thigh, and when it is unstable to the vein wall, the thrombus breaks off and further spreads to the right heart and to the pulmonary artery. If a thrombus forms in one of the left chambers of the heart (parietal thrombus), it can enter the cerebral arteries with the development of ischemic stroke, the system of coronary arteries with the development of acute myocardial infarction, or into the mesenteric arteries with the development of mesenteric thrombosis.

a) occlusion of the vessel by a thrombus and thromboembolism in the example of leg veins
The second group of causes includes a pathological process characterized by the formation and fixation of plaques on the inner wall of the arteries, consisting of a core and a tire. The core contains excess cholesterol, and microclots can settle on the tire. In addition to the fact that the plaque itself causes narrowing of the vessel from the inside, it can destabilize, while the athero-thrombotic masses will also be carried through the bloodstream until they obliterate any artery. More often, the formation of plaques affects the arteries of the brain, coronary arteries, arteries of the lower extremities.

How is vascular blockage manifested?
The clinical picture of obliteration of the vascular lumen is characterized by a wide variety of symptoms. First of all, it depends on whether the process developed acutely or proceeds for a long time. In addition, the localization of obliteration plays an important role in the clinic.
The most common form of vascular blockage is thrombosis of the veins of the lower extremities. The insidiousness is that the disease can proceed completely asymptomatically and be an inconspicuous companion of venous congestion and insufficiency. The picture of an acute form can also be colorful - the patient begins to feel pain, the limb changes color, swelling develops.

acute blockage of the deep veins of the legs
And, for example, with blockage of the arteries of the lower extremities, due to obliterating atherosclerosis, a pathognomonic sign is intermittent claudication, when, due to exercise (walking), the need for oxygen in the skeletal muscles of the lower leg increases, and the obliterated arteries cannot satisfy this need. After a certain number of steps, the patient experiences a dull or sharp pain in the legs, which is why he is forced to stop constantly.

blockage of the arteries of the legs with plaque in atherosclerosis
With obliteration of the lumen of the coronary arteries of the heart, the clinical picture will depend on the percentage by which the lumen of the artery is blocked from the inside. If the blockage of the vessels of the heart is less than 50%, the patient will experience rare attacks of retrosternal pain of the type, and with significant stenosis (70-90% or more), it is likely to develop an acute one with sharp retrosternal pains that stop only with the introduction of narcotic analgesics, as well as with a general serious condition patient. Some patients may develop a painless or atypical form of acute myocardial infarction.

Long-term, but not critical obliteration of cerebral vessels leads to development. Usually, when confirmed, the doctor mentions that the patient has atherosclerotic encephalopathy. This pathology usually occurs in the elderly and is manifested by mood changes, tearfulness, resentment, memory loss and cognitive (thinking) processes. A long-term blockage of cerebral vessels leads to a decrease in intelligence up to senile (senile) dementia.
Acute blockage of arteries in the brain provokes the development of acute. Again, depending on the location of the stroke, the patient has symptoms of varying severity - from mild speech impairment (dysarthria) and slight facial asymmetry to severe paralysis of the limbs (para- and tetraparesis), often with impaired swallowing and respiratory functions.

Blockage of blood vessels in the mesentery thrombus is a severe surgical pathology that requires urgent surgical intervention, since the lack of blood supply to the mesentery leads to development with subsequent peritonitis and sepsis (blood poisoning). It is manifested by such acute pain in the abdomen, nausea, vomiting and the rapid addition of peritoneal symptoms (symptoms of peritoneal irritation, indicating the development of peritonitis).
How is vascular blockage diagnosed?
Due to the fact that blockage of a vessel of any localization is a potentially dangerous condition that requires timely assistance, a doctor of any specialty should know what diagnostic methods can be used to confirm or exclude signs of vessel obliteration.
In order to visualize the affected vessel, ultrasound diagnostics is used, in particular,. Such methods allow you to reliably assess the affected area of the artery or vein, as well as assess the patency of the blood vessel and the degree of blood flow disturbance. Ultrasound is used to diagnose blockage of blood vessels in the legs, as well as in the case of atherosclerosis of the carotid arteries that feed the brain.

In case of suspicion of blockage of the heart vessels, it is carried out with the introduction of an X-ray contrast agent into the lumen of the coronary arteries and followed by a study of the obtained images.
With the development of acute blockage of cerebral vessels, antiplatelet agents are used - in particular drugs based on acetylsalicylic acid to prevent increased thrombus formation (aspirin, thromboAss, acecardol, aspirin-Cardio, etc.). If complications develop, the patient is prescribed tablet forms of indirect anticoagulants (farvarin, phenylin, neodicoumarin, etc.) for a long time. Of the modern drugs, the most common are such as xarelto and pradaxa.

When blocking the veins of the lower extremities, they are used on the basis of heparin (heparin ointment, lyoton and hepatrombin gels), in tablets - for example, Phlebodia, as well as elastic bandaging of the thighs and legs or wearing (stockings and knee socks).
Obliterating atherosclerosis of the lower extremities is treated with vasodilators (nifedipine, amlodipine) and lipid-lowering drugs - statins (atorvastatin, simvastatin, etc.).
In the event that a patient develops an acute blockage of cerebral vessels, the treatment tactics is to treat ischemic stroke with the help of intravenous administration of appropriate drugs. Chronic atherosclerotic encephalopathy is treated with a course of nootropic and antihypoxic drugs (piracetam, actovegin, mildronate, etc.).
In some cases, a patient with vascular occlusion may require surgical treatment - coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) and stenting for angina pectoris and infarction, lower extremities, installation in the lumen of the inferior vena cava in order to prevent the migration of a blood clot along the venous bed, etc.
Are there possible complications of blockage of blood vessels?
Obliteration of a vessel of any localization can cause significant harm to human health, since in the absence of blood supply, ischemia and hypoxia of the organ develop, as a result of which the cells die - necrosis develops. Similar pathological processes in the lower extremities can lead to limb amputation, and in the vessels of the heart, brain or mesentery - to the death of the patient. But with timely detection of embolism and obliteration, as well as with successful treatment, the risk of complications can be minimized, while the quality of life and its duration will undoubtedly increase.
Almost all diseases of the cardiovascular system are directly or indirectly related to unhealthy diet. The main "mistakes" that patients with such diseases make are the inclusion in the diet of an excessively large amount of protein and food rich in animal fats.
Most often, this leads to the fact that already at 40-50 years old, atherosclerotic plaques form in the vascular system. They, in turn, worsen the speed of blood flow, increase the chance of developing a stroke or heart attack, varicose veins, thrombosis.
That's just most of the useful trace elements are destroyed during thermal and mechanical processing. That is why various kinds of sausages or sausages do not bring practical benefits - they only give kilocalories and a feeling of fullness. Only needs to be used.
And processed animal fat also becomes harmful - it produces carcinogenic compounds which may lead to the development of cancer in the future.
And the negative impact of these harmful substances on the vessels of the heart and brain has been confirmed by studies. So, it is better to refuse such meat, giving preference to home cooking.
4. Mayonnaise and similar sauces
 Homemade mayonnaise is quite a healthy product, although it contains a considerable amount of cholesterol (it is found in chicken and quail eggs).
Homemade mayonnaise is quite a healthy product, although it contains a considerable amount of cholesterol (it is found in chicken and quail eggs).
And the one that is offered on store shelves often contains palm oil, saturated trans fats. All these substances in excess provoke the accumulation of low-density lipids., which are extremely willing to settle on the walls of blood vessels.
And there are practically no useful trace elements in such sauces - the same mayonnaise is pasteurized before being sold for long-term storage.
Ketchups, sauces, borscht dressings - all these products are now produced using a similar technology. It is better to refuse them altogether and learn how to cook them at home from natural ingredients (given that the shelf life of such “dishes” will be only a few days).
5. Margarine
 Classic margarine is made using ghee and butter (their derivatives). Such a product in moderation is useful for the human body.
Classic margarine is made using ghee and butter (their derivatives). Such a product in moderation is useful for the human body.
But the margarine that is now produced does not bring any benefit to the body at all. You can safely refuse it completely. It is based on palm oil.- vegetable oil, 90% of which is practically not absorbed by the body. And in addition to it - added trans fats that increase the risk of developing cancer.
As practice has shown, daily consumption of at least 50 grams of margarine (in any form, that is, including as ready-made pastries) increases the likelihood of atherosclerosis by 12 times.
6. Carbonated drinks
 They contain a huge amount of sodium combinations (which, when in excess in the body, act as toxins), as well as sweeteners - carbohydrates, which, at high concentrations, are transformed into lipid compounds.
They contain a huge amount of sodium combinations (which, when in excess in the body, act as toxins), as well as sweeteners - carbohydrates, which, at high concentrations, are transformed into lipid compounds.
Look here.
Frequent consumption of sugary carbonated drinks (including sparkling mineral water) increases the risk of cholesterol plaque formation even if the level of that same cholesterol is quite low (less than 4 mmol/l).
7. Mechanically deboned chicken
 Most often included as an additional component to sausages, sausages. The basis of such meat is chicken skin, which contains a huge amount of cholesterol.
Most often included as an additional component to sausages, sausages. The basis of such meat is chicken skin, which contains a huge amount of cholesterol.
Even when preparing homemade soups, it is recommended to get rid of it. Moreover, it contains even more cholesterol than chicken yolks.
Controversial food
There is a category of products that indirectly have a positive effect on the cardiovascular system, but at the same time increase the risk of developing certain chronic diseases. These, for example, include salt, red wine. Why should their presence in the diet be limited?
Dry red wine
 On the one hand, it improves blood formation, optimizes the balance of red blood cells. On the other hand, it contains a large amount of carbohydrates.
On the one hand, it improves blood formation, optimizes the balance of red blood cells. On the other hand, it contains a large amount of carbohydrates.
And modern technologies for the production of such wine lead to excessive content of fusel oils in such drinks- they are the most powerful toxins derived from ethyl alcohol.
If you really drink such wine, then rarely and in small portions up to 30 milliliters.
Coffee
 Coffee contains plenty of antioxidants- they prevent the oxidation of healthy cells. And caffeine slightly dilates the vessels of the brain. But at the same time, it increases blood pressure, thereby increasing the load on the heart.
Coffee contains plenty of antioxidants- they prevent the oxidation of healthy cells. And caffeine slightly dilates the vessels of the brain. But at the same time, it increases blood pressure, thereby increasing the load on the heart.
Caffeine itself is a narcotic substance with a powerful somatic effect. Its daily use
in larger doses may increase the risk of developing chronic diseases of the cardiovascular system. And due to the short-term expansion of blood vessels, it can provoke the movement of formed blood clots and blockage of the supply vessels.
At the same time, moderate consumption, which is confirmed by numerous studies.
It is especially dangerous to drink coffee in combination with nicotine - both of these components contribute to the expansion of blood vessels. Over time, this leads to thinning of the walls of the veins, capillaries, which will become pliable to rupture.
Salt
 Salt is the largest source of chlorine and sodium. The first is mainly used in the synthesis of gastric juice, sodium - regulates salt metabolism, and the more it accumulates in the body - the more actively the kidneys work and potassium is “washed out”.
Salt is the largest source of chlorine and sodium. The first is mainly used in the synthesis of gastric juice, sodium - regulates salt metabolism, and the more it accumulates in the body - the more actively the kidneys work and potassium is “washed out”.
Look here.
And we should not forget that salt does not carry any nutritional value for humans, but in a small amount it is still necessary (for the normal functioning of the gastrointestinal tract).
Useful video
For a more detailed acquaintance with the topic, we recommend watching the video:
Conclusion
In total, a healthy diet is a guarantee of good health and the normal functioning of the cardiovascular system and clean blood vessels. And some products should still be discarded. First of all, it is store-bought mayonnaise, margarine, which are based on harmful fats. The same applies to various kinds of sausages, sausages - they have practically no nutrients, but there is a lot of cholesterol. And most importantly, follow a balanced diet, where no foods or dishes predominate.
The health, intelligence, and mental activity of a person depend on the state of the blood vessels. Blockage of cerebral vessels is accompanied by a deterioration in blood circulation in the brain, insufficient supply of oxygen and nutrients, which in the future can lead to serious consequences.
What is dangerous blockage of blood vessels
An obstruction in the blood vessels of the brain caused by the accumulation of air bubbles, fat or thrombus is called an embolism.. Penetrating into arteries with a narrow lumen, particles provoke their blockage, disrupting blood flow and causing tissue destruction from a lack of oxygen.
If untreated, the pathology can cause:
- cerebral infarction;
- thrombus formation;
- cerebral hemorrhage;
- dementia.
Pathology is most often observed in the elderly, but it can also occur in young people under the influence of adverse factors.
Symptoms
The circulatory disorder of the brain is asymptomatic at first. However, there are some signals indicating the development of pathology.
 Common symptoms of vascular disease include:
Common symptoms of vascular disease include:
- tendency to frequent dizziness and fainting;
- sleep disorder;
- headaches, migraine attacks;
- memory impairment;
- fatigue;
- numbness of hands and feet;
- deterioration in coordination;
- mood variability.
After that, other signs may be added:
- gait disturbance: a person may shuffle or mince;
- noise in ears;
- visual impairment;
- prolonged migraines;
- false need to urinate.
Lack of therapy leads to the progression of the disease and the appearance of new symptoms:
- noticeable disorder of coordination of movements;
- deterioration of intellectual abilities;
- various disorders of the urinary system.
Severe cases of blockage of the arteries often end in complete immobility, as well as death..
In the advanced stage, systematic medical care is required: the patient may cease to control his actions and lose his ability to work.
Causes
 Chronic blockage of the lumen of blood vessels, which impedes blood flow, can occur as a result of trauma, atherosclerosis, as well as various diseases: diabetes, high blood pressure, vasculitis.
Chronic blockage of the lumen of blood vessels, which impedes blood flow, can occur as a result of trauma, atherosclerosis, as well as various diseases: diabetes, high blood pressure, vasculitis.
Other reasons for the development of pathology include:
- lack of physical activity;
- genetic predisposition;
- chronic stress;
- negative habits: excessive drinking, smoking;
- irrational nutrition.
The use of fatty foods and foods containing additives leads to the accumulation of cholesterol in the arteries, which, in turn, is a prerequisite for the development of atherosclerosis.
Diagnostics
 A neurologist will help to identify the pathology, who will assess the neurological symptoms, the mental abilities of the patient, as well as the degree of manifestation of reflexes. However, for an accurate diagnosis, the following studies will be required:
A neurologist will help to identify the pathology, who will assess the neurological symptoms, the mental abilities of the patient, as well as the degree of manifestation of reflexes. However, for an accurate diagnosis, the following studies will be required:
- ultrasound diagnostics;
- computed tomography;
- angiography;
- electroencephalography.
These methods will help determine the state of the brain, the size and localization of lesions and the nature of the disease.
Treatment
Therapy of the disease depends on the clinical picture and the form of pathology. With an exacerbation, the use of medications will be required to help reduce symptoms and improve cerebral circulation.
Most often, an integrated approach is used, including the use of drugs, dietary and lifestyle adjustments, as well as alternative medicine recipes. Some cases require surgery.
Medicines
 The most commonly used drugs are:
The most commonly used drugs are:
- statins - drugs that reduce the production of cholesterol, such as simvastatin, zocor;
- fibrates - medicines that prevent atherosclerotic plaques, lipanor, fenofibrate;
- papaverine, aminophylline are used to expand the vessels of the brain;
- to strengthen the immune system, prescribe antioxidants and vitamin-mineral complexes;
- to improve blood circulation in the brain, cavinton, vazobral are used.
The duration and dose of medication is determined by the attending physician. In some cases, the patient has to take drugs for the rest of his life.
However, no medicine will have the desired effect without observing a balanced diet.
- exclude animal fats and smoked meats;
- refuse fried foods, spicy salty foods, fast food;
- limit the consumption of sweets and soda;
- enrich the diet with vegetables, fruits, and seafood.
In addition, you need to monitor your body weight, give up negative habits, walk more often and exercise.
ethnoscience
You can clean the arteries from harmful deposits with folk remedies. Home remedies for blockage are used as adjunctive therapy.
In the acute or advanced stage of the disease, alternative medicine may become useless.
Rose hip
Showed excellent results in the elimination of vascular obstruction in the brain rosehip infusion. For cooking, you need to insist 50 g of fruit for 6 hours. Take a decoction of 200 g, several times a day, for a month.
Hawthorn
The fruits are poured into 500 g of boiling water, boiled, honey is added to the drink and consumed 20 g before meals, twice a day.
 This folk remedy helps to remove cholesterol plaques from the arteries and strengthen the walls.
This folk remedy helps to remove cholesterol plaques from the arteries and strengthen the walls.
For cooking, you need 200 g of walnut partitions and the same amount of vodka.
The infusion is kept for 14 days in a dark place.
Use 20 drops of the product, diluting it with 50 g of water, three times a day, for half a month.
Sea buckthorn oil
To improve the vessels of the head will help the daily use of 1 teaspoon of oil before meals. The course of therapy is 21 days. After a break of 1 month, the treatment is repeated.
Garlic
 Garlic is an excellent natural remedy for the prevention of colds. Useful properties allow it to be used to cleanse the vascular walls of cholesterol:
Garlic is an excellent natural remedy for the prevention of colds. Useful properties allow it to be used to cleanse the vascular walls of cholesterol:
- For cooking, a few cloves of garlic are crushed with a meat grinder, poured with alcohol and left in a dark place for 10 days. The composition is filtered and taken 20 drops, diluted with 100 g of water, half an hour before meals, three times a day. The course of treatment is 30 days. This tool will help cleanse the arteries and remove cholesterol deposits.
- Peeled heads of garlic are placed in 200 g of milk. The composition is boiled until the garlic softens. Milk is drained and taken 1 tablespoon three times a day.
- The following recipe will help to effectively clean the vascular walls. For cooking, you need 1 head of garlic and 1 lemon in a peel. The ingredients are ground with a meat grinder, poured with 1 liter of water, insisted and consumed 50 g three times a day, 1 month. The course of therapy is twice a year. This tool will help stabilize the pressure and strengthen the immune system.
Useful for blood vessels will be the use of freshly squeezed juices from celery, tomato, carrot and pomegranate.
To prevent blockage of blood vessels, it is necessary to follow a healthy lifestyle, eat rationally, do not neglect regular physical activity, and also systematically undergo a medical examination. This is especially true for people at risk.
 Balabol, balabolit, blah blah - etymology Balabol which means
Balabol, balabolit, blah blah - etymology Balabol which means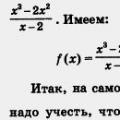 Aperture: what is it and why is it important for a smartphone?
Aperture: what is it and why is it important for a smartphone?