Profitability in agriculture. The specifics of the formation of profit and profitability in agriculture
Profitability indicators are important characteristics factor environment for the formation of profits of enterprises. When analyzing production, profitability indicators are used as an instrument of investment policy and pricing.
The main profitability indicators can be grouped into the following groups:
1) indicators of return on capital (assets),
2) indicators of product profitability;
3) indicators calculated on the basis of cash flows. Profitability indicators used in economic calculations characterize relative profitability. There are indicators of profitability of products and profitability of the enterprise. The profitability of products is tried on in 3 versions: the profitability of sold products, marketable products and individual products.
Profitability is the most important economic category, which is inherent in all enterprises and organizations that operate on the basis of cost accounting. It means profitability, profitability of the enterprise.
The problem of profitability, methods of its quantitative measurement is constantly in the spotlight in the development of methodological and instructive materials. In this regard, noteworthy is the proposal of economists to introduce a classification of profitability indicators into absolute and relative, depending on the method of their quantitative expression. Absolute indicators of profitability are gross and net income. However, the absolute sizes of net income, profit and gross income do not allow to fully compare the economic results of the production activities of enterprises. The economy can make profits of a thousand rubles and a million. In both cases, production is profitable, and the efficiency may be different, since it depends on the size of production, product structure, production costs, and so on. Therefore, to characterize the economic efficiency of production, relative profitability indicators are also used, which are expressed as a ratio of two comparable values: gross, net income, profit, and indicators of the efficiency of using certain production resources or costs. Relative profitability indicators can be calculated in terms of money or, most often, as a percentage. With their help, the profitability of agricultural production can be expressed both in terms of gross and sold (marketable) products.
In practice, mainly relative indicators of the profitability of sold products are used, which are punished by the norm or level of profitability. They are calculated both for all products sold by the enterprise, and for its individual types. In the first case, the profitability of products will be defined as the ratio of profit from products sold to the costs of its production and sale.
The profitability of all sold products is calculated in the same way as the ratio of profit from the sale of marketable products to the proceeds from the sale of products: in relation to the balance sheet profit to the proceeds from the sale of products. Profitability indicators of all sold products give an idea of the effectiveness of the current costs of the enterprise and the profitability of products sold.
In the second case, the profitability of individual types of products is determined. It depends on the price at which the product is sold to the consumer, and the cost for this type of product.
All of the above profitability indicators characterize the economic efficiency of using current production costs to obtain products. However, agricultural enterprises not only produce current production costs, but also make capital investments to increase and upgrade fixed assets, the cost of which is included in the production costs of each year not in full, but in part equal to the amount of depreciation. Therefore, it is important to know the efficiency of using one-time costs materialized in the means of production. For this purpose, relative indicators of profitability of production assets are used, which are calculated as a percentage of profit to the average annual cost of fixed and tangible current assets separately, as well as total (fixed and tangible current assets taken together) called the rate of return:


where NP is the rate of return;
P r - profit;
About f - fixed assets;
About bf - revolving funds.
These indicators characterize the efficiency of use in the first case of the main, in the second - material circulating, in the third - the total means of production. They show how much profit is received per unit value of the respective means of production. How more profit received per ruble of means of production, the more efficiently they are used.
Equally important are the indicators of profitability of investments in the enterprise. They are determined by the value of the property at his disposal. When calculating, indicators of balance sheet and net profit are used. The value of the property is determined by the balance sheet.
Equally important is the profitability of turnover, reflects the relationship between profit and turnover and shows the amount of profit received per unit of goods sold. Since accounting of business transactions is carried out in monetary terms, the profitability ratio of sales, multiplied by 1000, shows how much profit was received from 1 thousand rubles. goods sold. The higher the profit, the higher the profitability of trade. The profitability ratio of sales characterizes the share of profit in the turnover. By the ratio of net profit and turnover, one can more accurately judge the financial result of a trading enterprise.
This indicator is of great importance in foreign practice. Thus, in the United States, the Department of Commerce annually publishes data on the average net return on sales for each industry and large trading firms and companies. The position of the company in the domestic market is determined on the basis of this indicator, which indicates the degree of strength of its financial condition.
The assessment of the net return on sales is long-term in nature, since it determines the investor's decision to invest in the capital of a trading company by buying it. valuable papers.
In foreign practice, the indicator of profitability of turnover is called the commercial margin. It is expressed as a percentage, and its value ranges from 5 to 30%, depending on the nature and scope of the trading company.
In addition to profit, when calculating the return on investment, you can use the proceeds from the sale of products. This indicator characterizes the level of sales per one ruble of investments in the property of the enterprise.
Regulation of the overall economic profitability is reduced to the impact on both components of its indicators - return on sales and capital turnover.
To characterize the effectiveness of the use of equity capital, the share of profit in equity (equity) is determined by the ratio of profit and the average value of equity capital:
P k \u003d P p / K s, (6)
where R to - return on capital;
P r - profit;
K c - the average value of capital.
The indicator of return on equity is important for the shareholders of a trading enterprise. It serves as a criterion for assessing the level of quotation of shares of a joint-stock trading company on the stock exchange, this indicator allows investors to assess the potential income from investing in shares and other securities. Based on this indicator, it is possible to determine the period (number of years) during which the funds invested in a joint-stock trading enterprise are fully paid off.
The profitability of the enterprise's own funds is determined by the ratio of net profit to its own funds, determined by the balance sheet. It is advisable to calculate the return on long-term financial investments. The profitability of long-term financial investments is calculated as the ratio of the amount of income from securities and equity participation in other enterprises to the total volume of long-term financial investments.
Along with indicators of turnover, capital, fixed and working capital, other indicators are also used to calculate the level of profitability (coefficients): distribution costs, trade area, the number of personnel, each of which emphasizes a certain aspect of the results of the trading enterprise.
The level of profitability, calculated by the ratio of the amount of profit from the sale of goods to the amount of distribution costs, shows the effectiveness of current costs. An increase or decrease in distribution costs directly affects the decrease or increase in profits. This indicator of profitability determines the effectiveness of a trade transaction for goods.
Profitability, calculated in relation to the number of employees employed at the enterprise, characterizes the efficiency of using work force and shows the amount of profit received per employee. Along with this indicator, the gross and net profits are determined in relation to the actual amount of labor costs, taking into account the amount of mandatory contributions to off-budget funds (for social insurance, pension fund, employment fund, medical insurance fund). This indicator of profitability reflects the size of the gross and net profit received per 1 thousand rubles. funds spent on wages and social needs. The smaller the number of employees of the enterprise, the more profit per employee, which indicates an increase in the efficiency of the use of labor. Here the principle is directly manifested: with a smaller number of employees - a greater effect. In addition, it is possible to determine the dependence of the results achieved economic activity enterprises from the result of the work of each employee.
IN agriculture it is not uncommon for the production of any product to be unprofitable or unprofitable. Then, instead of the “rate or level of profitability” indicator, other indicators can be used - the level of unprofitability (the level of profitability with negative sign) or the level of cost recovery, which is calculated by the formula:
where Оу is the level of cost recovery;
DV - cash proceeds from the sale of products;
Sk - commercial (full) cost.
It is recommended to study the system of profitability indicators of a trading enterprise in dynamics and, if possible, in comparison with the indicators of other similar trading enterprises.
Profit and profitability in the conditions of the formation of a market economy are the most important indicators of the economic activity of agricultural organizations and enterprises. These indicators reflect all aspects of the activities of enterprises: the volume and structure of turnover, the rational use of resources, the implementation of measures to improve organizations and technologies of production processes, etc.
The amount and level of profit are formed under the influence a large number various factors that have both positive and negative effects on them. The number of factors that determine the amount of profit and profitability can hardly be clearly limited, it is very large. Weight factors can be divided into the main ones, which have the greatest impact on the amount and level of profit, and the secondary ones, the influence of which can be neglected. In addition, the entire set of factors can be divided into internal and external. They are closely related. Internal factors affecting profit and profitability include resource factors (the size and composition of resources, the state of resources, their operating conditions), as well as factors associated with an increase in revenue.
The main external factors that form the profit of an agricultural enterprise include the following factors: 1. Market capacity. The revenue of an agricultural enterprise depends on the market capacity. The larger the market capacity, the greater the ability of the enterprise to make a profit.
- 2. Development of competition. It has a negative impact on the amount and level of profit, because. it leads to an averaging of the rate of profit. Competition requires certain costs that reduce the amount of profit received.
- 3. The size of the prices. In a competitive environment, price increases do not always lead to an adequate increase in selling prices. Agricultural enterprises tend to work less with intermediaries, choose among suppliers those who offer goods of the same quality level at more low prices. 4. Prices for services of transport, public utilities, repair and other enterprises. The increase in prices and tariffs for services increases the operating costs of enterprises, reduces profits and reduces the profitability of trading activities.
- 5. Development of the trade union movement. The company seeks to limit the cost of wages. The interests of workers are expressed by trade unions that are fighting for higher wages, which creates the prerequisites for reducing the profits of the enterprise. 6. Development of activities public organizations consumers of goods and services. 7. State regulation of the activities of agricultural enterprises. This factor is one of the main ones that determine the amount of profit and profitability.
The determining factor in the content of the concept of "profitability of production" is the amount of profit. In this regard, the establishment of profitability factors is, first of all, the establishment of factors influencing the formation of profit. Profit factors can be divided into two groups:
- - factors of an internal order, depending on the manufacturer of the product and of a subjective nature;
- - factors of an external order that do not depend on commodity producers and are objective.
Internal factors include the quantity of products sold, its quality, and production costs.
The number of products sold depends on the volume of gross output and the level of its marketability. With an increase in the volume of gross output, there is an increase in products to be sold, since the growth rate of its domestic consumption is usually lower than the growth rate of gross output, which creates conditions for an increase in the level of marketability and an increase in cash proceeds on this basis. The quality of products affects the amount of profit also through cash receipts, since products are more High Quality provides a higher selling price.
Finally, the amount of cash proceeds depends on the timing of the sale of products, its structure and markets. So, for example, early vegetables, potatoes are sold at higher prices than late ones. Products are sold at different prices depending on the sales channels: when they are sold to the state, to consumer cooperatives, and on the collective farm market.
An important factor in profit is the cost of production. Decrease or increase in production costs has a significant impact on the amount of profit.
External factors include market demand for products, supply and competition of product manufacturers. High or low demand for a particular product, as well as the presence or absence of competitors, determine both the quantity of products sold and the level of prices for it, which ultimately affects the amount of profit.
Factors of profitability of agricultural production can be extensive and intensive. Extensive factors - such. Which have an impact on profitability by changing the amount of products sold, and intensive - on the growth of selling prices and reducing the cost of production.
Thus, the determination of reserves for increasing the profitability of agricultural production is reduced, on the one hand, to the determination of reserves for increasing cash proceeds from sales, and on the other, reserves for reducing the cost of production.
In the system of the market mechanism of managing profitability belongs to one of the central places. A feature of this economic category as an element of this mechanism is the complex nature, the variety of functions performed. Most often, the level of profitability is considered as the main estimated indicator with the rate of return in the lead role. We agree with this statement, but we consider it wrong to focus only on this function when assessing the place of profitability in the economic mechanism. Equally important is the stimulating function. Profitable production and profit making are an important incentive for the development of farms. Entrepreneurship as one of the main factors of progress in the market conditions is not accidentally defined as an activity aimed at making a profit. The laws of the market economy do not allow the production of products, the sale of which causes damage. The current situation with livestock production is unnatural. Another function is restrictive. It confirms this position - the production of livestock products in the public sector is constantly declining.
An important direction in the management of any enterprise, including agricultural, is the management of its profitability.
After all, it is the level of profitability of products, assets, capital that reflects the financial viability of the enterprise to ensure the well-being of employees and owners of this enterprise, to ensure the profit of the enterprise.
Solving the problems of the agrarian sector of the economy getting out of the crisis is objectively related to the transfer of management systems of agricultural enterprises to a qualitatively new level, taking into account market conditions and business principles. The system for managing the profitability of an enterprise in agriculture, which has developed in the conditions of an administrative-command economy based on stable economic conditions, high provision of enterprises with all types of resources, comprehensive state support.
In the course of market transformations, the main prerequisites for using this system have almost completely disappeared, so research on managing the profitability of agricultural enterprises in a market economy is relevant today. Despite this, the analysis of the level of profitability of the production of agricultural enterprises, as well as methods for calculating profitability indicators and the specifics of their practical application agricultural enterprises are still underexplored.
Most domestic scientists did not focus on the study of a comprehensive mechanism for managing the profits of agricultural enterprises as a factor in their successful functioning in the conditions of market competition. Scientific and practical developments of this issue through the prism of international experience are extremely relevant today.
Tasks of the enterprise economy
Definition 1
An enterprise is a business entity that economic activity for the purpose of making a profit.
It is a system of internal relationships aimed at obtaining a monetary result.
Enterprises play an important role in the country's economy, linking the state and the population. The population, buying products, saturates their needs. The state, in turn, by taxing the profits of the activities of economic entities, replenishes its budget. Thus, we can say that the success of enterprises is important for all subjects of market relations.
Under the study of processes associated with the production, marketing and sale of economic goods, a separate discipline is singled out in economic theory - the economics of the enterprise.
This is due to the fact that the economic entity itself is a system that includes subsystems. In addition, the enterprise is exposed to the influence of factors of the external and internal environment, which in one way or another change the entire manufacturing process. Environmental factors, which in microeconomics are considered as equivalent, in the economics of the enterprise, taking into account the characteristics of the subject, acquire their own specific influence.
Structurally, an enterprise is determined big amount internal relationships, so the economy of the enterprise faces a variety of tasks for analysis and control. Such tasks include:
- organization of the production process, creation of a production structure and infrastructure network within the enterprise;
- ensuring the uninterrupted functioning of the subject by debugging the mechanism for the supply of raw materials and materials;
- development and implementation of action plans;
- pricing;
- optimization of the use of labor resources;
- social security of the labor process;
- environmental protection activities;
- development and implementation of new technologies;
- accounting policy;
- rational organization of the management process.
Remark 1
Thus, we can conclude that the enterprise not only plays an important role in the country's economy, but also largely determines its development trends.
Features of agricultural activity
Agriculture is one of the most important sectors of the national economy. It not only produces food products that meet the needs of the population, but is also a source of raw materials for the processing industry. The higher the level of development of this industry, the higher the social satisfaction of society and the more stable the material and technical base of the country.
In addition, a developed agro-industrial complex provides an intrastate economic balance, a stable political environment and food independence.
However, this industry is not able to compete equally with other sectors of the national economy, so it requires some state control and assistance.
State support can be expressed in:
- regulating the price of certain products;
- subsidizing;
- special lending programs;
- tax benefits;
- infrastructure development;
- legislative regulation;
- carrying out irrigation works.
Regulation of the market price allows you to maintain the profitability of production.
Definition 2
Profitability is the value of the efficiency of resources and finances invested in the production process.
This indicator allows you to analyze various aspects of the organization's activities.
Profit, being the financial result of economic activity, determines the ratio of income to the costs aimed at obtaining them.
Profitability also allows you to evaluate the effectiveness of certain types of costs, thereby making it possible to make adjustments to production and management.
With the transition from a planned model to a market one, agricultural market entities began to independently plan their activities, focusing on maximizing income and investment efficiency.
Profitability of an agricultural enterprise
The specifics of the industry determines the factors influencing the formation of the profitability of an agricultural organization. Among them are:
- the size of the market share;
- competition;
- pricing;
- transport tariffs;
- state regulation.
The profitability of an agricultural entity determines the form of turnover, the feasibility of using resources, and also makes it possible to increase the efficiency of the organization of the technological process.
To calculate the overall indicator of profitability of an agricultural entity, the following formula is used:
R = P/T $\cdot$ 100%
where P is profitability, P is profit (net or gross), T is the value of turnover without VAT.
This calculation allows you to determine the effectiveness of invested capital.
The total income and profitability of an economic entity are directly proportional to each other. This indicator more accurately determines the financial result of the enterprise.
The level of profitability is affected by the turnover of capital. So, by calculating the ratio of the turnover of goods to the amount of capital, you can understand what kind of return comes from each ruble. The turnover and turnover of capital are directly dependent on each other.
The profitability of production assets is also determined according to the principle common with other industries:
P = (P(O + M)) $\cdot$ 100%
where P - profitability, P - net or gross profit, O - the average cost of fixed assets, M - the average cost of working capital.
When using leased premises or equipment in the activities of an agricultural enterprise, their cost must also be included in the calculation.
Specific factors of agricultural activity are the distribution costs, the area of land under crops, the number of labor resources.
Remark 2
Analysis of profitability in relation to distribution costs shows the profitability of commercial transactions.
In relation to the personnel involved, profitability determines the profitability per employee.
If we take the area under crops as the denominator, then we can calculate the profitability of one square meter earth.
It is best to conduct a constant analysis of the profitability of an agricultural enterprise, which will allow you to track changes in dynamics and correlate them with indicators of past periods.
Profitability in agriculture depends on income agrarians and expenses which he carries. For high profitability in crop production necessary produce, remove, preserve and profitably sell at the peak of prices agricultural products.
Let's try to analyze some of the constituent elements of both parts of profitability.
After working in a vertically integrated holding, I can’t get around the issue of management structure and motivation, since if the correct, well-coordinated work of all organs is disrupted in the body, then it is foolish to expect records.
The work of the enterprise as a whole depends on building the correct hierarchy of subordination, motivation and personality of the leader of the company. When considering this issue, I would like to recall Socrates: "In every science, one must reach only a certain limit, which should not be crossed."
The general laws of physics, mathematics, geometry, and other sciences take place by analogy in all aspects of our activities, so for building a management structure and well-coordinated motivated work of staff, the rule of vector addition is important.
Following the recommendations of Socrates, we consider the multiplication and division of vectors to be redundant, but if the one who sits at the top of the pyramid forgets about the addition and subtraction of vectors, then we get the situation described by Krylov in the fable "Swan, Cancer and Pike".
In the picture you see the following characters:
BusinessMent is a character that unites all controlling structures, which are mainly recruited from the bodies of the Ministry of Internal Affairs and the FSB to control the work of enterprises and prevent theft and theft, here I also include "deputies - looking" from shareholders.
Manager - a professional who must manage the enterprise alone, but in fact without permission management company and BusinessCops can't do anything by themselves. Moreover, he must manage the enterprise free of reports, instructions, orders and explanatory notes. In practice, if there is time left for leadership, then very little.
The last numerous personnel - the employees of the enterprise are depicted as a grandmother with a bag of bread and an insignificant set of other products, because. money for more to the ordinary worker.
Vector all characters multidirectional, and most importantly have nothing to do with the interests of shareholders - making a profit. IN Lately, in many structures the so-called labor simulation system through deprivation of KPI or whatever i call "punitive system of de-motivation": the agreed money is obtained only with "ideal" work without comments. Under such conditions, sycophancy, squealing and a host of other “charms” develop, but not as a normal job. There are no economic incentives except kickbacks and theft, and the forward movement of the enterprise depends entirely on the quality of the selection of employees by the personnel department - honest professionals and creative employees out of habit push the enterprise forward, contrary to the system. Danuyu demotivation system, I think not efficient.
The management company satisfies its desire to “rule” by intervening in processes that are often not understood. There is a bunch of orders and orders to which subordinate enterprises are required to respond. Instead of the production of grain and tilled crops, such enterprises generate a bunch of papers that might not have existed with normal IT structure between links and browsing information from 1C.
An alternative to this system"Swan, cancer and pike" can be contrasted with the popular image of riding with the breeze - "Russian Troika". All efforts are directed in one direction - profit! To do this, you must follow the principle: "God bequeathed to share" or distribution of % of the company's profit to all employees.
Here's a brief about management, practically in elementary truths.
Fair prices.
The income of the enterprise depends on the prices prevailing in the market. There is an opportunity to jedge price risks in the market, but only a select few knowledgeable enterprises resort to it. I do not dwell on them, since the Otkritie Bank and Information Systems will voice these aspects in their detailed reports.
With regard to price fluctuations for the growing season. For example, given dynamics of average - monthly prices for wheat 3 cells. for 10 years provided by the agency "Strategist".
An attempt to find some pattern in their change ended in a fiasco. None patterns like a certain month of profitable implementation could not be found.
Everyone understands that prices should depend on world production, carryover stocks and global consumption. However, pyramid games with the transfer of world financial resources from currency to currency, various promotions, Mrs. bonds different countries, wood products, various products make the grain market is hardly predictable. When analyzing statistics side by side, you can see whether the market will rise or fall, but it is almost impossible to say when this rise or fall will occur.
In fact, one can say that there was a "zombie" of traders according to the method of "Pavlov's dogs": USDA signal - trader's reaction"purchase" or "sale".
At the same time, one should not forget that for 1 commodity contract there are 100 “fictitious” speculative contracts on the exchange that do not have the purpose of supplying real agricultural products.
In this situation agricultural producers have to work at their own risk. To reduce these risks, banks offer hedging instruments through fixing current prices, and trading platforms advise opening opposite transactions of the same volume on exchanges. The most advanced farmers will be able to take advantage of these tips, the rest is left with one way to ensure profitability - cost reduction. The conditions for this are not the most suitable: the growth in material and technical means outstrips the growth in prices for agricultural products for more than a decade, but there are opportunities for profitable crop and livestock farming and this agricultural technologies.
Agricultural technologies.
Agricultural technologies are the way to the planned cost of agricultural products, planning agrotechnological operations, determining the quantity and model range equipment necessary for the cultivation of a particular working area, taking into account its characteristics. To build agricultural technologies comes to the aid of a computer and programs for agronomists. The initial data and the first step for automating the crop production process are electronic cards fields .
Fields in in electronic format
allow you to visualize the binding of information to work areas. The investor gets the opportunity to specify the area cultivated and lands in use, see legal status land plots, calculate the logistics of transportation, more precisely plan production costs.
The cost of performing measurement work is not significant compared to the annual error in financing the agricultural production process. In order for the measurement data to be legitimate in various state structures, it is necessary to demand a license from the "measuring officers" for geodetic and cartographic activities, otherwise the measurement data can only be used within the enterprise itself.
It is convenient to immediately download a map of the region, and possibly Russia, so that the dispatcher of the enterprise, commercial services and other specialists of the enterprise can calculate the mileage of vehicles and sales logistics.
Agronomists of the enterprise will be able to make soil maps for each field , data of agrochemical surveys, yield by years, plan crop rotations, compile technological maps etc. The procedure for working with investors and consultants is also simplified due to the availability of all data in a compact electronic form.
Computer technology makes it possible access for all departments enterprise and all specialists, if it is possible to connect computers to a network or connect to a server.
For more complete automation of work in the fields and transmission of actual data use is possible monitoring systems. Systems installationGPS/Glanass and connected sensors for fuel consumption, filling bunkers, fixing the unloading of friend or foe, electronic scales, seeding depth, recognition of aggregated implements allows you to get actual online data on the progress of agrotechnological operations.
Payback such systems depends primarily on theft at the enterprise and the inefficiency of the use of equipment. According to the enterprises that install mobile control units fuel economy averages 30%-50% as well as increasing productivity and improving the quality of work. In this case, the communication channel is cellular communication that transmits information by SMS messages, and to determine the location of the global positioning system GPS or GLONAS.
In any case, the investor and the manager receive a powerful mechanism for monitoring the work of equipment and personnel, which in turn raises the discipline and manageability of all departments of the enterprise.
Mentioning about agricultural technologies, it is impossible not to mention the scientific approach (in conjunction with the software package and the equipment monitoring system) to the planning of agrotechnological operations based on the totality of soils, texture, slopes, moisture availability, temperature data, field history analysis, availability nutrients in the soil.
The result of automation using computer programs and monitoring systems, as well as building agricultural technologies on a scientific basis by graduate students of the Timiryazev Academy under the guidance of Academician Kiryushin V.I. is Russian Hectare Harvest, which is part of Synergy Group of Companies. The average grain yield increased by 1.75 times or by 175%, while the cost per hectare rose less than the inflationary rise in prices for fuels and lubricants, plant protection products and goods and materials. In other words, the volume of purchases of goods and materials did not change, and the yield increased significantly relative to gross harvest previous years, as well as relative to the average yield in the region.
The need for a scientific approach in crop production can be shown in one unjustifiably forgotten agro-technological operation - deoxidation (liming or gypsuming) of soils.
During the years of perestroika, the volume of acidity equalization fell from 4.7 million hectares. up to 0.2 million ha. At the same time, the application of fertilizers decreased not by 23 times, but by 7 times, which indicates a further increase in the HP index towards acidity. Acidity has become a limiting factor in many agro-enterprises, especially those producing sugar beets.
For example, the average data on yield losses in the Kursk region and data on potatoes carried out on one of the farms are given.
Reserves of profitability in the storage of grain on the farm.
In case of simple transshipment through the elevator, the agrarian must pay the elevator for acceptance, cleaning, shipment and several days of storage - 400-450 rubles / ton. Monthly storage costs will average 88 rubles/ton.
The analysis of statistical series shows that the price of grain fluctuates within 1000-1500 rubles/ton during the year.
The elevator often eats up the lion's share of this difference and the agrarians, taking into account the cost of money and storage costs, there is no economic benefit to keep the grain.
The situation changes if the agricultural producer has its own storage facilities, but depending on the year they are sometimes not enough, sometimes they are redundant. Grain bags of 200-250 tons can be purchased by farmers exactly as much as the grain harvested.
In this case, the total storage costs will amount to 230-250 rubles/ton. taking into account equipment or 150 rubles / ton. without technology. .
The most expensive operation is shipment - 245 rubles / ton. including wagon supply. The supply of a wagon will amount to 7.5 thousand rubles per wagon or 150 rubles per ton, elevator services for loading 95 rubles per ton.
|
Creation of a grain loading point in the presence of railway access roads - "mobile loading into a wagon pays off" in a month, even if the cost of loading operations is 50 rubles / ton.
Many contributory factors have a cost, and each of the factors has a variety of details on which the cost of growing a particular crop depends. I stopped only on some aspects and on some examples from practice.
To discuss the pros and cons, we gather at events where we can ask questions of interest, express our opinion and discuss the experience of applying and financial results of technological solutions.
I invite everyone to an active dialogue and open discussion on any position, as there is a detailed presentation and information about suppliers on any of the topics voiced.
 Balabol, balabolit, blah blah - etymology Balabol which means
Balabol, balabolit, blah blah - etymology Balabol which means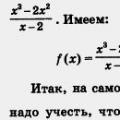 Aperture: what is it and why is it important for a smartphone?
Aperture: what is it and why is it important for a smartphone?