Modal verbs Must, Have To, May, Might: Used Rules. Be always in the mood
17.02.2015
Modal verbs in English are not so much. Earlier, I wrote about the use of CAN and COULD, Will and Would, as well as Shall and Should.
And today we will consider the rules for the use of modal verbs mUST, have to., may. and might.
The first thing you need to remember the English modal verbs - they do not change in times (they have "substituents") and after them the main verb is used without a particle to.: cANplay., must.pay., wouldgo. etc.
Also modal verbs in the proposal themselves act as auxiliary verbs:
- Can You Swim?
- Would You Play?
- May I Go?
Must vs. Have to.
Modal verb must. It serves to express the responsibility (obligation) and the need (Necessity), the Russian language in the affirmative offers is translated as "must".
Verb have to.
it does not look like a modal verb, however, performs its function. Have to.
acts as must.
in the past and future times.
The main difference in use must. and haveto. - These are their emotional aspect.
If a must.means "must do something because I need it so or want", then haveto.means "Must do something, because it is necessary for someone, it's not my desire - I have to do it."
For example:
- I Have to Pay The Bills Because My Wife Is Ill.
- I Must Stop Smoking. IT's Really Bad for My Health.
In negative proposals must. Expresses the strictest ban "It is impossible, prohibited": You Mustn't Smoke Here.
While have to.in negative proposals, it should not be, you should not, you don't have to do, but you can do if you want "and needs an auxiliary verb: You. don't have to. Pay for this.
Also must. Expresses the subordination of various types of general laws, that is, something needs to be done because it is so accepted in society.
BUT have to. expresses subordination to private "laws", that is, conscience forced you, moral principles or duties.
For instance:
- We Must Pay The Taxes.
- HE HAS TO TELL HER THE TRUTH.
May vs. Might
First, modal verbs may. and mightused to express the "feature of action", and both in the present and in the future.
For example:
- IT May Be True. \u003d IT Might Be True.
- He May Know. \u003d He Might Know.
- Take An Umbrella with You. IT MIGHT BE RAIN LATER.
- We Haven't Decided You Where to Go for Our Holidays. We May Go to Ireland.
In fact, may. expresses a little more possibility of action than might (as if 70% by 30%).
In some cases there is no big difference: you can use both modal verbs.
If you are talking about an unreal situation, better use might.
To describe a possible action or event in the past, use may Have (Done) or mIGHT HAVE (DONE).
For example:
- I Wonder Why Kate Didn't Answer The Phone. She Might Have Been Asleep.
- I CAN't Find My Purse Anywhere. Oh, I May Have Left IT in the Shop.
Secondly, in order to ask or give permission, to express wishes used only may..
For example:
- Happy Birthday! MAY ALL YOUR DREAMS COME TRUE!
- May I Stay with You Tonight?
- You May Have Another Cookie If You Like.
For the practice of consumption of modal verbs must. and have to. I suggest you perform the following exercise.
- Translate into English usingmust. andhave to.. Usehave to. only in cases wheremust. It is impossible to use:
1. You must talk to it.
2. I had to write about this sister.
3. MUST BE, they are talking about it now.
4. I have to read this book.
5. They must be played in the yard.
6. Mom got sick, and I had to lead my brother to school.
7. Must be, she recognized you.
8. I had to go there myself.
9. You will have to wait a bit.
10. They had to take care of her.
For modal verbs training may.and might, Perform the following exercise in the comments:
- Fill in skips by one of the modal verbs (May, Might):
1. You ... Use My Computer If You Need.
2. It ... be Freezing Outside. MOST PEOPLE ARE WEARING WARM COATS AND SCARVES.
4. He ... Have Been At Work.
5. He Who Falls Today, ... Rise Tomorrow.
6. ... I Bring My Friend to the Party?
7. She ... Have Been Asleep WHEN YOU CALLED.
8. I ... Come to the Cinema with them. I Haven't Decided Yet.
9. Happy New Year! ... IT BE LUCKIER THAN THE PREVIOUS ONE!
10. Don't Throw It Away, IT ... Come in Use, You Never Know.
Answers Publish in the comments a little later.
Modal verbs are a new concept for Russian-speaking and starting their study, you should clarify for yourself what kind of word type and what they differ from ordinary verbs:
This is a small group of words that do not indicate the action, but only the possibility, admissibility, probability, or the need to make any action
Act:
She writes poem. - She Writes Poems..
Probability of action:
She can write poems. - SHE CAN WRITE POEMS. Modal verbs are not expressed, but the possibility of action
- The modal verb stands before the meaning and together with it form a complex verbal lean.
- He Must Work A Lot If He Wants To Become a Good Specialist. - He must work a lot if he wants to become a good specialist
- The verb standing after modal, is always in infinitive form, but in most cases without an infinitive particle -To
- You may take my laptop. - You can take my laptop
- They do not need negative and questioning types of offer in auxiliary verb. Denial and question are built using the modal words themselves.
- May I Take Your CopyBook? - May I take your notebook?
YES, YOU MAY.- Yes you can - I CAN NOT TRANSLATE THEESE QUOTATIONS INTO English. - I can't translate these expressions into English
- May I Take Your CopyBook? - May I take your notebook?
- In Present Simple Tense (present time) in the third person, they do not have a typical end of -S.
- She Must Make a Choice. -
- She should make a choice
What to choose - may or can?
The topic of modal verbs cannot be called difficult, but among them there are couples of words with the "equal" translation into Russian. Such couples of words, of course, have certain semantic shades in English, which determine their use. Today we will look at one of these harmful couples:
may - Can. — be able to
Use cAN or may. Very often it is difficult for newcomers, although their translation seem to be no different. However, I think, having studied this table, you will understand that there are clear differences between them, which is not so difficult to remember. Why is it so important to deal with this? Because it is cAN and may. Are among the most frequently used in English.
Modal verb CAN - expresses the ability to mental or physical. Shows that actor has the strength to perform an action
- I can read in russian, Bulgarian and FRENCH. - I can read in Russian, Bulgarian and French
- I Can Work 10 Hours A Day, But I Am Very Tried At The End of the Working Day. - I can work for 10 hours a day, but I am very tired by the end of the working day
MOY modal verb - expresses some of the approval or permission to perform an action. Indicates that the subject got the opportunity to do something
 Modal verbs CAN and May have different semantic shades
Modal verbs CAN and May have different semantic shades - He May Use This Desk When He Prepare His Homework. - He can use this table when will perform homework
- Granny, You Got A Letter. May i read it to you? - Grandma, you got a letter. Can I read it to you?
Application CAN and May in informal speech
What has been said above is the "irregular" rule of use cAN and may. in standard English. But what we observe in informal, conversational English is somewhat different - modal verb cAN Ows out May. From use.
So, asking permission, the child does not use may.As follows:
MOM, CAN I Play In The Yard? - Mom, can I play in the yard?
YES, you can. - Yes.
At the same time, even adults, knowing the rules and the semantic subtleties of these words, they still neglect them, counting modal verb may. Too obforn. Talking about this phenomenon in modern conversational English, I do not urge you to speak as well - on the contrary, my advice will still be the right use of word data in relevant situations.
Video: What is the difference between Can and May?
Why do we need modal verbs in English? What modal verbs should be memorable, and what no? How to build phrases with modal verbs? Answers and many examples british offers With modal verbs you will find in this article.
What is a modal verb?
Modal verbs are unusual because they are never used by themselves. Modal verb is always used in a pair with another - semantic verb. It is the meaning verb that shows what actions are we talking about. And the role of modal verb is to show the attitude of the speaker to this action.
The easiest way to understand the purpose of modal verbs on the examples. Take a look at the offer:
I Play Football.
I'm play soccer.
And now, let's add to this proposal modal verbs of Can, Must, May and we will watch how the meaning will change:
I. cAN Play Football.
I can play football.
I. must. Play Football.
I have to play football.
I. may. Play Football.
I am allowed to play football.
In all three sentences, the same semantic verb - Play (Play). But look at how different the sense of the sentence we got, applying different modal verbs.
Thus, modal verbs need to be used when we are talking about:
- features / inability to perform an action;
- availability / lack of need to perform an action;
- council / Order / Recommendations Perform Action;
- assessment of the probability of action.
This is not a complete list of what modal verbs in English are applied. Next, we will consider in detail the 10 main English modal verbs, which they have and how to apply them correctly. Let's start with the top three of the most common modal verbs.
Three main modal verbs.
For most situations, it will be enough to know 3 modal verbs - cAN, MUST and MAY. These are the most consumable modal verbs in English. The verb CAN is generally among the ten most consumed english words And no conversation without it does. The main values \u200b\u200bof these verbs are shown in the table:
Examples of using:
He. cAN Swim Fast.
He can swim quickly.
I. must. Be Strong.
I must be strong.
You. may. Call Me Tomorrow.
You can call me tomorrow.
She. may. be Right.
Perhaps she is right.
In fact, each of these modal verbs has many values. Here I bring the most common translation. You can read in detail with all the verbs of the "Big Troika" by links:
But to use modal verbs in their speech, a little know their translation. It is necessary to still learn how to make proposals with modal verbs.
Modal verbs in English: the rules of use.
Modal verbs in English behave differently as most of ordinary verbs. To competently build offers with modal verbs, you need to know several rules. Here are the basic rules for using modal verbs:
1. As already mentioned, the modal verb is always used in a pair with a semantic verb.
Moreover, the semantic verb is always taken in an indefinite form and a particle TO. The combination of modal and semantic verb is called modal legend. In the affirmative offer, the modal fault is placed in place of the usual faith, that is, immediately after the subject.
Right:
I CAN SPEAK SPANISH.
I can speak Spanish.
You Must Help Me.
You have to help me.
Wrong:
I Can To Speak Spanish. You Must to Help Me.
2. Modal verbs do not change on persons. The end of "-s" in the third person is not added to them.
Right:
She Can Speak English.
She can speak English.
HE MUST HELP ME.
He must help me.
Wrong:
She Cans Speak English.
HE MUSTS HELP ME.
3. Modal verbs do not form a future time.
If in a proposal containing modal verb we are talking about the future, then this is usually clear from the context.
For example:
You Must Pass Your Exam Later.
You have to pass the exam later.
I CAN Go for a Walk Only Tomorrow.
I can go walk only tomorrow.
4. Of all modal verbs of English language Only two have the forms of past time. These forms are shown in the table:
| 1 form (present) | 2 form (past time) |
| cAN | could. |
| may. | might |
To get a question from the affirmative offer, you just need to make a modal verb not first place.
You can drive. - CAN You Drive?
Can you drive a car?
I MUST GO. - MUST I GO?
I have to go?
6. Negative proposals are also formed without auxiliary verb to Do.
Just negative particle not. It is put immediately after the modal verb. At the same time, with the modal verb of the CAN particle NOT is written to the CANNOT. The negative shape of modal verbs in English is often reduced:
In a negative form, many modal verbs acquire the value of the ban. Moreover, the strictness of the prohibition depends on which modal verb is used:
may not - a softer form - "you can not"
cannot - the most mild from possible prohibitions - "You can not", "not desirable"
Examples:
You must not smoke in this room!
You can not smoke in this room!
Children May Not Go for a Walk Without Parents.
Children can not walk for a walk without parents.
You Cannot Call Her. Wait 15 Minutes.
Do not call her, wait 15 minutes.
Of the last two rules there is an exception. The modal verb of the Have To require auxiliary verb DO in question and negative proposals.
Probably, it will not be superfluous to remind you that modal verbs have to. and ought To. Require after a particle to. What is also an exception to the general for all modal verbs of English Rules.
How Often Do You Have To Work on Sunday?
How often should you work on Saturdays?
Modal verbs in English - a complete list.
Are you not enough three most common modal verbs? It's time to dig deeper! Consider in order all the basic modal verbs of the English language.
Modal verb CAN (Could)
In the affirmative sentences used to say about physical / mental capabilities or ability to do anything.
She Can Play Piano.
She can play piano.
In question offers, expresses a request:
Can You Repeat Your Questions?
Could you repeat your questions?
In negative proposals, the modal verb CAN in addition to the obvious value "I can not / can not / cannot" sometimes it has the value of the ban.
You can "T Lift This Bag.
You can't raise this bag. (since it is too heavy)
You can "T Drive SO Fast.
You can't go so fast. (You forbidden)
The modal verb can have the form of the past time - Could. In addition to the last time, COULD in question deals is used to express a polite request.
I Could Play The Violin.
I knew how to play a violin. (past time)
COULD YOU PASS ME PEPPER?
Could you give me pepper? (polite request)
Modal verb May (Might)
If you look at the dictionary, you will find that the modal verb may be translated as well as the verb CAN - i can / can / may / may. But, the difference between May and Can is and it is substantial. Unlike the verb CAN, the modal verb may not expresses a physical or mental opportunity, but permission to perform action received from someone.
She May Do What She Want.
She can do everything that wants. (She is allowed to do what he wants)
The second value of the modal verb may - it allows express (Perhaps I will do, maybe I will do).
I May Visit You Tomorrow.
I may visit you tomorrow.
In such proposals, May can be replaced by MIGHT. Using Might instead of May says not about the last time, as it was possible to think, but about the smaller confidence of the speaker in the suggestion.
Modal verb Must.
This modal verb we use to say that the action must be executed. That is, when it comes to a sense of duty.
WE MUST HELP OUR PARENTS.
We must help our parents.
MODAL VIMOL MUST can also be used to express. In this meaning, it looks like a modal verb May. Using MUST instead of May speaks about the greater confidence of the speaker in what he says.
SHE MUST BE STUDENT.
She probably student.
MODAL VIMOL HAVE TO
The verb has to to your value similar to the modal verb of Must. He also talks about the debt, necessity or responsibilities. Modal verbs Must and Have To distinguish:
- have to express the duty associated with external circumstances;
- must expresses the duty associated with the internal need, a sense of debt or the personal opinion of the speaker.
Examples of offers with modal verb Have to:
You have to work more.
You have to work more.
Modal verb shld
Modal verb should can be used to:
1. Give advice
You are il. You shald go to the clinic.
Are you ill. You need to go to the clinic.
2. Report responsibility or debt. In this value, modal verbs Should and Must are similar, but should sound softer or with a shade of doubt that the action will be executed.
Your Company Should Send US A REPORT TODAY.
Your company must send us a report today.
3. To say about the expected action or action possible with a high probability.
IT IS Night now. He should be at home.
Now night. He must be at home.
Modal verb Ought to
Just like the MUST, the modal verb of Ought To reports that the action must be executed. But at the same time, the proposal with Ought to sound less categorically than a similar offer with MUST and contains a shade of a friendly recommendation or council.
Modal verb Need
Unlike other modal verbs in English, the verb Need can perform the function of not only modal, but also semantic verb.
Semantic verb Need translates as to need. Use the semantic verb Need when we say that you need some thing.
I need a good car.
I need a good car.
As a modal verb, Need is used only in the negative form "Need Not" and in its meaning it looks like "Must Not". The difference between the modal verbs of Need Not and Must Not Need:
- must NOT speaks of a strict ban on the action;
- nEED NOT indicates the optional action.
For example:
You Need Not Account to Me.
You do not have to report to me.
Modal verb shall
This modal verb has several values. It can express:
- promise
- warning
- threat
For example:
He Shall Do His Work.
She will do his job. (Promise)
DON "T GIVE HER MY BOOK. SHE SHALL LOSE IT.
Do not give her my book. She will lose it. (warning)
Modal verb Will (Would)
The basic value of the modal verb Will in English is to express agree to do any action.
I WILL PAY OFF MY DEBTS.
I pay my debts.
Will has other meanings.
Synonyms for modal verbs.
Some modal verbs in English have synonyms. The synonyms of modal verbs are phrases that have the same meaning as the modal verb, but at the same time they are hidden and form times according to general rules.
As you remember, modal verbs cannot be used in the future. Therefore, in the future, the modal verb is replaced by the corresponding synonym. For example:
You Will Be Able to Understand chinese.
You will be able to understand Chinese.
Modal verbs in English - exercises with answers.
If you read before that place, you probably have already a lot about modal verbs. It is time to consolidate your knowledge by performing several practical exercises. You will find more exercises by this link.
THE EXERCISE 1. Put the desired verb instead of dot. To check with the correct answer, click the "Right Answer" button.
EXERCISE 2. Translate proposals into English.
THE EXERCISE 3. Correct the error in English proposals.
English is a very polite language. What is worth at least the fact that everyone appeals to each other on "you". When communicating, it is important to choose the right forms, because, although many forms have the same translation into Russian, in English they are perceived with varying degrees of courtesy and formalities. Expression of permission in English - a bright example of this.
To express permission in English there are several ways:
In this article we will talk about modal verbs. IN spoken Speech we can ask permission to give permission or forbid. Let's look at what modal verbs express each of these functions and what is the features of their use.
Please resolutions (Asking for Permission): CAN, COULD, MAY, MIGHT
To ask for English permits, we have a large selection of funds: modal verbs Can, May, Could, Might.
Might - The most formal option, the rest differ in the level of courtesy. Could. and may. - more polite forms than cAN . Although the Russian questions with these verbs will be translated equally ( May I...? , May I...?) in English selection proper form Depending on the situation, communication plays a big role. If you do not know a person very well, then to ask for permission, use may. or might . If you want to politely ask a friend, then use could. . San I. ...? - Less formal and polite, but universal option.
MUM, CAN I GO FOR A WALK? - Mom, can I go to walk?
Jane, Could I Take A Look At Your Report? - Jane, can I look at your report?
Excuse Me, May I Use Your Pen? - I apologize, can I use your handle?
Might I Ask You A Question, Mister Jones? "May I ask you a question, Mr. Jones?"
Please note that such questions are usually not answered simply. "YES" or "NO"since it is not just general issuesThey transmit a certain modal function. To answer briefly, usually say "Sure", "of Course", "Certainly", "Why Not?" or "i" m afraid not ".
Since we started talking about how to ask for permits, let's break out of modal verbs for a minute and consider several more expressions:
Is it ok if i ...? - Can I...? ()
Is IT All Right if i ...? - Can I ...? / Nothing, if I ...?
Do you mind if i ...? - You do not mind if I ...?
If you need to ask a polite question, use would For its construction. Do not forget that after Would follow verb on the second form (v2):
Would you mind if i v2 ...? - You do not mind if I ...?
Would IT BE OK / ALL RIGHT IF I V2 ...? - You do not mind if I ...?
Giving permission: CAN, may.
In order to give permission not used modal verbs Could. and Might. They can only be found in matters, but reply, that is, give permission permissible only with Modal verbs CAN and May. They are very easy to use, as they do not change according to childbirth and numbers and are translated as "can":
You may smoke in this room. - You can smoke in this room.
Now When You Have FINISHED Doing Your Hometask You Can Go for a Walk. "Now that you finished doing homework, you can go walk."
The main difference between each cAN and may. - what CAN is used mainly in informal communication, and may - more formal and polite option:
You can Borrow My Pencil IF Yours is Broken. "You can take my pencil if your broke."
You may ask the Questions at the end of my presentation. - You can ask your questions at the end of my presentation.
Refuse permission: CAN "T, MAY NOT, MUSTN" T
To deny, do not give permission or prohibit anything, there are three options: cAN "T, MAY NOT and mustn "T. . Could. Not used in this feature.
The most "strong" refusal, when not just refuse, but rather, prohibit:
You musn "T Eat Ice-Cream, You Have Sore Throat." You can't eat ice cream, you have a sore throat. "
Students Mustn "T Cheat AT The Exam. - Students are forbidden to write off on the exam.
And, of course, CAN, which is used in everyday communication in most situations:
Could I Pay In Cash? - I "M Sorry, But You Can" T Pay In Cash.
- Can I pay in cash? - Unfortunately, you can't pay in cash.
CAN I Drive? - You can "T, I" LL Drive MySelf.
- Can I drive the car? - No, it is impossible, I will lead.
When they talk about permission, verbs also consume. We will talk about their use in the next article.
There is a whole category of words in English, which can be safely called a special, different from other groups of vocabulary. These words are modal verbs: CAN, COULD, MUST, MAY, MIGHT, SHULD, NEED, HAVE TO. Although they are not used as independent lexical units, as they express only the need, the ability or the possibility of performing the action, their role in the language is incredibly large. What are these words and when they are used?
CAN
CAN is rightfully considered the most common word in the modal group. Thanks to him, we can tell you that we can / can something or capable of something.
CAN is used to refer:
- intellectual or physical real opportunity to perform anything;
- requests, permissions, prohibition;
- doubts, distrust, surprise.
But it is necessary to remember that the modal verb CAN itself does not indicate the action, therefore, after it, another verb must go, directly indicating the process. This rule concerns all other words discussed below.
Could.

Must.

Modal verb MUST denotes the change, namely:
- duty or some duty due to personal beliefs, principles, traditions;
- council, recommendation or order;
- probability / assumption implementation.
Must is used not only in the present time, but also in the future. It is important to remember that in all cases its form is not modified.
May.

Modal verb May indicates the ability to perform an action or assumption of such an opportunity. IN common sense It is translated as you can / may / can be TD. May is used in cases where it is necessary to express:
- an objective possibility of performing actions to which no one hinders;
- formal request or permission;
- the assumption caused by doubt.
Might

Might is the form of the past time May. Also used to indicate the ability / request / assumption of performance. One of the special values \u200b\u200bof the word MIGHT is an expression of easy condemnation or disapproval. It is interesting that at least a modal verb might and is considered the form of the past time, it is used to designate the implementation of the process and in the present, and in the future.

The modal verb shalde is similar to MUST, but is not so strict. So, Should is used when the task is to express the duty or debt, stylistically weakened to recommendation or council. Also, SHOLD is used to refer to reproach or regret due to the fact that it has not previously been completed or the desired action can be carried out.
Need

Modal verb Need should be used to express the need or acute need to perform action. Accordingly, if Need is present in a negative design, it denotes the lack of necessity / permission to do something. Also, Need meets in question designs - here it indicates doubts about the feasibility of the implementation of the process under consideration.

Main distinctive feature has To the fact that it denotes the obligation to perform actions due to specific circumstances. Based on this, the modal verb of Have To is recommended only when it is necessary to specify the forcedity of actions caused by the current situation, and not personal desires. Have to to be used in all times, but at the same time there is their own form: the present - have to or has to, past - HAD TO, FUTURE -WILL HAVE TO.
Out of doubt, without modal verbs, it is impossible to build competent and stylistically tidy speech. Therefore, choosing ways to study English with which you can familiarize yourself, be sure to include the study of this category of vocabulary in the selected methodology. Moreover, now you have a useful theoretical base that will help you successfully cope with the task.
 What is a hot water supply of an apartment building
What is a hot water supply of an apartment building Water supply of an apartment building
Water supply of an apartment building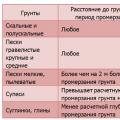 Calculation of the Load for the foundation Installed Electrical Instruments
Calculation of the Load for the foundation Installed Electrical Instruments