How To Find Gross Harvest Formula. Calculations of the gross collection of products. Gross grain harvest and harvest
Harvest (gross harvest)- this is the total volume of production in physical terms, obtained from the entire area of harvested main, repeated and inter-row crops of agricultural crops. The yield is measured in natural units of mass (tons, centners, kilograms, etc.) and characterizes the total scale of production for each individual type of crop production.
Accurate data on the size of the crop (gross harvest) can be established only after harvest. However, information about the future harvest is needed in earlier periods to determine the expected production of crop products and calculate the requirements for production resources before the start of harvesting. For this purpose, the yield indicators are estimated in relation to different periods of plant development and periods of agricultural production.
There are the following harvest indicators: species harvest, standing harvest before the start of harvesting, actual harvest, net harvest.
Species harvest- this is the yield expected based on the state of crops at different stages of plant development, which is usually determined by an expert (eye) method, or by a selective method (by imposing meter marks), taking into account the state of the crops (density, development, appearance, etc.). The definition of the specific yield in economic practice is aimed at making operational management decisions in the technology of crop production.
Standing harvest before harvest is actually grown, but not yet harvested. Its size can be determined in the same ways as the species yield, as well as by calculation based on sample data on the actual harvest and losses during harvesting from typical plots.
Actual harvest(gross harvest) is actually the capitalized tax for each type of crop production after harvest. The actual yield for a group of grain and leguminous crops can be expressed in the initially recorded mass (bunker harvest) and in the mass after processing (granary harvest); for fiber flax and rapeseed - in bulk after processing, i.e. minus from the initial gross collection of unused waste and shrinkage during the finalization of the crop; for other types of crops, the yield is determined by the physical mass of the actually received and recorded gross harvest of products.
Pure harvest- this is the actual collection (usually after revision) minus the seeds of the corresponding types of crops used for this harvest. The net yield can be calculated for cereals, legumes, flax seeds, rapeseed, and potatoes.
Under yield understand the generalizing indicator of the average harvest of each type of agricultural products per unit area. Depending on the type of agricultural crop and the scale of its production, it is customary to determine the yield per hectare, 1 are or 1 m 2.
For various indicators of the yield (gross harvest), it is possible to calculate the corresponding yield indicators, i.e. species yield, standing yield before harvesting, actual yield, net yield.
In the agricultural enterprises of the Republic of Belarus, the yield of almost all agricultural crops is calculated per unit of spring productive area. For annual and perennial grasses (for hay, green mass and seeds), the yield is determined per unit of actually harvested area.
In statistics, one should distinguish between individual (for one crop) and average (for a homogeneous group of crops) yield. To calculate the average yield, the formula for the arithmetic weighted average is used:
where is the average yield; - individual yield of each crop; - the sowing area of this culture. Individual and average crop yields are the most important indicators of the level of agricultural land use, to a large extent determining the efficiency of the work of agricultural enterprises, farms and personal subsidiary plots.
It should be noted that the yield of each agricultural crop per unit of sown area in natural terms makes it possible to evaluate and compare the work of the economy only for specific crops, provided that the natural soil fertility is the same. With an objective comparative assessment of the work of agricultural enterprises, it is necessary to calculate the gross harvest for each crop per 1 point-hectare of sown area.
In the process of growing agricultural crops, a countless number of factors affect the yield, which can be conditionally divided into two large groups - natural (soil-climatic) and economic.
Natural (soil and climatic) factors (soil quality, depth of soil waters, topography of the territory, duration of the growing season, amount and intensity of precipitation, sunny days, temperature regime, etc.) affect the yield objectively and independently of human activity. The natural factors of the formation of agricultural crops cannot be changed, but sometimes they can be adjusted by the skillful application of economic factors. A high level of development of productive forces makes it possible to largely compensate, for example, the low natural quality of soils, smooth out excessive waterlogging or replenish the lack of moisture during the period of active growth and development of plants.
The economic factors of crop formation are determined by the existing level of agricultural technology and are directly manifested through the implementation of agricultural measures aimed at increasing the yield of agricultural crops. Various agrotechnical measures can be conditionally divided into two groups: a) material investments (lime materials, fertilizers, seeds, pesticides, growth stimulants, etc.); b) agrotechnical work (tillage, delivery and application of lime materials, fertilizers, pesticides, sowing and planting, inter-row cultivation of crops, harvesting, etc.).
The statistical study of the factors of the formation of the yield of agricultural crops is complicated by the fact that accurate information about many factors in the current accounting and reporting of agricultural enterprises is not provided. So, for example, the temperature regime during the growing season of crops is not reflected in the documents of agricultural enterprises and, therefore, they usually use the information services of specialized agrometeorological, hydrological and other organizations.
Statistical identification of the influence of each individual factor on yield can be identified using the following methods:
a) the method of simple analytical grouping according to the factor under study for a fairly large sample of farms with similar conditions, but having significant differences in the factor under study. The significance of the influence of the factor under study on the yield must be confirmed by the use of analysis of variance;
b) the use of the correlation-regression method for a sample of the same farms,
as when conducting an analytical group. The found correlation coefficients, correlations and regressions will indicate a quantitative measure of the dependence of the yield on the factor under study.
Statistical impact assessment the level of agricultural intensification on the yield of agricultural crops can be carried out by the indicated methods, and the total cost of all agrotechnical measures per 1 hectare of the sown area of a certain agricultural crop will act as a factor (grouping) attribute.
The crop structure is the percentage of the gross harvest of each crop in the total harvest.
For a group of homogeneous crops, the specific gravity of the yield of an individual crop is calculated by the formula
 ,
,
where, - specific gravity (in%) and natural volume (in kilograms, centners, tons, etc.) of the harvest of each crop, respectively; - total yield for a group of crops.
The sown area is a plot of arable land occupied for sowing a variety of agricultural crops.
The sown areas are distributed (classified) according to various qualitative characteristics: biological characteristics of crops, production purpose, accounting categories, etc.
Depending on the biological characteristics of crops, all crops are divided into annual, biennial and perennial (permanent) crops. It is customary to refer to the group of annuals those crops, the growing season of which on the same area can last no more than one agricultural year.
According to their production purpose, annual and biennial crops, usually placed in a crop rotation, are divided into the following groups: cereals and legumes, industrial, potatoes and vegetables and melons, fodder, green manure crops. In turn, these crops are subdivided into winter and spring crops according to the cultivation time, and according to the sowing methods - into continuous and row crops, bare and undercover.
Harvest (gross harvest) is the total volume of production in kind, obtained from the entire area of harvested main, repeated and inter-row crops of agricultural crops. The yield, measured in simple absolute units of mass (tons, centners, kilograms, etc.), characterizes the overall scale of production for each individual type of crop production.
There are the following yield indicators: species yield; standing harvest before the start of timely harvesting; actual harvest; clean harvest.
The specific yield is the expected expected yield, based on the state of crops at different stages of plant development, which is usually determined by an expert (eye) method, or by a selective method (by imposing meter marks), taking into account the state of crops: density, development, appearance, etc. Definition and the assessment of the specific yield are common in economic practice and are aimed at making operational management decisions in the technology of production.
The standing crop before harvest is actually grown, but not yet harvested. Its size can be determined in the following ways:
by calculation based on continuous data on the actual collection and sample data on losses during harvesting from typical plots; by imposing meter marks on crops before harvesting (if conditions permit); by eye assessment of crops by experienced specialists.
The actual harvest (gross yield) is the capitalized harvest for each product after the crop is harvested. The actual yield for a group of grain and leguminous crops can be expressed in the initially recorded mass (bunker harvest) and in the mass after processing (granary harvest); for fiber flax and rapeseed - in bulk after processing, i.e. minus from the initial gross collection of unused waste and shrinkage during the finalization of the crop; for other types of crops, the yield is determined by the physical mass of the actually received and recorded gross harvest of products.
Yield is understood as an indicator characterizing the average harvest of each type of agricultural product per unit area. In agricultural organizations, it is customary to determine the yield per 1 ha, in personal subsidiary plots - by 1 are or 1 m 2.
Table 7 - Dynamics of sown areas
The data in the table show that in recent years there has been an increase in the sown area for grain crops, in 2013 their area amounted to 9799 hectares.
Table 8 - Dynamics of gross harvest and yield
|
Indicators |
||||||
|
Productivity, c / ha |
Gross collection, c |
Productivity, c / ha |
Gross collection, c |
Productivity, c / ha |
Gross collection, c |
|
|
Cereals and pulses - total: |
||||||
|
Incl. Winter cereals |
||||||
|
Spring cereals |
||||||
|
Legumes |
It can be seen from this table that the yield and gross yield are increasing due to the increase in cultivated areas and favorable weather conditions. In 2011, the gross harvest amounted to 118300c / ha, and in 2013 - 164634c / ha.
Gross harvest of agricultural crops is the total volume of harvested agricultural products, which can be calculated for one specific crop or for a specific group of crops. The term has been used since 1954. Natural units are the measure of measurement. A synonym for this concept is gross agricultural output.
Gross harvest of grain crops is one of the types of gross harvest of agricultural crops. It directly depends on the harvest, being, in fact, its equivalent.
What are grains?
Cereals are one of the most important types of agricultural crops for humans. They play a major role in providing humanity with food, and the areas they occupy are maximum in comparison with those of other groups of agricultural crops. In addition to food, grain is used to produce alcohol and other organic substances, including those used for the production of biofuels. The third purpose of cereals is the production of pet food.
All cereals are divided into cereals and legumes. The former belong to the family of cereals and include such species as wheat, rice, oats, corn, rye, millet and other crops less known in our country. The exception is buckwheat, which belongs to the buckwheat family.
Legumes belong to the legume botanical family. In some cases, cereals only refer to cereals. The main crops are wheat, rice, barley, oats, corn and buckwheat.

The main ones are the USA, Russia, Argentina, the European Union, Canada, Australia. They account for over 85% of total world grain exports. The main countries consuming grain are China, Turkey, Japan and Saudi Arabia. Given the agricultural potential of China, it could be an important exporter of various agricultural products, but due to its high population, on the contrary, it is forced to purchase it.
Corn, wheat and rice add up to 43 percent of the world's total calories.
Gross grain harvest and harvest
The grain yield is the total volume (or mass) of grain ripened in the fields. Except for losses during harvesting, the gross grain harvest is equal to the harvest. Under unfavorable weather conditions, due to large losses, it can turn out to be significantly less than the yield. However, the calculation of the size of the crop is carried out precisely according to the gross harvest. Since it is quite difficult to calculate the lost grain. When they say that such and such a crop was harvested, they mean exactly the gross harvest.

What is yield?
The yield of grain crops is understood as the mass (or volume) of ripe grain per unit area (usually 1 ha). There are several types of yield:
- Planned yield is the average volume of grain production that can be obtained from 1 hectare under current conditions.
- Potential yield is the maximum amount of grain that can be obtained from one hectare under favorable conditions.
- The expected yield is an approximate estimate of the future harvest (gross yield) harvested from 1 hectare of sown area.
- Actual yield is the average weight (volume) of grain obtained from 1 hectare of sown area.
- The growing yield is the entire mass of grain grown on one hectare of the sown area. It is determined by collecting all grain from a certain area before harvesting or by other methods. Allows you to estimate the amount of losses occurring during harvesting.
Harvesting refers to the totality of agricultural work to remove ripe grain from agricultural fields. It belongs to the final stage of growing a culture. Over time, the degree of mechanization in harvesting increases.
Dynamics of harvest and grain yield over the past 100 years
The yield and the total gross harvest of crops in Russia do not change exactly the same. Let's take a closer look at the dynamics. Before World War II, the yield and gross harvest remained unchanged, experiencing only local fluctuations. Then both indicators began to take off quickly. Since 1970, the gross harvest has ceased to increase, while yields have continued to grow, albeit at a slower pace. This indicates the beginning of the reduction of agricultural areas.

In the 90s, the gross collection fell sharply. The yield fell to a lesser extent. In the 2000s, the gross yield increased slightly, and did not reach the level of the 70s and 80s, but the yield increased sharply. Such a picture suggests that in the 90s, the reduction in acreage was combined with a decrease in crop yields, which indicates a total decline in agriculture. In the 2000s, the reduction in acreage continued, but the sharp increase in yields more than compensated for this effect.
What wheat harvest is expected in 2018?
According to the Ministry of Agriculture, the gross harvest of wheat in 2018 will be 64.4 million tons, and the total grain harvest will be 100 million tons. At the same time, due to weather conditions, the total loss of grain mass will be at the level of 30 million tons. Such data was reported by a representative of the ministry to the TASS agency.

Reasons for the decline in harvest in 2018
Unfavorable weather conditions (especially drought) are the main reason for the lower forecasts for gross grain harvest in 2018. The most affected by the drought were such subjects of the Russian Federation as the Republic of Crimea, the Volgograd region, as well as Altai and Kalmykia. Also, the emergency mode due to a shortage of soil moisture can be introduced in the Rostov and Astrakhan regions, to a lesser extent in the Saratov and Samara regions, as well as in some places on the territory of the Stavropol, Krasnodar territories and the Republic of Adygea.
In other areas, the risk to crops is waterlogging. These regions are: Arkhangelsk Region, Yakutia, Altai Territory, Novosibirsk Omsk and Kemerovo Regions, as well as Trans-Baikal Territory.
A difficult situation with harvesting due to heavy rainfall is observed in the Sverdlovsk, Kurgan and Tyumen regions. Here, a shift in the sowing time of crops is expected by about 2.5 weeks. According to the ministry, all this can also lead to a decrease in the harvest.
At the same time, the total gross grain harvest in 2017 became a record and amounted to 135.4 million tons, of which 85.9 million tons fell on wheat. Annual grain exports reached 52.4 million tons.
gross fee- General collection of products from the entire sowing area. [GOST 16265 89] Topics agriculture General terms harvesting ... Technical translator's guide
gross harvest of agricultural crops- gross harvest of agricultural crops, the volume of produced (actually harvested) products over the entire sowing area of various agricultural crops. Calculated for individual crops (cotton, potatoes, sugar beets, sunflowers ... ... Agriculture. Big encyclopedic dictionary
The volume of actually produced (collected) products from. NS. cultures; accounted for separately. crops or some groups of crops from the entire sown area. Calculated since 1954. To determine the volume of V. s. with. because all produced with. ... ... Great Soviet Encyclopedia
GROSS AGRICULTURAL CROPS- the volume of produced (actually harvested) products over the entire sowing area decomp. with. NS. cultures. Calculated by dep. crops (cotton, potatoes, sugar. beets, sunflowers, etc.) or dep. groups of crops (legumes, cereals and ... ... Agricultural encyclopedic dictionary
GROSS, gross, gross. 1. Consisting of the entire proceeds, without deducting expenses (bargaining econ.). Gross income. Gross revenue. Gross collection. 2. General, gurtovoy, performed by a mass, some kind of set (special region). Gross span ... ... Ushakov's Explanatory Dictionary
collection- a (y); m. see also. assembly, assembly 1) to collect 2), 3), 4) Collection of cotton. Collection of honey. Collection of medicinal herbs. Tax collection ... Dictionary of many expressions
A (y), m. 1. Action according to the verb. collect (in 8 and 9 digits). Cotton picking. Collecting honey. Collection of medicinal herbs. Tax collection. 2. What is collected, the total amount of which l. collected. Gross harvest of grain. || Levied or collected for which l. money,… … Small academic dictionary
- (GRP) an indicator that measures gross value added, calculated by excluding intermediate consumption volumes from the total gross product. At the national level, the GRP corresponds to the gross national product, which ... Wikipedia
A (y); m. 1. to Collect (2 4 characters). C. cotton. S. honey. C. medicinal herbs. C. taxes. 2. What is collected, the total amount of which l. collected. Gross with. grains. // Charged or collected for what l. money, deductions. Insurance s. Excise tax ... encyclopedic Dictionary
Annual gross income of a business entity- Annual gross income (Vd) income received by an economic entity on average for one year is equal to the difference in the cost of production of biological resources and material and technical costs for collection, storage, transportation and sale of products. ... ... Official terminology
PATENT FEE- tax (collection), often used as alternative systems of taxation of income of small and medium-sized enterprises (as a rule, handicrafts and trades), as well as taxation of income of persons engaged in entrepreneurial activities. ... ... Encyclopedia of Russian and International Taxation
The agricultural industry uses specialized vocabulary for calculations and calculations. Its meaning can sometimes be inaccessible to a person who does not carry out activities in this sector and is in no way interested in it. The definitions associated with calculating the volume of goods produced are especially difficult to understand. For example, the term "gross production" requires some explanation. It seems simple at first glance, but in fact it hides the difficulties of calculation and definition.
Deciphering the concept of "gross"
By itself, this word is ubiquitous in economic science and practice. It appears in such an important macroeconomic indicator as GDP (gross domestic product), GNP and GRP - its national and regional varieties. The word itself can be explained as the totality of something, the total amount, mass, volume. It can be an action performed by a group, some multitude. For example, the gross flight of a crane, that is, an aggregate of cranes. If you look at the list of synonyms for this concept, you can find the following words: massive, solid, general and others in the same spirit.
In economics, this term serves to denote income from the sale of goods and services, to characterize the general collection of products, for example, the collection of vegetables or fruits. The concept of income should not be confused with the concept of profit, since the key feature of income is the absence of any deductions from the total amount when calculating. If the term gross is used in conjunction with the concept of collection, then most often a similar combination can be seen in the agricultural industry. In this case, the gross harvest is a characteristic, or rather a measure of the harvest collected at a time from the entire sown area.
Agricultural crops
Sometimes the term is used in abbreviated form as an abbreviation for VSSK. This definition means the total volume of cultivated plants harvested from sown fields. Moreover, from crops, both basic and intermediate. It can be a calculation both for individual crops (for example, potatoes, wheat, rye, etc.), and for whole groups of crops (fodder, cereals, vegetables, fruits, etc.).
As for the calculations across the country, they are divided into two categories: aggregate for all categories of agriculture and a separate one for entities involved in the cultivation of agricultural crops. As a result, individual entities (farms, organizations) are calculated within the administrative districts of territories and regions. As for the quantities of measurement, units of mass are used as them - from kilograms to tons.
This is a concept that can be expressed in different ways. It is also sometimes referred to as actual collection. Weighing is carried out both during the harvesting period and after everything sown has been collected from the fields. For a fairly long period of time, the actual collection was characterized by bunker weight. Its distinctive feature is the weighing of the harvested crop together with weeds, uncleaned soil, undried moisture. Until 1990, bunker weight was the most important crop indicator. After that, it is replaced by a weight indicator, which excludes the presence of moisture, earth, dirt and other elements that are not directly related to the product. Then this amount is on average 10% less than the primary collection.

Harvest and gross yield
In fact, this is the same concept, they are synonymous with each other. But only with some reservations. The fact is that in agriculture there are several types of crops. In addition to the above-mentioned actual, which will represent the gross harvest, there are three more types of crops:
- Species. It, unlike the actual one, represents the expected harvest. On the basis of the data obtained in the analysis of the potential volume of the harvest, the tactics of collection are built in the future and management decisions are made. As the main method of obtaining information about the possible future level of production, the imposition of meters or simply determination by eye is used. To determine the visa yield, the condition of the seedlings, their density and appearance are also important.

- Standing harvest. In essence, this is the same as a specific crop. That is, it is measured and calculated using the same technique. The only and key difference is that the growing crop is already grown, but not yet received. Before the gross collection, this is the previous stage.
- Clean. This is the final stage of harvesting. After cleansing of any foreign objects, the proportion of seeds that is necessary for future crops is also subtracted from it. So, for example, if the bunker harvest of wheat amounted to 308 thousand tons, then the net harvest, taking into account the deduction of garbage, moisture and part of the seeds for further work, will be only 208 thousand tons.

Yield
Yield and gross yield are interacting phenomena and complementary concepts. The first is an agricultural indicator that speaks about the average collection of cultivated plants from a certain unit of area. It can be calculated from 1 m 2, from 1 are or 1 hectare.
Each type of crop, from specific to pure, you can choose your own yield indicators. They are calculated differently for one specific culture (individual) and for a group of cultures (average). These individual and average indicators are extremely important in that they show the degree of efficiency of the use of agricultural land.

How to calculate gross tax?
It is very easy to calculate the actual yield. To do this, you just need to multiply the area of all crops from which the products are harvested by the yield indicator. Within the framework of calculating the gross harvest, it becomes difficult to determine the numerical indicator of the yield. In this case, you need the average yield described above.
You can find it using the following formula for the arithmetic weighted average:
In it, the letter S is the area on which crops grow, and Y is an individual indicator of yield.
General conclusion
What does gross tax mean in terms of economics? First of all, it is one of the fundamental concepts in agriculture. It denotes the cumulative collection of products from the entire crop area. Concepts such as "gross harvest" and "harvest" are synonymous with each other. Also, in practice, they are often referred to as the actual harvest. Its distinctive feature is the calculation of the total volume of harvested products without deducting seeds for further sowing. If this deduction has been made, then the actual crop flows into its “pure” variety. It is not difficult to calculate the gross harvest: you need to multiply the area under crops by the average yield.
 Who and how makes money on import substitution and innovations in agriculture R
Who and how makes money on import substitution and innovations in agriculture R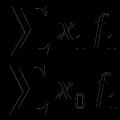 What is the industrial production index, its role and calculation
What is the industrial production index, its role and calculation Calculation of the design population of the city Term in metallurgy
Calculation of the design population of the city Term in metallurgy