Creative work "laurel tree". Laurel family Useful properties of bay leaves
"Flowering Plants" - Sagittal. Cucumber. Brush. The structure of the flower. By dismemberment of the leaf blade. Edge. Creeping stem - a stem that creeps along the ground, but does not take root. Ascending. Lobed. Stipule. Cordate. Hanging. Oval. The trunk is the main stem of the tree. Basket. Panicle. Corolla petals not only protect the pistil and stamens, but also attract pollinating insects.
"Biology of organs of flowering plants" - Flower. Functions: Photosynthesis Oxygen release. Functions: Carrying out substances Carrying out leaves to light. Variety of flowering plants. Stem. Functions: strengthens and retains in the soil absorbs water and mineral salts. Find the stem of the plant. Name the parts of the flower. What plants are more in nature: unicellular or multicellular?
Angiosperms - The number of flower parts is a multiple of 3. Perianth. Reticulated leaf venation. Class Dicotyledons. Peduncle. The embryo has one cotyledon. Classification (example). Review notes. The embryo has two cotyledons. Class Dicotyledonous About 200 thousand plants, almost 300 families. Family Compositae (Astrovye). Exceptions:
"Reproduction of angiosperms" - Development of angiosperms. Topic: Sexual reproduction of angiosperms. Fertilization scheme in flowering plants. Common raspberry 11. When and by whom was double fertilization discovered? 1. Sexual reproduction of plants is carried out by A. spores B. seeds C. buds G. vegetative organs.
"Reproduction of angiosperms" - Question number 1. What are the names of the plants formed from the root buds of the mother plant? Cuttings. What is the name of the male gamete of an angiosperm plant? What kind of cuttings are used in agriculture for plant propagation? Question number 4. Kidney vaccination. Vegetative reproduction. Sexual reproduction.
"Angiosperms Division" - Cruciferous. Why are angiosperms so diverse and dominant in the biosphere? Seed structure. Characteristics and meaning. Leaf vein. The presence of a flower Angiosperm Double fertilization Variety of life forms. Monocotyledonous dicotyledons. Legumes. Dicotyledons. Signs of angiosperms.
The homeland of the plant is the land of the Mediterranean, where you can find trees reaching 15-18 meters in height. In our regions, the plant is grown in the Crimea and the Caucasus. All parts of the tree contain essential oils, which are used in the cosmetic industry. It is the presence of oils that gives the laurel such a specific aroma.
In the kitchen, each housewife keeps fragrant leaves of a noble laurel, popularly called lavrushka. In cooking, this is the most common seasoning, but few people know that this spice can be successfully used for medicinal purposes.
Bay leaf - composition
100 g bay leaves contain:
Bay leaf - 18 beneficial properties
-
Digestive health
The essential oils of the leaves are able to have a positive effect on the gastrointestinal system, soothing inflammation in case of intestinal irritation. Organic compounds of the leaves, acting as a good diuretic, reduce intoxication when toxic substances enter the body.
Some proteins are difficult for our stomach to digest, but the enzymes found in laurel contribute not only to their absorption, but also reduce digestive disorders such as celiac disease, associated with damage to the villi in the small intestine. Enzyme-rich decoction of the plant relieves heartburn, provides rapid breakdown of proteins. In cases of indigestion, or excessive gas formation, take a decoction made from 5 grams of leaf, 250 milliliters of water with the addition of a piece ginger This article lists 18 undeniable benefits of drinking tea with ginger, 6 popular recipes for preparation and use for various diseases. and a teaspoon of honey. This drink will restore the work of the gastric tract, increase appetite and restore strength.
-
Respiratory diseases
Essential oils, extracted from spices and mixed with ointments, relieve respiratory diseases. The soaked leaves are used as a compress, leaving it on the chest overnight. Laurel vapors, possessing the quality of a natural antibiotic, will create not only an aromatherapy effect, but also help to better discharge phlegm.
For a long time, the symptoms of colds and respiratory diseases were treated with infusions and decoctions of the plant. The manifestations of acute respiratory infections were removed by inhaling laurel vapors, and when coughing and sneezing, the leaves were boiled in 200 grams of water and the mixture was taken during the day.
-
Hair health
If you want to improve the condition of the head follicles, or eliminate dandruff, you just need to add a few leaves to the water and rinse the strands with a solution. This procedure will have a healing effect, eliminate dry skin and dandruff.
-
Anti-inflammatory action
The sheets contain unique phytonutrient compounds that are known for their ability to relieve a variety of irritants. People with arthritic pain apply leaves to the affected areas of the body in the form of applications, thereby reducing pain and swelling of the affected areas. Such applications are performed with the addition of castor oil to the laurel mixture, pre-grinding the steamed leaf raw material.
Pain from stretching tendons and rheumatism is relieved by the oil obtained from the plant. With a headache, it is enough for them to massage their temples, or simply inhale its vapors.
-
Heart health
The presence of caffeic acid in organic compounds of bay leaves is aimed at improving heart function. Rutin strengthens the capillary walls of blood vessels, and caffeic acid helps to remove "bad" cholesterol from the walls of the arteries.
Powerful compounds of rutin, salicylates, caffeic acid and phytonutrients improve heart function, preventing heart attacks and strokes. In case of heart disease, it is recommended to use a decoction made from 1 teaspoon of leaves, 1 teaspoon of rosehip flowers, boiled in 300 ml of water. The final volume of the liquid should be 80 ml. Such a decoction will positively affect the work of the heart.
-
Cancer prevention
A unique combination of phytonutrients, catechins, eugenol, parthenolide and clinalool protects the body from the harmful effects of free radicals and prevents healthy cells from mutating, which is important in the prevention of malignant neoplasms.
The above chemical components, being a catalyst, help to strengthen the body's defenses and increase their resistance to various types of cancer. So, the presence of parthenolide is able to inhibit the formation and spread of cancer cells of the cervix.
-
Relief of anxiety and stress
One of the most significant properties of the plant is its natural ability to relieve anxiety and excessive excitability. Linalool, a constituent of the sheets, reduces the amount of stress hormones, preventing them from being over-read, helping the body stay in a balanced, calm state.
-
Diabetes care
Diabetes research has noted the ability of bay leaves to improve insulin receptors and regulate insulin levels in the blood. The plant is recommended for patients with type 2 diabetes, as a means capable of lowering glucose and cholesterol levels, thereby eliminating the manifestation of exacerbations of diabetic episodes. To obtain the maximum positive result, powdery raw materials of the leaves are consumed throughout the month. The plant's antioxidants enable the body to process insulin, helping people with insulin resistance.
-
Helping the female body
Lavrushka rich in folic acid is especially useful for the intrauterine development of the unborn child, as it activates the process of blood cell formation, which is important for the intrauterine formation of the fetus.
Douching with bay leaf infusion improves the vaginal mucosa, and oral administration normalizes the monthly cycle in women.
Decoctions and infusions are able to actively stimulate the contractile activity of the uterus, they are used to regulate the menstrual cycle.
IMPORTANT!Excessive consumption of concentrated infusion can cause uterine bleeding.
-
Relaxing action
A few drops of laurel oil diluted in water and drunk before bed will help you relax and induce a healthy sleep.
-
Ability to stop nosebleeds
In the case of nosebleeds, use boiled 2-3 leaves in 150 ml of water, drinking the mixture for an hour.
-
Insect bite remedy
Due to lauric acid, the plant is classified as a natural repellent that has the ability to repel insects. A paste made from soaked and grated leaves is used to treat mosquito bites and even snakes. Using antifungal and antibacterial qualities, she is treated for bruises, bruises and cuts.
-
Help for healthy hair and skin
In cosmetology, the plant is valued for its rich composition of minerals, vitamins and antioxidants, which it shares during procedures aimed at maintaining healthy skin and hair. Decoction rinsing can help get rid of dandruff by improving the structure of the hairline and strengthening the follicles.
Oil based on laurel raw material is a good tonic for the scalp. It will relieve the plant from the manifestations of head lice. For this purpose, 50 grams of leaves are brewed in 500 ml of water, the solution is applied to the damaged strands for 3-4 hours, then washed off. The hair after the procedure acquires a healthy color and shine.
-
Disinfectant properties
Both the leaves and the trunk of the tree have disinfectant properties. A tincture made from 5 drops of oil and 100 ml of water relieves ear pain and removes age spots on the face.
-
With sinusitis
The essential oil of the leaf, having antiseptic and antibacterial properties, will help relieve inflammation of the paranasal sinuses with sinusitis. At the same time, it perfectly replaces drugs of chemical origin. The oil is instilled into the sinuses, one drop at a time. To relieve complications of the disease, steam inhalation is recommended. This procedure is also allowed for children.
-
Antiallergic action
The soothing and cleansing properties of the leaf are used to eliminate allergic reactions, suppuration and diathesis in children. For this purpose, it is added to the water for baths and rubdowns.
-
Sweating feet
A fragrant bath of 5–7 leaves, possessing a bactericidal effect, will improve the condition of the skin of the feet and get rid of an unpleasant odor. This procedure should be performed for 10 minutes about a week, at the end of wiping dry the soles of the feet.
Bay leaf - medicinal recipes
Stomach ailments
To improve the work of gastric peristalsis, you should skip several leaves in a blender, squeeze the juice out of them and dilute it in one glass of water. Take on an empty stomach.
8-10 Lavrushki boiled in half a liter can relieve flatulence. The broth is drunk in half a glass in the morning and in the evening.
Kidney inflammation
Five grams of finely chopped leaves are boiled in 500 ml of water for about 5 minutes. Let it brew, filter and use one tablespoon twice a day, morning and evening. Already after three days, relief comes.
Diabetes
To improve the condition, 5-6 leaves are brewed in 250 ml of boiling water. The solution is insisted in a thermos for about a day and taken 30 minutes before meals.
From cough
10-12 steamed leaves in 500 ml of water will help relieve cough symptoms. The solution should be boiled down to the readings of 250 ml and taken chilled, 3 tablespoons a day.
For joints
In case of pain in the joints, crushed 2-3 leaves are dipped in a glass with vegetable oil and heated in a water bath for about 30 minutes. A warm mixture is applied to the area of diseased joints with osteochondrosis and arthritis.
With increased arterial indications
To lower blood pressure, boil 3 lavrushki in 300 ml of water, insist until the broth turns pink. Take 50 ml three times a day.
With throat cancer
An alcoholic infusion is prepared. Half a glass of leaves is poured with 500 ml of vodka. Insist 14 days, occasionally shaking the tincture. Strain and take 1 tablespoon 30 minutes before meals.
From hemorrhoids
In folk medicine, plants have long been used for "uncomfortable" disease. 25 leaves are steamed with three liters of boiling water. It is taken in small sips during the day.
To strengthen the immune system
Place 10 leaves in 300 ml species, bring to a boil and boil for about 5 minutes. Insist for a while and take a tablespoon 3-4 times a day. In the season of colds, to consolidate the effect, you can repeat the procedure after two weeks.
Contraindications to the use of bay leaves
With the blackening of positive qualities, the plant has a number of contraindications:
- use during pregnancy is not recommended;
- breastfeeding;
- with frequent constipation;
- exacerbations of peptic ulcer disease;
- with severe forms of diabetes;
- liver disease;
- used in large doses acts as a poison;
- after cooking, the leaves should be taken out of their dishes, so as not to inadvertently injure their oral cavity with sharp edges.
In ancient Rome, laurel was used to relieve snake bites. Wreaths were made from it and decorated with them the heads of the winners of Olympic competitions and military battles.
In Greece, the plant was hung in homes as incense. Hands were washed with water flavored with essential oils as early as the 1st century AD. Decorative items and home decorations were made from wood.
The aromatic components of the plant were used for smoking meat and fish.
The cosmetic industry actively uses the essential oils of the leaves in the production of massage oils and soaps.
Laurel is added to the Bloody Mary cocktail. In Western countries, it is even used in the preparation of desserts.
If you wear a few leaves of noble laurel on your body, this will relieve you of hallucinations.
If the spice is stored for more than a year, it loses its quality and acquires a bitter taste.
If the leaf is affected by brown and black spots, do not use it.
The plant is not so whimsical that you can grow it at home in a pot.
After chewing the leaves for a while, you can achieve not only freshness of the mouth, but also whiten your teeth.
"The structure of flowering plants" - Fruit. Biology, grade 7. From which organ of the plant is the fruit formed? Flowering plants. What plants are called flowering plants? A shoot is an organ of a plant, consisting of a stem with leaves and buds. What is inside the fetus? The external structure of a flowering plant. The seed is the reproductive organ of seed plants.
"Reproduction of angiosperms" - Question №4. Flower grafting. Double fertilization. Artificial pollination. Propagation of angiosperms. Question number 1. Kidney vaccination. Question number 2. Tissue culture. Self-pollination. In which part of the seed does the ovule cover develop after fertilization? Pollination by the wind. Ovule. Sexual reproduction.
Angiosperms - Department of Angiosperms. Why angiosperms? The embryo has two cotyledons. Flowers are three-membered. Family Onions. Core root system 11. Homework. Classification (example). Families: Cruciferous Rosaceae Solanaceae Moths Asteraceae, etc. The number of flower parts is a multiple of 3. Stamens.
"Cotyledons" - Monocotyledons. Dicotyledons. From the pistils of the raspberry flower, juicy drupes are formed - the elements of the fruit are polydrupes. By the number of cotyledons, plants are. Fruit - berry (nightshade, tomatoes, potatoes, peppers). Reed. The fruit is a box (dope). The fruit is a capsule (tobacco, scented tobacco, petunia, henbane). Inflorescence is a brush.
"Biology Grade 6" Angiosperms "- Order. Plant taxonomy. View. Composite. Cabbage. Characteristics of families. Rosaceae. A family of plants from the class of monocots. Dicotyledons. Systematics of family representatives. Angiosperm taxonomy. Systematic units. Solanaceous. Puzzle questions. Cereals. Cruciferous.
"Angiosperms department" - 2) Rosaceae. 3) Legumes. Tsvetkov classification. Banksia Ipomoea. H (5) l (5) t5p1. Class Dicotyledons. 4) Solanaceae. Department of Flowering Plants. Sea buckthorn. FAMILIES: Cereals О (2) + 2Т3П1 - wheat Liliaceae О6Т6П1 - tulip Palms. Food-grade Medicinal Forage Decorative Construction Technical Fuel Poisonous.
Laurel (Laurus) - a genus of evergreen trees or shrubs of the family Laurel (Lauraceae).
The crown of the laurel is leafy, predominantly pyramidal in shape. The leaves are alternate, leathery, whole-edged, slightly wavy at the edges. Flowers in umbellate axillary inflorescences. Fruits are single-seeded, drupe-like, blue-black.
Laurel leaves are widely used in cooking. The content of essential oil in the leaves reaches 3-5.5%. It contains eugenol, pinene, myrcene, camphor, linalool, and various organic acids.
Laurel is common in the Mediterranean region, the Canary Islands, Transcaucasia, Georgia, the Crimean Peninsula, Germany, Asia.
Genus Laurel (Laurus) has three main types - Laurel noble (Laurus nobilis), Azores laurel (Laurus azorica) and. Although in modern English-speaking taxonomy, the genus has about 40 plant species.
Types of laurel
It grows on various soils in forests in the coastal strip, at an altitude of 300 m above sea level, in the Mediterranean region, in Western Transcaucasia (USSR). Shrubs or trees 4-8 m tall. The branches are bare. Leaves are simple, oblong-lanceolate, leathery, 7-20 cm long and 2.5-8 cm wide, pointed, glabrous, glossy, on short petioles. The flowers are small, collected in umbellate inflorescences, located in the axils of the leaves, 1-2, yellow. Blooms in April-May. Valuable food (spicy), essential oil and ornamental plant. It is widely used for landscaping interiors, as well as for outdoor exposure in summer (in tubs and pots outside of subtropical regions). Suitable for placement in cool rooms.
There are a number of forms that differ in the shape and size of the leaves.

Laurel Azores (Laurus azorica) , or Canary laurel (Laurus canariensis) ... Grows in moist laurel forests in the lower belt of the mountains in the Canary Islands, Azores and Madeira. Trees up to 15 m tall; pubescent shoots. Leaves are ovoid, up to 10-12 cm long and 2-6 cm wide, dull green. The flowers are collected in umbellate inflorescences, located in the axils of the leaves in several, light yellow. Blooms in April-May. Decorative look.


... Homeland - Southwest China, about. Taiwan, Korea, Japan, North Vietnam. It is widely cultivated in Asia, South India, Sri Lanka, Indonesia, Malacca, Philippines, East and North Africa, in the south of the USA, Brazil, Australia. Evergreen tree with alternate, petiolate, lanceolate, entire, bare, shiny, covered with small translucent dots (submerged cells with essential oil) leaves. The flowers are small, six-dimensional, yellow-green, collected in angular paniculate inflorescences. All plants contain essential oil, in which the main component is camphor (up to 94%); the greatest amount of camphor is found in wood, where it is localized in essential oil cells - bags. In China and Japan, camphor is obtained by steam distillation of wood chips. With fewer yields, camphor is obtained from twigs and yellowed leaves. There is little camphor and a lot of safrole in the essential oil of spring leaves. Camphor is one of the most important drugs that stimulate the central nervous system. Strengthens the activity of the heart in diseases accompanied by acute cardiovascular failure, as well as in shock conditions (in 10 and 20% sterile oil solutions or inside in powders). Outwardly - for rubbing with rheumatism, arthritis, etc. in the form of an oil solution, liniment and ointments.


When growing laurel, it should be borne in mind that adult plants do not grow well in too warm rooms with dry air. Young, with good care, can adapt to these conditions.
Lighting. A location with a bright light suits the Lavra. The plant is able to tolerate straight  Sun rays. In the summertime, it is recommended to keep the laurel outdoors. Keep in mind that after prolonged cloudy weather (for example, after winter), or the purchased plant is gradually taught to direct sunlight in order to avoid sunburn.
Sun rays. In the summertime, it is recommended to keep the laurel outdoors. Keep in mind that after prolonged cloudy weather (for example, after winter), or the purchased plant is gradually taught to direct sunlight in order to avoid sunburn.
In winter, the laurel should be kept in a bright and cool room.
Temperature. In summer, the optimum temperature for laurel is in the range of 20-26 ° C, in autumn the temperature is gradually lowered, in winter it is recommended to keep the laurel at a temperature not higher than 12-15 ° C, in this case, wintering is less painful for the plant.
Watering. In summer, plants are watered abundantly, with soft, settled water, as the upper layer of the substrate dries up. In hot weather, you can water it twice a day. By autumn, the amount of watering is reduced. In winter, water is limited, preventing the earthen coma from completely drying out. Watering is carried out two to three days later, after the top layer of the substrate has dried.
Air humidity. The laurel prefers high humidity. The plant should be regularly sprayed with soft, settled water. You can put a container with laurel on a pallet with wet expanded clay, pebbles or moss. In this case, the bottom of the pot should not touch the water.
Fertilizer. Laurel is fed during the growing season once a month with mineral fertilizer.
Features. Laurels tolerate cutting and pruning well; they can be given any decorative shape (round, pyramidal, etc.). Pruning is done around mid-August, when growth ends. The eyes remaining on the plants will develop well before winter, will mature, and in spring, with the beginning of growth, they will give strong shoots. In spring pruning, the strongest apical ocelli are removed, the growth from the remaining underdeveloped ocelli is small.
Transfer. The laurel grows slowly. Young plants are transplanted as needed (when the roots fill the pot), about once every 2 years, adults - after about three to four years. The substrate for planting can consist of leaf (2 parts), turf (1 part), humus soil (2 parts), peat and sand (1 part each). The plant prefers a slightly alkaline or neutral soil mixture. Laurel grows better in a small container, therefore, during transplantation, the dishes are taken according to the earth and the development of the root system (it is advisable to increase the size of the pot by 2 cm, no more). This is also taken into account when transplanting plants in tubs (increase the size of the tub by 5 cm). The bottom of the pot or tub provides good drainage.
Reproduction. Plants are propagated by seed, cuttings and division.
Sowing of seeds is carried out in the spring in bowls, boxes, pots. The substrate is made of sod land - 1 hour, leaf - 1 hour, sand - 0.5 hours. The temperature for sowing must be at least 18 ° C. Seedlings dive in the phase of 1-2 leaves at a distance of 2 × 2 cm. The substrate is the same. As they grow, they are planted in 7-centimeter pots, 1 piece each. Composition of the soil: turf - 2 hours, leaf - 1 hour, peat - 0.5 hours, sand - 0.5 hours. When caring for young plants, regular watering, spraying, bright location, temperature 10-12 ° C are required.
Shoots are cut into cuttings in spring (in April) and in summer (approximately from mid-June to mid-July). They should be mature, but not lignified, with two or three internodes. Cuttings are taken 6-8 cm long. After shortening the leaves, the cuttings are planted to a depth of 1-1.5 cm at a distance of 10 × 10 cm. A two-layer substrate is recommended: the bottom layer consists of turf soil (about 3-4 cm), sand is poured on top of it with a layer of 2-3 cm. Optimum temperature for rooting 16-20 ° C. The cuttings take root within a month, after which they are planted in 7-9 cm pots. The composition of the soil is the same as for planting seedlings. Plant care is the same as for seedlings.
Possible difficulties
Leaves turn yellow and curl. The reason is insufficient air humidity. The humidity should be increased.
Gets damaged
The healing properties of laurel
In medicine, leaves, fruits, extracts and infusions from all parts of the plant are used. The leaves, a well-known spice, have a stimulating effect. They are used for amenorrhea, colic and hysteria. They stimulate the secretion of fluid from the body. In folk medicine, they are used for flatulence. Fruits have the same property.
Bay leaf induces appetite and aids digestion. The essential oil has antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory properties, which makes it useful in aromatherapy. It is indicated for respiratory diseases, infections, muscle pains, neuralgia, dry scalp.
In folk medicine, extracts from all parts of the plant are recommended as an anticancer agent, for localized tumors, an agent that stimulates the nervous system. It is believed that these extracts can be used for facial skin care. Bay oil is a part of ointments for rubbing with rheumatism and ointments for scabies mites.
Other uses of laurel
Dry laurel leaves are used in the canning and confectionery industry and in cooking as an aromatic seasoning. It goes well with lavender, eucalyptus, lemon, rosemary, geranium, citronella, cinnamon and ylang ylang. For culinary purposes, the leaves are harvested from 4-5-year-old plants in November-December, when the highest content of essential oils is noted in them. Fatty essential oil is obtained from the fruit, which is used in some countries in medicine, veterinary medicine and soap making. Laurel wood is used for small crafts. Laurel noble decorative, easily tolerates pruning, and since ancient times has entered the culture.
It has been experimentally proven that fatty little laurel fruits can be used to make  candles and balls instead of cocoa butter. Its acute toxicity, according to RIFM, is oral LD50 3.9 g / kg (rats), derm LD50> 5 g / kg (rabbits). In the form of a 10% solution in petrolatum for 48 hours does not cause irritation of human skin and sensitization reactions. There is no phototoxic effect. The oil has no IFRA restrictions for use in perfumery and cosmetics.
candles and balls instead of cocoa butter. Its acute toxicity, according to RIFM, is oral LD50 3.9 g / kg (rats), derm LD50> 5 g / kg (rabbits). In the form of a 10% solution in petrolatum for 48 hours does not cause irritation of human skin and sensitization reactions. There is no phototoxic effect. The oil has no IFRA restrictions for use in perfumery and cosmetics.
At home you can cook tincture of dried laurel leaves on vodka or 40-70% alcohol. Crushed leaves are poured with alcohol at a rate of 1: 5. Close tightly and incubate at room temperature for 7 days. Then it is filtered and poured into a dark bottle, stored in a cool place.
To obtain aromatic oil you can recommend the following method: 30 g of crushed leaves are poured with 200 g of sunflower oil and insisted for 1 week. If you take this oil 1 tablespoon 2 - 3 times a day after meals, then it causes menstruation when they are delayed.
A decoction of laurel leaves is also prepared, which is useful for metabolic disorders in the pre- and postnatal period, for osteochondrosis, and inflammatory diseases.
For throat cancer: 1 glass of crushed bay leaf is infused in 0.5 liters of vodka for 2 weeks in a dark warm place, periodically shaking the contents, filter. Take 1 tablespoon 3 times a day 30 minutes before meals.
For external use an ointment of the following composition is recommended: 6 parts of bay leaf powder, 1 part of crushed juniper leaves and 12 parts of unsalted butter. All this is thoroughly pounded. For every 100 g of ointment, add 10-15 drops of fir or lavender oil.
Oil for strengthening and stimulating hair growth: by 4 tbsp. add tablespoons of jojoba oil (in drops): laurel - 4, lavender - 3, lemon - 3, rosemary - 3, rosewood - 3 and 1 tbsp. a spoonful of sesame or castor oil. In a warm form, apply the mixture to the hair and wrap the head with a towel. After 15-30 minutes, wash your hair with shampoo.
Dry laurel leaves are widely used in the culinary and confectionery industry.
Laurel in history
Laurel noble reminds of the romantic and harsh times of the Roman Empire, when the winner was staged lavish celebrations and crowned with a laurel wreath. The healing properties of laurel were well known in antiquity. So, traditional healers argued that a decoction of laurel leaves, taken internally, stops profuse menstruation. Hippocrates recommended the use of laurel oil against tetanus, and the leaves - to soothe pain during labor pains. The Arab physician Razes used the leaves as a specific remedy for nervous facial tics. Baths of a decoction of leaves with the addition of 4-5 drops of essential oil were taken for diseases of the bladder and uterus.
Laurel wreath and laurel branch are symbols of glory, victory, greatness.
 What is hot water supply for an apartment building
What is hot water supply for an apartment building Water supply of an apartment building
Water supply of an apartment building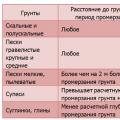 Calculation of the load on the foundation Installed electrical appliances
Calculation of the load on the foundation Installed electrical appliances