Prospects for the development of the enterprise. choice of strategic alternatives. Problems, experience and prospects of organization of information and analytical work Problems and prospects of organization
Management of objects of any nature, including such complex ones as society and the state, not least involves working with information. Moreover, management is conditionally divided into two main types - strategic and operational (operational-tactical). Each of them has its own specifics in content, organization and management, staffing and methods of intellectual activity. The scientific support of management, in turn, is based on fundamental, applied, expert and information-analytical research.
The aggravation of global and domestic - economic and political problems in Russia requires professional analytical support, at least for operational tasks to urgently "extinguish" the most dangerous "hot spots". There are clearly not enough resources to provide solutions to strategic problems, since in post-Soviet Russia information and analytical activity (IAA), where it still exists, is a kind of situational problem analysis.
At a time when Russia has not actually solved the problems of analytical support of operational management and management at the level of 3-5 year planning, the developed and intensively developing world has long switched to scientific and expert-analytical support of strategic management on horizons with a distance of 50 75 and over years.
At the same time, in Russia, experience in information and analytical work has been accumulated in various areas of management and various aspects of analytical activities. It is stated, for example, in the works of A.I. Doronin and Yu.V. Kurnosov. The implementation of the tasks of creating information and analytical management support is a large-scale complex multi-aspect problem of national importance. So, for effective analytical support of public administration and bringing it to a competitive level, purposeful work on a national scale is necessary. It is impossible to achieve the desired effect without such work. However, at the level of state power and administration, only sporadic efforts are being made so far, which are extremely insufficient without the organization of systematic work.
We will try to show the most significant points of experience in the field of staffing, since it is the personnel aspect of the activities of information and analytical units that is the key to the deployment of work on information and analytical support for managerial decision-making, including in public authorities and administration, in political, state, economic structures and public organizations.
In 2004, on the basis of the IPK of the civil service of the RAGS under the President of the Russian Federation (rector, Doctor of Economics, Professor Kh.A. Bekov, Head of the Department of State and Municipal Administration, Candidate of Psychology, Professor N.F. Lukyanova, Deputy Head of the Department, Ph.D. Associate Professor M. V. Talan), work was launched, the experience of which can be considered a successful pilot project. Let us outline the most important components of this experience.
1. At present, it seems possible to single out several options for proposals regarding the training and retraining of specialists in information and analytical work. In some of them, it seems possible to train an analytical worker in the system of higher professional education on the basis of a separate specialty. In the course of observing the experience of such activities in specific universities, a team of specialists gathered under the auspices of the IPK of the civil service came to the conclusion that an analytical worker should have a basic higher professional education in any specialty. This is a prerequisite for the formation of a qualified analyst, who, if he has the ability and, having completed a retraining or advanced training course, can become an employee of the analytical unit. The training of an “analytical worker” on the basis of secondary general education is inappropriate.
2. Retraining of managers and employees of information and analytical units can and should be carried out within the framework of advanced training programs. There are well-established mechanisms for organizing such work within the framework of the current legislation and the practice of financing advanced training courses.
So, in the IPK of the civil service, refresher courses were held, which were organized twice a year according to a 72-hour program. (In the process of training from 2004 to 2011, about 700 students from all federal departments of the Russian Federation, including some territorial divisions, as well as specialists from many regional authorities, were trained at the IPC of the civil service. Of course, this is a drop in the ocean from real needs, especially for such a small and therefore largely overview course). The educational and thematic plan included a wide range of issues:
Goals and objectives of the IAD in the management system, the role of the IAD in a complex political and social context, scientific, expert-analytical and information support for operational and strategic management (Doctor of Philosophy, Prof. A.I. Selivanov);
Psychological modeling of the personality of an analyst (D.Psych., Prof. N.M. Rakityansky);
Methods of System Analysis of Information in the Socio-Economic Sphere (Doctor of Economics, Prof. A.B. Doktorovich);
Methods of Information and Analytical Support for Legislative Activities (Doctor of Law, Prof. S.A. Komarov, Doctor of Law, Prof. A.G. Gurinovich);
Organization of information and analytical support for official activities in decision-making departments, methods of analysis and preparation of documents (VK Petrov, Candidate of Philosophy);
System of Methods of Analytical Activity (Doctor of Philosophy, Prof. Yu.V. Kurnosov);
Methods of analytical intelligence, business intelligence (Ph.D. A.I. Doronin);
Principles of organization and methods of using database management systems in information and analytical units of security services (Ph.D. S.G. Lobanov);
Organization of information and analytical support for management in the field of defense, methods for analyzing documents, including the example of the armed forces of Russia and the Bundeswehr of Germany (Doctor of Political Science V.K. Belozerov, Doctor of Political Science, Professor S.A. . Melkov);
Applied aspects of working with information from various databases, search engines, compiling an information portrait of an object, process, event (V.E. Mikhailichenko);
Organization and methods of information and analytical work in state territorial bodies (on the example of the Moscow region) (Ph.D. S.V. Belkin);
Methods of search and analytical work with information from the Internet (Ph.D. A.I. Masalovich);
Tasks and methods of information and analytical work in banking institutions (Ph.D. V.V. Babkin);
Psychological aspects of working with information (PhD in Psychology Prof. N.F. Lukyanova, PhD in Psychology Associate Professor M.V. Talan);
Various aspects of working with audit and control information (specialists of the Accounts Chamber of the Russian Federation) and other specialists.
3. According to the teachers, as experience was gained and the educational and methodological base developed, it was possible to switch to a 150-hour program. But this project was not implemented in the IPK of the civil service due to the reorganization of the RAGS under the President of the Russian Federation and the liquidation of the IPK of the civil service in 2011. However, we believe that the collective work done now allows the creation and implementation of courses of up to 500 hours. If such a course is developed, it will carry the necessary set of existing knowledge in this area, and will also allow the trainees to form some skills and abilities.
4. The most important role in the organization of work is the selection of teachers. The teacher at such courses should combine the experience of scientific, educational, methodological, practical analytical work and, preferably, leadership work in this area. In the IPK of the civil service, it was possible to select such a team, which consisted of analysts-practitioners of the civil service (the State Duma of the Federal Assembly of the Russian Federation, the Accounts Chamber of the Russian Federation, the Government of the Moscow Region), the Central Bank of the Russian Federation, current and retired senior officers of the FSB, the Ministry of Internal Affairs, the Moscow Region, former and current leaders and specialists of large non-state information and analytical structures.
5. The organizers of the project at the Department of State and Municipal Administration of the IPK of the Civil Service initially built the work on the principle of combining educational, teaching and methodological, research and organizational and scientific activities. The result of this work was the organization of conferences on information and analytical support of management on the initiative of the Institute of Civil Engineering in cooperation with the Institute of Scientific Information on Social Sciences of the Russian Academy of Sciences (INION RAS - Director Academician Yu.S. Pivovarov, Head of the Department, Candidate of Philological Sciences V.I. Gerasimov ).
These conferences have become annual, constantly increasing the number of participants - since 2010, about 700 people. The range of problems proposed for discussion was constantly refined. Some conferences were hosted by the Civil Service PKI independently. Scientific and educational-methodical developments of the team are reflected in a number of publications. Moreover, it was possible to carry out special scientific projects - in particular, a thematic issue of the journal "Bulletin of the Academy of Economic Security of the Ministry of Internal Affairs of Russia" was organized, on the pages of which various aspects of the use of information and analytical activities in order to ensure the internal and external security of the country were discussed.
6. In the course of training in a specially designed course, which included a psychometric examination and analysis of its results, work was carried out to identify and understand the analytical capabilities of each student through practical exercises using reflective-interpretive training. This made it possible for the students to form an attitude towards reflective interaction with their personal resource, to draw up a reference psychological portrait of an employee of the information and analytical unit, to develop a model for the selection and psychological training of personnel for information and analytical units.
Information and analytical support of public administration is a matter of ensuring the effective development of the country, its competitiveness and security;
Information and analytical activities should combine scientific, organizational, personnel, expert, analytical and informational aspects, which should form an integral complex of intellectual management support;
It is necessary to take into account the fundamental difference in ensuring operational (current) and strategic (long-term) public administration. Operational management is the management of the present, which involves responding to the situation that has arisen, while strategic management is the management of an object based on the achievement of some goal remote in time;
Strategic and operational management should be provided with a specific scientific and methodological base, a special organization of work, different personnel, different approaches to the interaction of intellectual structures with authorities and decision makers;
The task of forming a modern complex of intellectual support for public administration in modern Russia can no longer be consistently and effectively solved at the level of any one department or a separate region, or a separate enterprise. A comprehensive nationwide solution is needed;
The most important condition for the formation of a system of professional information and analytical management support in the country is the staffing of this area of social activity, the formation of a multifaceted professional community, as well as a general increase in the level of information and analytical competence, a culture of working with information, especially among public administration employees, including those who receive solutions. Without digressing aside, we briefly note that the hypothetical creation of effective analytical structures will not help to solve management problems without qualified consumers of analytical information capable of using it to carry out managerial functions. The high professional level of work with information in government and administration is the basis for the formation of analytical structures and a request to them for quality work.
Literature
1. See details: Selivanov A.I.. The complex of scientific, expert and information-analytical support of state strategic management // Bulletin of the Academy of Economic Security of the Ministry of Internal Affairs of Russia. M., 2011. No. 7.
2. Doronin A.I. Business intelligence. 5th edition. M., 2012.
3. Kurnosov Yu.V. Analytics as an intellectual weapon. M., 2012.
4. Here are links to published materials of some landmark conferences: Information and analytical activities in Russia: state and prospects (Collected materials of the First All-Russian Scientific and Practical Conference of Analytical Workers. At 2 o'clock). M.: IPK civil service, 2004; Information and analytical support of strategic management: theory and practice. Proceedings of the Second All-Russian Scientific and Practical Conference. M.: IPK civil service, INION RAN, 2006; Scientific, expert-analytical and information support of strategic management, development and implementation of priority national projects and programs. Proceedings of the third All-Russian scientific-practical conference. M.: INION RAN, AEB MIA of Russia, others, 2007; Scientific, expert-analytical and information support of national strategic planning, priority national projects and programs. Proceedings of the fourth All-Russian scientific-practical conference. At 2 pm M.: INION RAN, AEB of the Ministry of Internal Affairs of Russia, others, 2008; Scientific, expert-analytical and information support of national strategic design, innovative and technological development of Russia. Proceedings of the fifth All-Russian scientific-practical conference. At 2 pm M.: INION RAN, others, 2009; Scientific, expert-analytical and information support of national strategic design, innovative and technological development of Russia. Proceedings of the Sixth All-Russian Scientific and Practical Conference 27-28.05.2010. At 2 pm M., 2010. The seventh and eighth conferences (2011, 2012) are devoted to innovative development and regional aspects of management.
5. Information-analytical and staffing of program-targeted management. Reports of the anniversary scientific and practical conference dedicated to the 55th anniversary of the IPK of the civil service. T.1. M.: IPK civil service, 2007.
6. Theoretical and methodological foundations of systemic information and analytical research. Monograph. M.: IPK civil service, 2004; Analytical support for making managerial decisions. Monograph. M.: IPK civil service, 2005; Organizational and analytical support of management processes. Electronic educational and methodical complex. M.: IPK civil service, 2007.
7. Bulletin of the AEB Ministry of Internal Affairs of Russia. M., 2011. No. 7.
Nikolai Rakityansky, Doctor of Psychology, Professor, Lomonosov Moscow State University M.V. Lomonosov.
Alexander Selivanov, Doctor of Philosophical Sciences, Professor, Leading Researcher at the Institute of Microeconomics.
Introduction
The theme of the graduation project is the definition of problems and prospects for the development of the enterprise "Amurtorgexport".
The survival of economic entities in a market economy is associated with their ability to independently maintain their current and prospective solvency in conditions of environmental instability and entrepreneurial risk. For this, the correct choice of economic benchmarks and the ability to timely achieve goals are important. Therefore, the enterprise itself needs a strategic assessment of the prospects for the development of the enterprise, which would reflect the future of modern economic, financial and investment management decisions.
Strengthening the strategic nature of the choice of business goals is a priority for small businesses, as small firms are more vulnerable to changes in the economic environment and more receptive to new opportunities in the investment, economic and financial spheres of their activities.
However, since each firm is unique in its kind, the process of developing a strategy for each of them is individual and depends on the position of the firm in the market, the dynamics of its development, production potential, the behavior of competitors, the characteristics of the goods produced, the services provided, and many more factors. At the same time, there are fundamental points that help to talk about the methodological approaches used in the development of a strategy and the behavior of subjects in business, as well as in the implementation of the process of managing the implementation of strategic decisions. The application of methods of strategic analysis, selection, assessment of the prospects for the development of small businesses will be discussed in the message.
First of all, attention is focused on the fact that without a strategic analysis of the economic, financial and investment attractiveness of an enterprise, it is impossible to reasonably choose either the tactical or strategic policy of the company, which would ensure its sustainable growth.
From the standpoint of strategic management, the effectiveness of an organization's activities is determined not so much as the current profitability of using the production potential, but rather as a process of self-organization of the company, which ensures the constant growth of the company's own capital. With a strategic approach to the development of the organization, the current process of implementing the strategy has an active feedback effect on the content of strategic analysis and strategic choice. From the foregoing, it follows that the process of strategic management ensures the implementation of the goal, which can be fundamentally adjusted or implies the existence of alternative ways for the development of the enterprise.
For a quantitative assessment of determining the prospects for the future financial condition of an enterprise in the conditions of the Russian market and strategic choice, the calculations of the consolidated financial forecast for the development of a small business are adapted, taking into account changes in the company's growth strategies.
The purpose of writing this diploma is to assess the problems and prospects for the development of the subsidiary "Amurtorgexport", created to expand the activities of the main enterprise.
To achieve this goal, the following tasks were solved in the graduation project:
The technical and economic characteristics of the enterprise have been studied.
Analyzed the current state of the enterprise
A business plan was developed to assess the prospects for the development of the enterprise
The basics of life safety at the enterprise are described in detail.
On the basis of the performed analysis and calculations, conclusions were drawn and proposals were made.
When developing the graduation project, materials of normative, methodical literature, periodicals were used.
LLC "Amurtorgeksport" was founded on 24.01.97. in connection with the need to bring the organizational and legal form of the enterprise in line with the requirements of the current legislation of the Russian Federation. The company operates in Khabarovsk and is located at st. Yashina, 54. The enterprise is an independent economic entity, has an independent balance sheet, settlement and other accounts in banking institutions, a seal with its name, letterhead, company name, trademark. The enterprise carries out its production and economic activities for the purpose of making a profit, is responsible for the results of its activities and the fulfillment of obligations to suppliers, consumers, the budget, banks, manufactures products, performs work and provides services, provides for the needs of industry and the population in products (works, services) with high consumer properties and quality.
The enterprise "LLC" Amurtorgeksport "carries out the following activities: wholesale and retail trade in building materials, investment activities; foreign economic activity; marketing activities; commercial activities; production and sale of consumer goods (TYPE); provision of paid services to the population; repair and construction work; trade activities; organization and holding of exhibitions or similar events.
LLC "Amurtorgexport" offers a wide range of various building and finishing materials made from high quality raw materials using advanced technologies. In the proposed materials, along with imported components, which certainly ensure the high quality and stability of the resulting compositions, domestic components are used, which can significantly reduce the final cost of products without loss of quality. The offered materials are used at industrial and public facilities (shops, hospitals, schools, etc.).
Amurtorgexport LLC is the official representative of KNAUF GIPS LLC in the Far East. The history of the KNAUF GIPS LLC enterprise begins in 1950, when the Pavshinsky plant for the production of dry gypsum plaster was entered into the State Registration Register.
The main types of manufactured and sold products are:
KNAUF - sheets; KNAUF - profiles; dry building mixtures KNAUF, KNAUF - term.
The structure of the enterprise and the organizational structure of enterprise management
The organizational structure of the firm is understood as its organization from separate divisions with their relationships, which are determined by the goals set for the firm and its divisions and the distribution of functions between them. The organizational structure provides for the distribution of functions and decision-making powers between the executives of the company responsible for the activities of the structural units that make up the organization of the company.
Organizational structures can be divided into several groups: linear, linear-headquarters, product, territorial, mixed.
The line structure is for small businesses only. This is the oldest form of labor cooperation. All management goes from top to bottom and all services do not have the right to make independent decisions. Such subordination schemes are the simplest and most understandable for employees. The linear structure has the following advantages:
- each link has a clear idea of the scope of its powers and responsibilities;
- simplifies the process of maintaining discipline;
– the channels of business circulation are very simple and direct.
But this structure also has its drawbacks:
- centralization does not contribute to the improvement of the skills of workers at a lower level;
- employees of higher levels do not always have special knowledge;
- the expansion of the company leads to the creation of high structures, which makes it difficult to manage and mobility in decision-making.
Line-staff structure. In contrast to the linear structure, this structure, along with linear subordinates, includes functional groups that close to the administrative apparatus. A headquarters is being created to make very important decisions. The headquarters is organized in order to make this decision in a very short time. The organization of the headquarters includes 3 components: the head of the headquarters, employees for the leader and the premises.
This structure also has its advantages:
- a high degree of division of labor
- the presence of standard rules and ways to resolve a standard situation
- selection of employees on business qualities.
But not everything is so good in this structure. There are existing shortcomings related to this group of organizational structures:
- the exaggerated importance of standardization, behavior with the help of rules, procedures, norms leads to a loss of flexibility in the behavior of the organization itself
The functional structure provides for the creation of elements that specialize in certain functions (the transfer of instructions occurs according to the types of tasks assigned). The control elements are responsible only for the coordination and control of functional services.
This structure has its own advantages, different from others:
- drastically simplifies the selection of leaders
- the system allows you to select narrow specialists for services
– the quality of elaboration of all functional solutions in the field of technology of financial activity is improved. Structural solutions, etc.
– the role of standardization and regulations in the field of technology and design is growing
– all instructions are communicated to the performer, and this allows you to make correct management decisions
- the system allows you to remove the load from line personnel.
And accordingly, there are disadvantages:
- there are many arrows for each leader
- all management decisions must be coordinated. The flow of meetings and voting increases sharply
- departments are more interested in fulfilling functional goals than in strategic ones
- the chain of command from the head to the executor is excessively stretched, which leads to an increase in the term for the execution of orders and distortion in the transmission of information.
The product structure involves the creation in the structure of the company of independent business units - production departments focused on the production and marketing of specific types of products. This assumes the specialization of production departments in the parent company for certain types or groups of products and the transfer of authority to them to manage production and marketing subsidiaries. The functional services of the production departments simultaneously maintain close contacts with the relevant central services, receiving instructions from them on all issues of pursuing a single policy and coordinating activities within the firm as a whole.
The advantages of this structure are as follows: quick response to changing conditions (technology, demand, competition).
And there is only one drawback, but a significant one: the redundancy of functional units, since they have to be duplicated.
The territorial structure is guided by the geographical principle of activity according to the location of the organization's divisions.
A mixed structure involves a combination of different types of organizational management structures.
The most common combination of sectoral and regional principles in the construction of the organizational structure. This structure is the most common. This reflects the general patterns of development of the production process in modern conditions, which requires an integrated approach to the formation of the organizational structure of the company, taking into account the coverage of all parties, areas and areas of activity. Under these conditions, the combination of sectoral and regional aspects most fully satisfies the needs of the company's development.
The structure of the enterprise is determined by a set of tasks, in organizations like the object of study, consisting of many parts, a combination of linear and functional departmentalization is traditionally used to coordinate their activities.
The structure of the subsidiary "Amurtorgexport" is shown in fig. 1.1.
Fig. 1.2 Organizational structure of Amurtorgexport LLC
The meeting of founders is the highest official of Amurtorgexport LLC. Operational management is carried out by the director appointed by this meeting.
The leading employees of the enterprise are: director, chief economist, chief engineer, chief accountant, head of the personnel department.
At the second level of management, directly subordinate to the director and his deputies are: heads of warehouses, store manager and head of the delivery service.
The director of the enterprise acts on behalf of the enterprise without agreement, including representing its interests, making transactions on behalf of the enterprise in accordance with the established procedure, approving the structure and schedule of the enterprise's staff, hiring employees of the enterprise, concluding, amending and terminating employment contracts with them, publishing orders, issues powers of attorney in the manner prescribed by law. The director of an enterprise is liable for losses caused to the enterprise.
The chief engineer determines the technical policy and direction of development of the enterprise, the ways of reconstruction and technical re-equipment of the existing production, the level of specialization and diversification of production in the future. Provides the necessary level of technical preparation of production and its constant growth, increasing the efficiency of production and labor productivity, reducing costs, rational use of production resources, manages the development of measures for the reconstruction and modernization of the enterprise, prevents the harmful effects of production on the environment, creates safe working conditions, exercises control over the observance of technological discipline, rules and regulations on labor protection, safety, fire safety. Manages the activities of the technical services of the enterprise, controls the results of their work, the state of labor and production discipline in subordinate units. He is the first deputy director of the enterprise and is responsible for the results of the efficiency of production activities.
The chief accountant carries out the organization of accounting of the economic and financial activities of the enterprise and control over the economical use of material, labor and financial resources, the safety of the property of the enterprise. Provides rational organization of accounting and reporting. Organizes accounting of incoming cash, inventory and fixed assets, timely reflection on the accounts of transactions related to their movement, accounting for production and distribution costs, execution of cost estimates, sales of products, performance of work, results of economic and financial activities of the enterprise, and as well as financial, settlement and credit operations. Provides control over: the legality, timeliness and correctness of paperwork, the preparation of economically sound accounting estimates of the cost of production, work, payroll with employees of the enterprise, the correct calculation and transfer of payments to the state budget, contributions to state social insurance. Works to ensure strict observance of staff, financial and cash discipline. Manages the company's accounting staff.
The head of the planning and economic department manages the work of economic planning at the enterprise, aimed at organizing rational economic activity in accordance with the needs of the market and the possibilities of obtaining the necessary resources, identifying and using production reserves in order to achieve the greatest efficiency of the enterprise. Participates in the development of enterprise strategies in order to adapt its economic activities and management systems to changing external and internal economic conditions in market conditions. Supervises the preparation of medium-term and long-term comprehensive plans for the production, financial and commercial activities of the enterprise. Ensures that the plans are communicated to the departments of the enterprise. Together with the accounting department, it provides methodological guidance and organization of work on accounting and analysis of the results of production and economic activities, the development of rational accounting documentation. Manages the work of the department.
The head of the personnel department leads the work on staffing the enterprise with workers and employees of the required professions, specialties and qualifications in accordance with the goals, strategy and profile of the enterprise. Participates in the development of personnel policy and personnel strategy of the enterprise. Organizes the timely registration of the reception, transfer and dismissal of employees in accordance with the labor code, regulations, instructions and orders of the head of the enterprise. Storage and filling of work books, and maintaining the established documentation on personnel. Provides preparation of documents on pension insurance. Organizes timesheets, compiling and executing vacation schedules, provides control over the state of labor discipline in the divisions of the enterprise, analyzes the causes of turnover, loss of working time. Manages department employees.
The head of the logistics department organizes the provision of the enterprise with all the material resources of the required quality necessary for its production activities and their rational use. Provides preparation of the conclusion of contracts with suppliers, the coordination of conditions and terms of delivery. Prepares claims against suppliers in case of violation of their contractual obligations. Provides control over the state of stocks of material resources. Organizes warehouse operations. Participates in the inventory of material assets. Manages department employees.
The head of the delivery service ensures that the enterprise fulfills the tasks of the transportation plan for all technical and economic indicators in compliance with traffic safety requirements. Manages the activities of the operational service of the enterprise. Ensures timely preparation of accounting and reporting on work on all technical and operational indicators. Controls the results of work, the state of labor and production discipline in a subordinate unit.
The organizational structure of management is linear-functional and is built on the direct subordination of the lower levels of management to the higher. The head performs all management functions, all specialists and structural divisions report directly to him and receive instructions only from the store director.
The advantage of this structure is the simplicity of vertical links with minimal horizontal links, the disadvantages are the lack of linkage between the goals of departments, the difficulty of coordinating management functions horizontally, and a significant number of managerial personnel.
This organization has its own methods of personnel management. One of the most modern and progressive methods of personnel management at Amurtorgexport LLC is management consulting (or consulting)
Management consulting is a type of intellectual professional activity in which a qualified consultant provides objective and independent advice that contributes to the successful management of a client organization.
Consultants provide professional assistance to executives. Experienced consultants go through many organizations and learn how to use their experience to help new and old clients in a variety of situations. Hence, they are able to recognize general trends and common causes of problems. Moreover, professional consultants constantly monitor the literature on management issues and the development of theories of methods and management systems, as well as the situation in the market. Thus, they act as a link between management theory and practice.
Consultants mostly give advice. This means that they are only advisors and do not have direct power to make decisions about change and implement it. Consultants are responsible for the quality and completeness of the advice. Clients bear all responsibility that stems from the acceptance of advice.
Counseling is an independent service. The consultant evaluates any situation, offers objective recommendations on what to do to the client, without thinking about how this could affect his own interests.
Every company must have its own psychologist who monitors the mental health of employees. The company in question was no exception. There is also an organization of social and psychological work.
The main goal of social and psychological work at the enterprise is to maintain a favorable psychological climate and prevent conflict situations. The formation of a favorable socio-psychological climate for the labor collective is one of the most important conditions for the struggle for the growth of labor productivity and the quality of products. The conflict within the team arises between the employees of the company in the course of their activities. These are disagreements between employees over working and weekends, due to the dissimilarity of characters and unwillingness to give in to each other, as well as disagreements between the manager and his subordinates, arising for the following reasons:
the employee does not come to work on time without good reason;
does not want to work or does not work well;
· at the workplace the subordinate is in a state of intoxication;
disrespectful to superiors and does not listen to advice and demands;
a shortage of funds was discovered;
The manager delays wages or calculates them incorrectly;
· because of a bad mood, he vents evil on subordinates, undeservedly accuses, makes them extreme.
The firm and its employees try to follow certain conditions to prevent conflict situations. It happens in the following way. First of all, it is the creation of conditions that prevent the emergence and development of conflict situations.
The company respects the agreements and decisions made with the participation of all employees. Employees try to discuss all amendments or cases of non-fulfillment of promises immediately and together with the entire team. But agreements are sometimes not fulfilled, this happens as a result of some kind of emergency, which is an exception.
When planning the assortment, indicators such as the structure of the assortment, its completeness and stability are used.
The structure of the assortment is characterized by the specific share of each type (or) product name in the general set. Assortment structure indicators (C i) are relative indicators and are calculated as the ratio of the number of individual products (A i) to the total number of all products (S i) included in the assortment:
C i \u003d (A i / S i) * 100%
Table 2.1.1.
Product range of Amurtorgexport LLC
Calculation made on the basis of the data given in Table 2.1.1. led to certain results:
С i KNAUF - sheet = (12 / 28) * 100% = 42.8%
С i KNAUF - profile = (5 / 28) * 100% = 17, 86%
C i Dry building mixes = (6 / 28) * 100% = 21.48%
С i KNAUF - term = (5 / 28) * 100% = 17.86%
C i Knauf - sheet = (16 / 44) * 100% = 36.4%
С i KNAUF - profile = (8 / 44) * 100% = 18.2%
C i Dry building mixes = (9 / 44) * 100% = 20.4%
С i KNAUF - term = (11/44)*100% = 25%
Thus, in the assortment structure the largest share is occupied by KNAUF - sheet, but in 2003, its share slightly decreased due to the expansion of assortment positions of other goods. In particular, the range of Knauf-term has been significantly updated.
The specifics of the trading activity of the analyzed enterprise does not allow to update the assortment with new items annually. But within each product group there is a constant renewal.
Calculate the Completeness Coefficient (Kp) for each product group:
Kp KNAUF - sheet \u003d (16/12) * 100% \u003d 133.3%
Kp Knauf - profile = (8 / 5) * 100% = 160%
Kp Dry building mixes \u003d (9 / 6) * 100% \u003d 150%
Kp KNAUF - term \u003d (11 / 5) * 100% \u003d 220%.
Thus, we see that the assortment has grown significantly.
The assortment of Amurtorgeksport LLC cannot be called stable, the assortment is being updated, but this renewal is spontaneous, so a number of measures are needed to optimize the assortment.
The basis for improving the structure of the assortment should be a sales analysis, through which consistently purchased goods are identified; all automation programs that exist today can help with this. But in order to evaluate the categories of "best and worst" sales of goods, you need to track them for at least the last year, and ideally - for the last few years. This will allow you to objectively evaluate the data and accurately determine the seasonality of sales of certain goods, although it must be taken into account that during this time the well-being of buyers could change, new ones could appear.
From the position of a manufacturing enterprise, wholesale trade is an important link in distribution, which can and does solve its marketing problems.
From the point of view of marketing, the role of wholesale trade is to meet the needs of retail enterprises to the maximum, supplying them with the necessary goods in certain volumes and on time. Being usually located in large settlements (cities), wholesale companies are also well aware of the needs of end customers. Therefore, they, on their own or with the help of a product manufacturer, are able to organize powerful marketing support for retail trade.
As modern experience shows, wholesale companies in most cases carry out marketing functions better than the manufacturer, since they have well-established ties with retail trade, as well as a good warehouse and transport base. Today, wholesale companies provide their customers not only with goods, but also with a wide range of related services: advertising at the point of sale, organization of sales promotion events, delivery of goods, pre-sale preparation, including packing and packaging of goods under the brand name of a retail enterprise or retail chain.
The analyzed enterprise carries out several activities that bring him profit. The main directions are presented in Table 2.2.1.
Table 2.2.1.
Types of profit-generating activities of Amurtorgexport LLC
Continuation of the table. 2.2.1.
Trade and procurement transactions concluded by Amurtorgexport LLC can be grouped by volume:
Rice. 4.1. Differentiation of concluded transactions by volume
Moreover, in the reporting period there was an increase in the volume of small-scale wholesale transactions. This is due to the development of small retail trade in the city of Bikin.
So we can draw a conclusion on the section. The LLC "Amurtorgexport" enterprise is engaged in three main types of profit-generating activities. These are trade and purchasing activities, leasing of warehouse premises and provision of services to tenants.
Trade and purchasing activity also consists of three types of activities: retail, small wholesale, large wholesale. Most of this trading and purchasing activity is occupied by small wholesale. This conclusion can be drawn from the diagram.
Analysis of fixed assets
The uninterrupted implementation of the trading process is facilitated by the presence of the company's fixed and working capital.
Fixed assets are a set of tangible assets for production and non-production purposes, which are used over a number of years and gradually wear out over the entire service life, do not lose their natural form.
In accordance with the accepted classification, the production fixed assets of enterprises are divided into the following groups:
but). Buildings (about 15%) - warehouses, a checkpoint, a sand dryer, a mobile building, a warm parking lot, a bomb shelter, etc.
b). Structures (about 25%) - reinforced concrete fence, territory fencing, dry sand pneumatic conveyor and fire tank.
in). Transmission devices (about 9%) - sewer networks, cable lines, fire pipelines, heating networks, oil pipelines.
G). Machinery and equipment (over 45%) - machine tools, compressors, jacks, presses, washing machines, a welding machine, an air collector, refrigeration equipment, a cash machine, computers, a printer, a beam crane, a bulldozer, a forging hammer, etc.
e). Vehicles - trucks, cars.
e). Other types of OS (about 0.3%) - sets of office furniture, a set of upholstered furniture, a typewriter, etc.
Calculate the coefficient characterizing the size of the share of fixed assets in assets:
To assess the technical condition of fixed assets, it is necessary to determine such indicators as the renewal coefficient, the retirement coefficient of fixed assets, growth factors, the income coefficient, the renewal coefficient, the renewal intensity coefficient, the stability coefficient, the wear coefficient, the shelf life coefficient, the capital productivity of the fixed assets, the profitability of the fixed assets.
The receipt coefficient characterizes the cost of newly received equipment in relation to the residual value of fixed assets.
The fixed asset retirement ratio is characterized by the ratio of the value of retired equipment and the residual value of fixed assets.
Growth factors determine the ratio of the change in the amount of equipment for a certain period to the amount of equipment at the end of this period.
The renewal ratio is determined by the ratio of the cost of the updated or modernized equipment to the residual value of fixed assets.
The renewal intensity ratio is the ratio of the change in the amount of modernized equipment for a certain period to the total amount of equipment at the end of this period,
The stability coefficient reflects the ratio of old equipment to newly acquired.
The service life coefficient determines the amount of equipment that has failed in relation to the total number of pieces of equipment.
The depreciation coefficient characterizes the ratio of depreciation to the residual value of fixed assets.
The return on assets of the OPF is defined as the ratio of the value of manufactured products to the average annual cost of fixed assets.
The profitability of the OPF determines the ratio of profit to the average annual cost of fixed assets.
Having calculated these indicators, we will group them for clarity in Table 2.3.1.
An analysis of this table allows us to conclude that significant changes occurred in the structure of fixed assets of Amurtorgexport LLC, which occurred mainly in 2001-2002. Positive factors include a decrease in the depreciation rate and an increase in the service life of fixed assets.
Table 2.3.1.
Indicators of movement and condition of fixed assets
Continuation of the table. 2.3.1.
From the table above, we can conclude that the company has been using equipment efficiently lately. So, for example, the income coefficient has increased very much, i.e. in 2003 new equipment was purchased. As a result, the wear rate dropped sharply. In addition, the purchase of new equipment had a positive effect on all remaining indicators. Thanks to it, indicators of suitability, capital productivity and profitability have increased. In general, we can say that the last year had a positive impact on the state of the company's fixed assets.
Labor force analysis
Human resources play an important role in the development of an enterprise. There would be no workers and managers and there would be no enterprise. They play the role of the driving force of the enterprise and it is simply necessary to study the changes associated with this criterion. Knowing the dynamics of change, we can conclude what is best for the enterprise, what is the best composition, it is possible that there is not enough staff or, on the contrary, there is a surplus. All these conclusions can be drawn by studying the dynamics of changes in labor resources. Table 2.4.1. just given such dynamics for three years.
Table 2.4.1.
Information on the share of personnel of various categories
With a general increase in the number of personnel, which is a consequence of the active development of the enterprise and an increase in the volume of work performed, there is a percentage increase in the share of production personnel, which is a positive trend.
It may also be interesting to consider the relationship between production and non-production personnel. These indicators are presented in Table 2.4.2.
Table 2.4.2.
Dynamics of indicators of LLC "Amurtorgexport" 2001-2003
Continuation of the table. 2.4.2.
The dynamics of the first indicator (the ratio of production and non-production workers) shows a trend towards an increase in the share of the former, which is a positive trend. The dynamics of the indicator consists of a reduction in non-production workers and an increase in production ones. Both of these phenomena are caused by a number of events - the introduction of new technologies that require large production labor costs and a decrease in labor costs for maintenance and adjustment, a decrease in the need for auxiliary operations, and a decrease in production volumes.
The proportion of administrative staff has been steadily declining in recent years.
It is also necessary to characterize such an indicator as staff turnover. Staff turnover is the most important indicator of the dynamics of the organization's workforce. There are several methods for calculating turnover, the most common is the ratio of the number of employees who left the organization (with the exception of those laid off due to staff reductions) to the average number of employees during the year. The higher the turnover rate, the lower the stability of the organization's staff.
Table 2.4.3.
Personnel movement in 2001 - 2003
The turnover rate is calculated as the ratio of the total number of employees to the number of dismissed employees.
Thus, in the period under review, the rate of staff turnover increased, the dynamics was 1.08%.
The traditional indicator of human resources statistics is the average age, calculated as the sum of the ages of all employees divided by the number of employees in the organization. However, this indicator is not informative enough, since the average age of 40 years can be obtained if the company has ten 20-year-old and ten 60-year-old employees.
It is much more productive to represent the age structure by grouping. Grouping results are presented in Table 2.5.4.
Table 2.4.4.
The structure of employees of Amurtorgexport LLC depending on age as of 01.01.2004
Thus, the largest number in the organization are people aged 36-40.
An analysis of the qualifications of the employees of Amurtorgexport LLC showed that the majority of the company's employees hold positions with appropriate specialized education. The prevailing number of employees has a higher education, from which we can conclude that the company employs experienced and highly qualified workers.
Drawing a conclusion on this issue, we can say the following. As it should be, production workers make up the majority of the staff, and over the past three years, it is their number that has increased the most. The ratio between production and non-production workers has also practically not changed. Only in the last year has increased slightly, but not significantly. In addition, the rate of staff turnover remains approximately stable, which indicates a small number of quitters.
The age group is dominated by people aged 36-40.
The company employs only highly qualified workers, most of whom have a diploma of higher education.
Operating cost analysis
As mentioned above, the main goal of the enterprise is to make a profit, and this is impossible if you do not take into account all the costs associated with the production of products.
The expenses of the enterprise include the following: expenses associated with the acquisition of goods for subsequent resale; business expenses; non-operating expenses; operating expenses; emergency expenses.
Table 2.5.1.
Cost structure analysis
| Name of indicator |
||||||
| Selling expenses |
||||||
| Total expenses |
||||||
The cost of production includes all costs associated with its production. These include: the cost of raw materials and materials, the cost of paying wages to workers, the cost of paying for electricity, equipment depreciation.
In the structure of expenses, the largest share is occupied by operating income and expenses, but over three years their share in expenses decreased from 88.3% to 38.15%. At the same time, the share of production costs increased from 5.8% to 25%.
Such dynamics indicates the inefficiency of cost management, since with a decrease in operating costs, an increase in cost is observed. It shouldn't be. Moreover, other expenses also increase, but not by much. In this case, it is necessary to take some measures to reduce the cost, otherwise soon the company will not be able to recoup the costs of production.
Analysis of financial results
The analysis of the financial performance of the enterprise includes, as mandatory elements, the study of:
1. Changes in each indicator for the current analyzed period (“horizontal analysis” of financial performance indicators for the reporting period).
2. Study of the structure of relevant indicators and their changes (“vertical analysis” of indicators).
3. Study of the influence of factors on profit ("factorial analysis").
4. Studying in a generalized form the dynamics of changes in financial indicators for a number of reporting periods
For vertical and horizontal analysis, we calculate Table 2.7.1. , using the reporting data of the enterprise from form No. 2.
Table 2.6.1.
Analysis of profit indicators
| Name of indicator |
|||
| Revenues from sales |
|||
| Cost of sales of goods, products, works, services |
|||
| Gross profit |
|||
| Selling expenses |
|||
| Profit (loss) from sales |
|||
| Balance of operating income and expenses |
|||
| Balance of non-operating income and expenses |
|||
| Profit (loss) before tax |
|||
| Balance of extraordinary income and expenses |
|||
| Net profit |
As can be seen from table 2.7.1. in the analyzed period, there is a trend towards an increase in revenue by 1419 thousand rubles. in 2003 and 9613 thousand rubles. in 2004.
The cost of sales in the reporting period increased by 40,405 thousand rubles. by increasing the purchase prices for raw materials and materials, as well as by introducing new equipment into circulation. Thus, the increase in the gross profit of the enterprise in 2003 amounted to 1838 thousand rubles.
Along with the cost of sales of products and services, other operating expenses should be noted among the factors that influenced the formation of profits of Amurtorgexport LLC. Operating expenses consist of the amounts of fixed assets written off the balance sheet due to obsolescence, the maintenance of mothballed production facilities and facilities, canceled orders and contracts. A positive trend is the reduction in the reporting period of the volume of operating expenses, in particular such a group as interest payable.
Compared with the beginning of the analyzed period, the level of non-operating expenses did not change significantly, however, due to a decrease in the volume of non-operating income by 1,194 thousand rubles, the balance of non-operating income and expenses amounted to -1,201 thousand rubles, which is 2,736 thousand rubles. less than in 2002
Thus, LLC "Amurtorgexport" needs to take a number of measures to increase profits from sales and reduce operating costs and prime cost.
For a more complete picture of the economic activity of the enterprise, you can conduct a general analysis of the financial condition of the enterprise in terms of balance sheet indicators.
The financial condition of the enterprise, its sustainability and stability depend on the results of its production, commercial and financial activities for the period under study. The main source of information for the analysis of the financial condition of the enterprise is the accounting (financial) statements (Appendices 1 and table 2.6.2.).
Table 2.6.2.
Aggregated analytical balance of Amurtorgexport LLC for 2003
Continuation of the table. 2.6.2.
| All period |
||||||
| fixed assets |
||||||
| Profitable investments in material values |
||||||
| Long-term financial investments |
||||||
| current assets |
||||||
| VAT on purchased assets |
||||||
| Long-term accounts receivable |
||||||
| Short-term accounts receivable |
||||||
| Short-term financial investments |
||||||
| Cash |
||||||
| Other current assets |
||||||
Analyzing the analytical balance, we can draw the following conclusions:
In 2001-2002, there was an increase in the volume of the balance sheet of Amurtorgexport LLC, which is a positive fact, as it demonstrates an increase in the volume of the enterprise's activities.
During 2001-2002, there was an increase in the share of non-current assets in the structure of the enterprise's own funds due to the growth in the volume of fixed assets, which indicates an increase in the volume of activities and an increase in the quality of customer service due to an improvement in such an indicator as capital-labor ratio. The growth amounted to 3.9% or 23838.0 thousand rubles.
Accordingly, during 2001-2002 there was a proportional decrease in the share of current assets, however, in absolute terms, their volume increased by 27867.0 thousand rubles. In the structure of current assets, there is an increase in both the share and volume of reserves, respectively, by 2.2% or 16,559 thousand rubles. The growth of this indicator indicates an increase in the volume of trade turnover of Amurtorgexport LLC.
The level of short-term accounts receivable remained the same, however, in absolute terms, it increased by 14,829.0 thousand rubles.
The share in the structure of the balance of such liquid assets as short-term financial investments and cash during 2001-2002 decreased by 2.3% and 5.9%, respectively. The decrease occurred not only in relative, but also in absolute terms: by 927 and 11637 thousand rubles. respectively. The decrease in these indicators indicates a decrease in the liquidity of the company's property.
Thus, during 2001-2002, there was an increase in the volume of working capital of Amurtorgexport LLC, its material and technical base developed, and the volume of trade increased.
The further development trend of Amurtorgexport LLC is shown in Table 2.6.2. and table 2.6.3.
Table 2.6.3.
Aggregated analytical balance sheet of Amurtorgexport LLC for 2003
| Dynamics |
||||||
| for the entire period |
||||||
| Capital and reserves |
||||||
| Authorized capital |
||||||
| Extra capital |
||||||
| Social Sphere Fund |
||||||
| Targeted funding and income |
||||||
| Uncovered loss of previous years |
||||||
| long term duties |
||||||
| short-term obligations |
||||||
| Loans and credits |
||||||
| Accounts payable |
||||||
| Indebtedness to participants for the payment of income |
||||||
| revenue of the future periods |
||||||
| Reserves for future expenses and payments |
||||||
| Other current liabilities |
||||||
An analysis of the structure of the asset allows us to conclude that the volume of the balance sheet in 2003 continued to increase, but in general for 2001-2002 the increase amounted to 879,651.0 thousand rubles, or 79.641% of the initial level.
In 2003, there was a significant decrease in the volume and level of non-current assets of the enterprise, due to the disposal of fixed assets in the amount of 27822.0 thousand rubles. Thus, during the reporting period, the volume of fixed assets decreased by 3908.0 thousand rubles, the level of this indicator in the balance sheet structure decreased by 20.2%.
By the end of 2003, the share of current assets in the structure of the balance sheet amounted to 95.3%, that is, during the year it increased by 24.2%; growth was 20.3%. The absolute increase is 883635.0 thousand rubles. The volume of such a group of current assets as reserves increased most sharply (by 59.8% or 848,352 thousand rubles), so during the analyzed period there is a tendency to increase the volume of this group of current assets.
In 2003, the share of short-term accounts payable decreased by 21.1% compared to the 2001 level. In general, for the period its volume increased by 18881 thousand rubles.
In 2003, the volume of short-term financial investments of Amurtorgeksport LLC increased by 4201 thousand rubles, but this does not indicate an increase in the liquidity of the balance sheet, since the share of this group of assets in the balance sheet structure decreased by 5.64%. In general, for the period the decrease was 7.9%.
Despite the growth in cash in 2003 by 9577 thousand rubles, the share of this group of current assets in the balance sheet structure decreased by 1.5%, thus, the trend noted in 2000-2001 remains. The decrease in general for the period amounted to 2060 thousand rubles. or 7.5%.
Table 2.6.3. allows us to draw conclusions about the structure of the balance sheet liability and the changes that occurred both in 2003 and in general over the period.
There were no sharp changes in the Capital and Reserves section. The volume formed by the end of 2021 of the loss in the amount of 51652 thousand rubles. remained the same, but its share in the balance sheet structure decreased by 13.9%.
The short-term liabilities of Amurtorgexport LLC underwent significant changes, the amount of which increased by the end of the reporting period by 823,591.0 thousand rubles. or by 0.403%, which was the result of an increase in accounts payable by 409,670.0 thousand rubles, while reducing short-term loans by 13,605.0 thousand rubles. or 12.8%.
It is also necessary to analyze the liquidity of Amurtorgexport LLC. The liquidity of an enterprise is the ability of an enterprise to turn its assets into cash to cover all necessary payments as they fall due. An enterprise whose working capital consists primarily of cash and short-term receivables is generally considered to be more liquid than an enterprise whose working capital consists primarily of inventories. Liquidity indicators are shown in Table 2.6.4.
Table 2.6.4.
Analysis of balance sheet liquidity by relative indicators
In 2003, there was a decrease in all liquidity indicators, so the company is insolvent. However, the fact that the company is actively engaged in economic activity indicates that this situation can be corrected through competent management and changes in the accounting policy of the enterprise.
It is also necessary to determine the financial stability of the enterprise. The economic essence of the financial stability of an enterprise is the security of its reserves and costs with the sources of their formation. Financial stability indicators are shown in Table 2.6.5.
Table 2.6.5.
Analysis of the financial stability of Amurtorgexport LLC in absolute terms, thousand rubles.
| 1. Sources of own funds |
|||
| 2. Non-current assets |
|||
| 3. Sources of own working capital for the formation of stocks and costs |
|||
| 4. Long-term loans and borrowings |
|||
| 5. Sources of own funds, adjusted for the amount of long-term borrowings |
|||
| 6. Short-term loans and borrowings |
|||
| 7. The total value of sources of funds, taking into account long-term and short-term borrowings |
|||
| 8. The amount of stocks and costs circulating in the asset balance |
Continued 2.6.5.
At the end of the reporting period, there was a significant shortage of own working capital, as well as the total value of the main sources.
Thus, we can conclude that over the past three years the company has been in a crisis-unstable financial condition.
A number of financial ratios are also used to characterize the financial stability of an enterprise.
It must be remembered that in conditions of constant inflation, the role and information content of the analysis of the financial stability of an enterprise in terms of relative indicators increases, which requires the calculation of a number of financial ratios. See table 2.6.6.
Table 2.6.6.
Analysis of financial stability by relative indicators
Continuation of the table. 2.6.6.
| Name of financial ratio |
|||
| The coefficient of the ratio of own and borrowed funds |
|||
| Agility factor |
|||
| Inventory and cost coverage ratio with own funds |
|||
| Industrial property ratio |
|||
| Long-term debt ratio |
|||
| Short-term debt ratio |
|||
| Accounts payable ratio |
Unsatisfactory, throughout the analyzed period, remain the values of the coefficients of autonomy, flexibility, the ratio of own and borrowed funds and the ratio of reserves and costs of own funds.
Based on the indicators calculated by us, we can conclude that both at the beginning and at the end of the period, the enterprise is in an unstable financial position.
The overall indicator of product profitability includes the following indicators: the profitability of all products sold, which is the ratio of profit from product sales to revenue from its realization tion (without VAT, the total profitability equal to the ratio of balance sheet profit to the proceeds from the sale of du shares (excluding VAT); return on sales by net profit, defined as the ratio of net profit to sales proceeds (excluding VAT); profitability of certain types of products. The ratio of profit from the sale of this type of product to its selling price.
The calculation of these indicators is presented in Table 2.6.7.
Table 2.6.7.
Profitability indicators of the activities of Amurtorgexport LLC
The analysis allows us to conclude that in the reporting period there was a decrease in such indicators as the profitability of current assets, the profitability of core activities, while the overall profitability of production increased significantly.
The analysis of business activity, which is manifested in the turnover of its funds and their sources, is of paramount importance for assessing the effectiveness of an enterprise.
Business activity indicators are calculated in days and turnovers. We summarize the calculations in Table. 2.6.8. and 2.6.9.
Table 2.6.8.
Business Activity Indicators (Days)
| Name of indicator |
Change |
||
| Return of assets, days |
|||
| Return of fixed assets (capital productivity), days |
|||
| Turnover of current assets, days |
|||
| Inventory and cost turnover ratio, days |
Continuation of the table. 2.6.8.
As can be seen from the table, in the analyzed period, the period of return of the company's current assets increased, at the same time, due to a decrease in the volume of fixed assets, the terms of their return were reduced. The negative factor is the increase in the period of return of reserves and costs and current assets. The activity of the enterprise is positively characterized by the reduction of the period of turnover of receivables and the period of return of equity capital.
Table 2.6.9.
Business activity indicators (in turnover)
| Name of indicator |
Change |
||
| Return of assets, about |
|||
| The return of fixed assets (capital productivity), about |
|||
| Turnover of current assets, about |
|||
| Inventory and cost turnover ratio, about |
|||
| Turnover ratio of current assets, about |
|||
| Accounts receivable turnover ratio, about |
Continuation of the table. 2.6.9.
A decrease in the values of the calculated coefficients in the analyzed period indicates an increase in the business activity of Amurtorgexport LLC.
Analysis of income, profit
An important role in the activity of the enterprise is played by financial indicators of work. In the graduation project, the income received for three years and the profit received also for three years are considered in order to compare the dynamics of changes in these indicators.
Information about the income and profit of Amurtorgexport LLC is presented in Table. 2.6.1.
It is not always possible to judge the state of a company by its income. You also need to take into account taxes. Based on this, the most important indicator is profit, which is discussed in table 2.1.7.
If we analyze the company's income, then from table 2.6.1. it can be seen that their sum varies in an interesting way. In 2000, income amounted to 1563 thousand rubles. And in 2001 they increased by 225%, and became equal to 3517 thousand rubles. But in 2002, their volume fell sharply. And compared with 2001, this decline amounted to almost 40%. It became equal to 2095 thousand rubles. Apparently because of this drop in income, the company began to suffer losses.
This can be seen from table 2.6.2. At the beginning of 2002, the enterprise suffered losses in the amount of -51,562 thousand rubles. But already in 2003 there was an increase in profit from -51562 to 3796 thousand rubles. The upward trend continues in 2004, where the profit amounted to 4,716 thousand rubles, which is 124% more than the previous year. But the growth rate is still very slow, so additional measures are needed.
An analysis of the activities of a commercial enterprise allows us to draw certain conclusions.
The basis for improving the structure of the assortment should be a sales analysis, through which consistently purchased goods are identified; all automation programs that exist today can help with this.
The LLC "Amurtorgexport" enterprise is engaged in three main types of profit-generating activities. These are trade and purchasing activities, leasing of warehouse premises and provision of services to tenants.
Recently, the company has been effectively using the equipment.
Most of the personnel are production workers, and over the past three years, it is their number that has increased the most. The age group is dominated by people aged 36-40. The company employs only highly qualified workers, most of whom have a diploma of higher education.
The company inefficiently allocates costs, and therefore may incur losses in the near future.
LLC "Amurtorgexport" needs to take a number of measures to increase profits from sales and reduce operating costs and prime cost.
But profit growth is very slow, so some additional measures are needed.
The third chapter of the diploma project is devoted to the substantiation of certain activities.
In the city of Khabarovsk, a subsidiary of Amurtorgeksport LLC, Amur LLC, is being created in order to store construction products manufactured at the main production site.
The position of Amur LLC in business involves further expansion of the network to 5 workshops (for two years of operation) and up to 12 workshops (for the next five years of operation).
The number of personnel of the LLC "Amur" enterprise will be 20 people, of which 15 are warehouse workers.
The proposed project is to create a new warehouse of Amur LLC, since the main warehouses of the Amurtorgeksport LLC enterprise cannot cope with the task due to lack of space. The creation of a new warehouse will ease the load on the rest of the premises.
Project funding sources:
Contributions of participants (authorized capital) - 100 thousand rubles;
Bank loan - 800 thousand rubles;
Loans from other individuals and legal entities - 500 thousand rubles.
Obtaining a bank loan is possible on the following conditions: the term of the loan is 6 months, the interest on the loan is 6% per annum.
The implementation of the project allows the company's economic interests to create a profitable and financially sustainable network of warehouses designed to solve the problems of improving transportation problems caused by excess products that need to be removed from the main production.
Amur LLC was established on April 10, 2004 in connection with the need to bring the organizational and legal form of the enterprise in line with the requirements of the current legislation of the Russian Federation.
The company operates in Khabarovsk and is located at st. Yashin 57. The enterprise is a subsidiary, but has an independent balance sheet, current and other accounts in banking institutions.
The enterprise carries out its production and economic activities with the aim of making a profit, is responsible for the results of its activities and the fulfillment of obligations to suppliers, consumers, the budget, and banks.
In order to make a profit, the company provides services for the storage of surplus production.
The main goal of Amur LLC is to make a profit. Meeting the needs of industry and the population in services with high consumer properties and quality.
The enterprise "LLC" Amur "carries out the following activities: wholesale and retail trade in building materials, investment activities; foreign economic activity; marketing activities; commercial activities; repair and construction works; trading activities; organization and holding of exhibitions or similar events.
LLC "Amur" offers a wide range of various building and finishing materials made from high quality raw materials using advanced technologies.
In the proposed materials, along with imported components, which certainly ensure the high quality and stability of the resulting compositions, domestic components are used, which can significantly reduce the final cost of products without loss of quality.
The offered materials are used at industrial and public facilities (shops, hospitals, schools, etc.).
Amurtorgexport LLC is the official representative of KNAUF GIPS LLC in the Far East. The history of the KNAUF GIPS LLC enterprise begins in 1950, when the Pavshinsky plant for the production of dry gypsum plaster was entered into the State Registration Register. Therefore, the main types of stored and sold products are: KNAUF - sheets; KNAUF - profiles; dry building mixtures KNAUF, KNAUF - term.
In addition, consumers are offered components and tools necessary for "dry" construction.
The branch of building and finishing materials is the base of the building complex. It includes more than 20 directions, which are differentiated by types of products and unite about 10 thousand enterprises. At the same time, only about 2.25 thousand of them are large and medium-sized with a total number of about 720 thousand employees. Thus, the basis of this industry is, first of all, medium and small enterprises.
The main share of products manufactured by small enterprises is made up of wall and non-metallic materials, local binders, concrete structures, and polymeric materials. Currently, the tariff and price pressure of monopoly enterprises (increase in prices for gas, fuel, gasoline, electricity and growth in transportation tariffs) creates additional difficulties in predicting the economic situation in the industry. It should be noted that the building materials industry is one of the most energy-intensive and cargo-intensive industries. The volume of transportation of products and raw materials by different modes of transport is 25% of the national cargo transportation, and the volume of mining operations in the industry exceeds similar volumes in ferrous and non-ferrous metallurgy.
Over the past few years, the industry of building and finishing materials has seen a slight increase - at the level of 4-6%, but these figures are still far from the 1990 level. The main reasons for this are the lack of investment, high depreciation and slow renewal of fixed assets, and a lack of qualified personnel.
The share of domestic products in the domestic market is about 93%. However, for some finishing materials, the share of imported materials reaches 20%, and in the coming years it is unlikely to be significantly reduced. This is due to the lack of modern technologies and equipment, as well as some types of chemical raw materials that cannot be purchased abroad due to lack of funds from enterprises.
Today, the domestic market does not experience a shortage of almost all types of building materials. At the same time, the growth in prices for cargo transportation, mainly associated with the growth in prices for petroleum products, reduces consumer demand for products.
Despite the difficult financial situation of individual enterprises, the situation in the industry as a whole can be called stable, and successfully operating organizations use their funds to finance promising projects and upgrade fixed assets. Thus, in particular, in 2001, 60% of capital investments were disbursed from enterprises' own funds, and only 3% from the federal budget. The remaining capital investments were made at the expense of attracted investors and bank loans.
According to the State Construction Committee of the Russian Federation, in 2002 the industry maintained a positive trend of increasing the volume of production of building materials, products and structures, but the growth rate is somewhat declining. The output of building materials industry in 2002 was at the level of 104.5% in relation to 2001 (in 2001 in relation to 2000 - 105.5%). The slowdown in the dynamics of industrial production relative to 2001 is due to significant depreciation of fixed production assets and a decrease in the dynamics of investment in fixed assets, low competitiveness of domestic goods and insufficient innovative activity in production.
Serious competition between domestic and foreign manufacturers continues in the domestic market. There is a tendency to increase the export of a number of building materials, such as cement, asbestos, sheet glass, linoleum, while the share of exports in the total output is 4-6%. The share of imports in total sales in the domestic market does not exceed 6-10%.
It should be noted that with a general improvement in the quality of domestically produced building materials, the share of products comparable to imported ones (in the total production volume) varies significantly for different building materials. The technical level of most enterprises in the industry lags far behind modern requirements.
According to the industry development concept for the medium term, one of the priorities for the development of the building and finishing materials industry for the period from 2003 to 2005 is to expand the range and increase the competitiveness of building materials of domestic manufacturers, the introduction of new, resource-saving production technologies. The forecast for the development of the building materials industry for 2003 provides for an increase in the volume of industrial output of the industry by an average of 4.5% according to the pessimistic version, according to the optimistic one - by 5% against the results of 2002.
According to the State Construction Committee of the Russian Federation, in 2003 it is planned to put into operation over 160 production lines and production facilities that ensure the production of competitive and import-substituting building materials, products and structures of a wide range. In particular, it is planned to commission additional capacities for the production of 250 million units. conv. bricks, effective multi-hollow and facing wall materials, including products made of cellular concrete - 50 million pieces. conv. bricks, 3 million sq. m of ceramic tiles, packed cement - 500 thousand tons, about 200 thousand square meters. m of thermal insulation materials and other materials and products. During the forecast period, existing enterprises will continue the reconstruction and technical re-equipment of the production of wall, roofing and waterproofing materials, the organization of new facilities for the manufacture of light structures based on a metal profile.
The decline in the role of large-panel housing construction in the overall structure of housing construction led to a decrease in the share of prefabricated reinforced concrete production, while the increased requirements for housing comfort provoked an increase in the production of finishing materials, in particular ceramic tiles. New requirements for thermal resistance cause an increase in the production of heat-insulating materials, and the development of low-rise construction - an increase in the consumption of roofing materials due to an increase in the area of pitched roofs.
The domestic industry of building materials is focused on the domestic market and generally provides the basic needs of the building complex. However, the share of imports of building materials, in particular linoleum, ceramic tiles, natural stone products, as well as sinks and sinks, in the volume of sales in the domestic market continues to be quite high - at the level of 20-30%.
The main consumers of this enterprise will be the following construction companies.
OOO "STROYKOMERTS" is engaged in construction, high-quality repairs, design, interior projects with a full cycle of construction works, architectural supervision, new technologies and materials, laying artistic parquet, etc. this enterprise is located at the address: Khabarovsk, per. Sports, 4.
Branch No. 3 of FSUE USS "Dalspetsstroy" at Spetsstroy of Russia as the main activity uses the production of prefabricated reinforced concrete structures for industrial and civil construction, the production of ready-mixed concrete and reinforcement. This enterprise is located at the address: Khabarovsk, 60 Let Oktyabrya Avenue, 12.
"AMURTRANSSTROY", CJSC engaged in repair and construction works: repair of heating mains, water conduits, sewers; internal and external finishing works; plumbing, welding works; roofs, facades. The address of this enterprise is as follows: Khabarovsk, UL. BRICK, 36B, OF. 4.
In the city of Khabarovsk, there are quite a few companies that specialize in the production of building materials. In order for Amurtorgexport LLC to function no worse than these companies, it is necessary to increase the volume of finished products. And this is impossible without the creation of appropriate warehouses. The main competitors of the construction company are two firms specializing in building materials. Branches of these companies are located in most cities of our vast Russia. In order to better demonstrate the capabilities of competitors, we will compile a table:
Table 2.
The results of the study of some firms - competitors
| Company name |
OOO "Novostroy" |
Parom LLC |
|
| Location |
Terrain type |
Suburb |
|
| Competitors |
|||
| Staff |
|||
| Working hours |
From 10-00 to 20-00 |
From 8-00 to 18-00 |
|
| Study time |
Working day |
Working day |
|
| Product prices |
From 200 rubles |
From 100 to 300 rubles |
|
| Clientele |
elite enterprises |
||
| Ordinary businesses |
|||
| Discount system |
|||
As can be seen from the analysis, the projected enterprise should have the following advantages:
1. Be located in the city center;
2. The staff should consist of a majority of males;
3. Work from 8-00 to 18-00;
4. The price of products should be no more than 100 rubles.
5. It is necessary to make sure that the services of the enterprise are used not only by the elite strata of society;
6. It is necessary to provide a system of discounts for regular customers.
Now let's create a comparative advantage matrix.
Table 3
Comparative Advantage Matrix
| Comparative indicators |
Projected enterprise |
OOO "Novostroy" |
Parom LLC |
| Location |
Suburb |
||
| Quality |
|||
| Price level |
below average |
above average |
|
| Extraordinary shape of products |
standard |
standard |
|
| Range |
10 types, but with subsequent expansion |
||
| After-sales service |
Warranty |
||
| Working hours |
From 8-00 to 18-00 |
From 10-00 to 20-00 |
From 8-00 to 18-00 |
| Reputation of the company, products |
New venture |
Regular customers |
Regular customers |
As can be seen from the matrix, the projected enterprise has a number of advantages (price level, design, after-sales service) or is not inferior to them (quality, location, assortment, working hours).
It is easy to explain the formation of a high level of prices in firms of competitors. The fact is that a higher mark-up on the cost of production is a kind of payment for the brand of the company. These competing firms are in demand in the road transport market and have existed for a long time. They are significantly promoted and therefore their brand is expensive. But the projected enterprise is new in this market, not yet promoted. And therefore, it makes no sense to overpay customers for a trademark. The price itself is formed by focusing on the average prices of competitors.
The organization of marketing work is entrusted to the employees of the commercial department of Amur LLC. Once every half a year, the company's employees conduct desk marketing research to assess the demand for the company's products. Its purpose is to collect data from various sources.
The necessary information can be found in newspapers, magazines, various brochures, directories, catalogs, brochures, exhibitions, etc. In addition, the necessary data can be found in own records related to the development of the enterprise.
A valuable source of information needed to draw up a business plan are records related to the sale of goods.
They may contain the necessary information regarding:
– seasonal and other fluctuations in demand;
– running and slow-moving types of goods;
– average sales volume per customer;
– profitability of various types of goods;
– causes of dissatisfaction and complaints from customers.
Based on this data, current business activities can be assessed, as well as a work plan for the future.
A lot of useful information can be gleaned from the processing of local government statistics published in the press.
So, for example, you can find out about the rate of inflation in the region; living wage of the population; the average salary of the population; degree of social differentiation; household spending on certain goods and services; exchange rates; tendencies of economic and social development of the region; problems and prospects for the development of individual sectors of the economy, etc.
This will allow you to get a fairly complete impression of the socio-economic situation in the region and the macroeconomic conditions for the development of the enterprise. In addition, you can get an idea about the features and trends of development
It is necessary to determine your market share and decide on which types of goods stocks should be increased, and which types of goods are not in demand at the moment.
There are other sources of information as well. Every day we use the services of the media: newspapers, magazines, radio, television.
Using the data obtained and your knowledge, you can create a visual representation of the current state and prospects for the development of the market.
According to forecast data, Amur LLC will be able to bring a daily production capacity of at least 6,000 units. product names.
For the production of construction and finishing products of proper quality, imported equipment is needed. To purchase it, Amur LLC issued a bank loan for a period of six months in the amount of 800 thousand rubles. The equipment will cost about 680 thousand rubles.
For the activities of the above company, land plots are needed, on which the warehouse building of Amur LLC will be built.
The storage of materials requires electricity for lighting and equipment, as well as fuel for vehicles to transport goods and products.
Preparation of production consists of the following stages (see Table 3.6.1.).
The quality of manufactured and stored products meets international standards due to the fact that foreign-made equipment is used in production. Having chosen the products of Amurtorgexport LLC, any buyer will evaluate the quality of the products by the highest scores.
Table 3.6.1.
Production stages
| Stage name |
Stage cost |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Acquisition of premises: Warehouse No. 1 for storage of building materials Warehouse No. 2 for preparing materials for transportation Warehouse No. 3 for storage of finishing materials |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Purchase of production equipment |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Purchase of vehicles |
The main requirement for the staff is high professionalism. The company "Amur" approaches the selection of personnel very carefully, as a competent and cohesive team is one of the main keys to the success of enterprises. The firm needs a mostly male population as workers in the shops, but if the weaker sex so wants to work here, then this is not forbidden. The administrative staff consists mainly of women, as they are considered the best workers in this category. The director of the enterprise is, of course, a man with a higher economic education, who is well versed in construction and finishing works. Workers work in a warehouse. A marketer works both in the shops and in the office. The forwarding driver is assigned to the GAZelle-330210 car, the second car is intended for the management personnel (manager and director). The operator works in the office. Behind him is a workplace equipped with a computer. The second computer is intended for the manager and director. The total number of employees of LLC "Amur" is determined in the amount of 20 people. Description of positions and requirements for them are presented in Table 3.7.1. Table 3.7.1. staffing Continuation of the table. 3.7.1.
The calculation of the wage fund is presented in table 3.7.2. The allowances of workers are determined depending on the amount of output that the firm will make per month. Allowances for other employees are made according to the results of their work (efficiency, diligence, initiative). The salary of each employee for the month is determined as the sum of the monthly salary and the allowance to this salary. Table 3.7.2. Calculation of the wage fund The organizational structure of Amur LLC is shown in Figure 3.7.1. The organizational structure allows you to build a hierarchy, the direction of interaction between employees and the distribution of responsibility within the personnel of the enterprise. Rice. 3.7.1. Organizational structure of the company LLC "Amur"
The risk of the project may be associated primarily with a gradual decrease in customer demand for construction products. This is due to the general downward trend in buying activity. The second main risk is the increased activity of competitors, they may use dishonest methods. Below in table 3.8.1. presents the risks distributed by the stages of the project. Table 3.8.1. Risks by project implementation stages
The risk associated with non-fulfillment of the supply contract has a very low probability, since the company itself produces products. The risk associated with the instability of demand. If, for example, a drop in demand occurs for qualitative reasons (non-compliance with consumer demands for the quality and price of goods), then in this case it makes sense to work with other suppliers, as well as to plan your own costs more carefully in order to reduce the trade margin. Risk associated with damage or loss of goods. This risk is reduced, because, firstly, the company has a full-time driver and a vehicle for transporting products, and there is also the possibility of transferring goods to avoid damage to another warehouse. The risk associated with the actions of competitors is quite large, since their actions can be unpredictable, so the company's policy is aimed at carefully studying and evaluating competitors not only in the process of preparing this project, but throughout the entire activity of the company. The risk associated with wear and tear of equipment is reduced due to a careful approach to the selection of equipment at the preparatory stage, as well as through the conclusion of warranty agreements with suppliers of this equipment. The risk associated with low qualification of personnel is reduced through careful selection of personnel and training of personnel upon hiring. The risk associated with staff turnover is reduced through the use of material and social incentives for employees by the enterprise. Environmental risks have been reduced by signing contracts for garbage collection, compliance with sanitary and hygienic standards at facilities. Precautions such as enterprise insurance can be taken to minimize risks. These events will include the following indicators: a) professional liability insurance; b) insurance of civil liability of enterprises that create an increased danger to others; c) cargo insurance; d) accident insurance; e) voluntary medical insurance; f) voluntary health insurance. To implement the project for the creation of a warehouse, Amurtorgexport Limited Liability Company establishes Amur Limited Liability Company, which will act in accordance with Chapter 4, Paragraph 2, Clause 4 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, the Federal Law of the Russian Federation "On Limited Liability Companies". According to the Civil Code, a limited liability company must have a founding agreement and a charter as constituent documents. In the case of one founder, only the charter is needed. The founder of Amur LLC is Amurtorgexport LLC. In accordance with this, Amur LLC has only a charter. The Company carries out its activities in accordance with the current legislation and this charter. The provisions of this charter, taking into account the changes made to it, retain their legal force during the entire period of the company's activity. If any of the provisions of the charter becomes invalid due to changes in legislation, then this circumstance is not a basis for suspending the operation of other provisions of the charter. An invalid provision of the charter must be excluded from it in accordance with the established procedure and (or) replaced with a legally permissible one. The authorized capital is formed from the contributions of participants, in this case, one participant. The amount of the authorized capital of Amur LLC is 100 thousand rubles. Before considering the complex set of financial strategy issues, a company must develop a method for projecting its future financial needs. Strategic planning has given financial management more subtle tools as it has replaced purely accounting estimates with firm plans and programs based on pure strategy. And this allows you to increase the accuracy of the control and monitoring processes and focuses more on the future than on the past, the method of determining the financial needs of the company. For a well-performing organization, the strategic approach not only provides a revolutionary financial planning system, but also provides a more efficient method. Financial planning methods allow a company to prepare an estimate of future profits according to a certain fixed and detailed strategy with a broad description of the capital investments that may be needed to implement this strategy. It will be, rather, a series of numbers, and not a single number, but the significance of the assessment will not change from this. An assessment should also be made of other sources of cash, depreciation, as these may also be related to existing assets and new investments, including the strategic plan. In tables 3.10.1 and Appendix 3.10.2. a statement of planned profits and losses and a statement of cash flows for the year invested are presented. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Introduction
In modern business, the issue of organizing enterprise management is one of the strategically important ones, and the owners of the company must find the answer to it even before the start of any type of activity. Since the science of management has been actively developing since the second half of the twentieth century, today there are one or two well-established approaches to management. Each of the approaches has its own specifics of management, features of the analysis of the organization's business processes and unique methods of leader behavior. In the course of this course work, I will consider the most famous and effective, according to modern authors, approaches to management, as well as their features of work in modern conditions, trends and problems in the development of this industry on a global scale. The object of study of the course work is the theory of organization on a global scale.
INTRODUCTION 3 CHAPTER 1 MODERN PROBLEMS OF ORGANIZATION THEORY IN SCIENCE 5 1.1 Basic concepts of organization theory 5 1.2 Modern problems of organization theory 13 CHAPTER 2 PROSPECTS FOR THE DEVELOPMENT OF ORGANIZATION THEORY 21 2.1 Prospects for the development of modern concepts of organization theory 21 2.2 New possibilities of organization theory 26 CONCLUSION 31 BIBLIOGRAPHICAL
Bibliography
1. Akimova T.A. Organization theory. Ed. Unity - Dana. 2003. - 368p.; 2. Akulov V. B. Keynesian model of macroeconomic regulation: the possibility of using it in the modern economy. St. Petersburg, 2003. - 213 p.; 3. Barinov V.A. Organizational design. - Textbook. - M.: INFRA-M, 2012. - 384 p.; 4. Biryukova V.V. Organizational change management. - Textbook for the preparation of bachelors in the direction 521500 "Management", Ufa: UGNTU, 2008. - 170 p.; 5. Vavilina A.V. Organization theory. A short course of lectures. - Textbook, Saratov State University. N.G. Chernyshevsky. Department of Management and Marketing. Saratov, 2009. - 150 p.; 6. Vavilina A.V., Kokueva A.A. Economic management of the organization. - A practical guide for independent work of students. - Saratov, 2008. - 227 p.; 7. Vesnin V.R. Theory of Organization in Schemes.-Tutorial. - Prospect, 2008. - 128 p.; 8. Vikhansky, O.S. Management: a textbook for universities in the direction of preparation "Economics" - M.: Master; M.: INFRA-M, 2010. - 575 p.; 9. Demchuk O.N., Efremova T.A. Theory of organization. - Flint Publishing House. - 2009,264 p.; 10. Dulshchikov Yu.S. Theory of organization. - Textbook / Yu. S. Dulshchikov. - M. : Publishing House of the RAGS, 2009. - 192 p.; 11. Drucker P. Practice of management. - M.: Williams, 2000. - 400 p.; 12. Zhavoronkov D.V. Theory of organization. - Textbook. Krasnodar, Kuban state. un-t, 2010. 120 p.; 13. Ivanov Yu.V. Organization and economics of the enterprise at different stages of the life cycle//Article. - Dubna: Problems of the regional economy. - 2008. - v.1 .; 14. Istomin E.P., Sokolov A.G. Theory of organization: a systematic approach. - St. Petersburg: Andreevsky Publishing House LLC, 2009. - 315 p.; 15. Klyukovkin V.N. Organizational structures of management. - Monograph. - Biysk: Alt. state tech. un-ta, 2010. - 165 p.; 16. Korolkov B.P. Fundamentals of self-organization. - Irkutsk, IrGUPS, 2011, -120p.; 17. Milner B.Z. Organization theory. M.: INFRA-M, 2002.; 18. Milner M. Organization Theory Textbook, "INFRA-M", 2008. 19. Sidorov S. V. Rules for the implementation of a systematic approach in the management of a developing school // “Knowledge. Understanding. Skill". - 2010. - № 2 - Pedagogy. Psychology.; 20. Smirnov E.A. Organization theory. Textbook M., RIOR 2009;
An excerpt from work
Chapter 1. Modern problems of organization theory in science 1.1 Basic concepts of organization theory An organization is a complex organism in which the interests of individuals and groups of people, incentives and restrictions, rigid technology and innovation, unconditional discipline and free creativity, regulatory requirements and informal initiatives are intertwined . Depending on the specifics of the organization's activities, a set of characteristics is formed, which are the uniqueness of each company. In this regard, each company individually must choose its own development strategy, formulate its long-term and short-term goals, internal and market behavior policies, as well as its own management approach that will allow it to operate with maximum efficiency. The formulation of the entire complex of these provisions is directly dependent on the experience and competence of the manager, as well as his team. Any process, regardless of its characteristics, is ordered and organized to a certain extent. If you decompose any of the organization's business processes, you can see that it consists of elements that interact with each other during implementation. Consideration of these elements is systemic and reflects the essence of the system approach in general terms. A systematic approach is a special method of cognition aimed at representing, studying, constructing a complex object as a single organized whole based on identifying its most important features, internal and external connections, and decisive factors of influence. A systematic approach to the study of organizations is based on the use of the category "system". Note that this concept is quite voluminous and has many different interpretations, which vary depending on the key in which they are considered. In conjunction with the concept of "system", definitions and terms such as "organization", "organization" are always considered. Such a relationship of terms is due to the fact that they can be considered as complementary. These terms complement each other and form one informative direction, the system is impossible without organization. The only difference between them is the volume of application, the system is a narrower concept, and the organization is wider. In a general sense, a system is the interaction of its elements that have different influences on each other in the process of this interaction. The organization appears not only as ordered elements, but the system as exclusively ordered. The properties of an organization are similar to the properties of systems. Let's consider system signs, properties of the organizations: ? Component; ? Structurality; ? Integrity. Each of the signs and shapes the organization as it is. Decomposing the process into elements, their interaction will definitely be determined. Such interaction may be direct or indirect, but it is an integral part of the system and its elements; ? Functionality; ? Emergence. Emergence proves the fact that a mere collection of elements does not constitute a system. The system, uniting into one whole, has such characteristics that were not characteristic of its individual elements; ? Sustainability is a property of an organization that reflects the constant desire for adaptation, that is, to maintain balance, disturbed by the influence of external factors. The components of an open system are inputs, the process of converting inputs, and outputs. Consider the process of interaction of elements in Figure 1. Fig. 1. 1 Elements of the system approach and their interaction The entrance is the initial stage of the formation of the system. Input implies all incoming flows and resources that are formed through combinations of material, financial and other flows. In fact, the input is the range of benefits and resources that the organization receives from the outside. The main process, considering the theory of organization, is - the transformation process is the impact on the input, that is, on the input streams. The system must be designed so that the necessary processes act on each input at a certain time and in a certain sequence to achieve the desired output, it is here that a systematic approach must be implemented in accordance with the regulation in production. The output of the system is what the organization works for, that is, the actual result. The result for the company may be finished products, services or components. At the same time, we note that due to the constant interaction of companies, the output product or service of one organization may be the input for another organization. There is a certain cyclical nature of the market here. After the spread of the system approach, in the middle of the twentieth century, the situational approach to management began to spread. The ideas of this approach are characterized by a large variability of management actions, depending on the situation. Thus, specific circumstances or a specific situation dictate a specific response mechanism. Of course, this situation directly affects the company that operates in connection with it. The second type of approaches to management, which is considered in the framework of the study of the theory of organizations, is the situational approach. This approach was formulated after the system approach and became widespread due to its uniqueness and individuality. The situational approach, when implemented, should always take into account the factors of formation of external and internal influences. The main factors and direction of impact are shown in Figure 2. Fig. 2. 2 The main factors that form a specific situation Note that the modern American management theory is based precisely on the elements of the situational approach. It is logical to establish relationships between specific situations and changes in the work of enterprises. Thus, the situational approach can be based on the identification of certain relationships between the effect and the cause of certain changes in the external and internal environment of the company. The main goal of this approach is to determine the variables in the system of interaction between market participants. The main task of situational management is to create a stock of ideas about similar management situations characteristic of a certain level of enterprise development and to develop decision-making algorithms in specific situations. If the company operates in an environment where the level of various risks is significantly increased on an ongoing basis, the use of situational thinking or a situational approach may be ineffective and lead to situations that can lead to negative consequences. Also, the irrationality of the application is fixed in cases where there are a lot of options for influencing. An example of such a situation is a large company with diversified production and an extensive organizational structure. It becomes very difficult to take into account all the options for the development of situations, which can also lead to adverse consequences. Thus, the use of a situational approach within the framework of the company's activities can become both a guarantee of the successful development of the company, which can dynamically respond to all changes in the environment, and the wrong decision of the manager, which can lead to negative consequences. One of the main methods of analysis used in this approach to management is SWOT analysis. SWOT analysis is a method of strategic planning, which consists in identifying factors of the internal and external environment of the organization and dividing them into four categories that reflect the strengths and weaknesses of the company, possible threats, and also. Thus, we note the main distinguishing characteristics of the situational approach: - this the approach does not imply the regulation of all processes, decision-making is carried out situationally; - we implement a situational approach in the absence of stable high risks in the market, as well as multivariate solutions; - situational analysis is applicable only in cases where the manager is ready to bear full personal responsibility for situational decisions; - the leader's ability to creative non-standard solutions will be a priority. Thus, the situational approach can be distinguished as an approach based on an experienced leader who will be able to quickly make decisions, take on authority and responsibility, as well as treat a particular problem in a non-standard way every time. Subject to all factors, the use of a situational approach will allow the company to grow and develop in the market. The next approach that will be considered within this block is the process approach. Its essence lies in the idea that in order to implement the process of enterprise management, it is necessary to manage individual processes. It should be noted that this approach changed and at the same time supplemented the theory of management. Thanks to the principles of the process approach, a modern vision of the company was formed as a single mechanism that should work together. In modern literature, there are many different definitions regarding the focal concept - "process". Consider the definition proposed by the International Standards ISO 9001: “A process is a set of interrelated and interacting activities that transform inputs into outputs”. Note that the concepts of "process" and "system" should be considered in a complex, as they are complementary. This statement is based on the fact that the process must be systematized, only in this case it is subject to management. This approach has been actively introduced by modern leaders due to the fact that it is precisely this approach that implies the active development of horizontal ties. Whereas the previous models of corporate governance implied only the development of vertical, linear links. Improving communication between structural divisions has a positive effect on many aspects of the company's work - improving the socio-psychological climate, raising the level of organizational culture, improving relationships between employees of different departments and divisions. Thus, the process approach supports this direction, which has a positive impact on the organization. Also, the process approach, due to the existing regulations, contributes to the operational work of the staff, without involving direct management in the work. The process approach assumes the presence of key elements, without which it cannot be implemented in the organization, the main elements of the process are shown in Figure 3. Fig. 3. 3 Interaction of elements of the process approach After analyzing Figure 3, we can conclude that the inputs of the process are elements that undergo changes in the course of performing actions. Process inputs can be information, material or cash flows. The outputs of the process are material, information or service flows. Service flows, in some literature, are also called return flows. It is the output streams that are the goal of the whole process, it is the results of the activity that determine the very activities of the company. The process approach underlies several popular and quite effective concepts for improving the work of organizations. To date, there are four areas that use the process approach as the main approach to improve performance.
The need to develop a new organization strategy appears when new goals arise or it becomes clear that it is impossible to achieve the goals set using the previous (current) strategy.
The variety of market situations implies a variety of strategies used by enterprises.
Enterprises, having different opportunities, tend to choose those strategies that allow them to work successfully in certain segments. There is a kind of demarcation of the positions of enterprises, depending on their resources and the economic conditions of the industry.
There are four main types of positions of enterprises in the market:
- 1 position - a leader operating in the field of mass production of goods;
- 2 position - a leader operating in the field of specialized production of goods;
- 3rd position - follower;
- 4th position - pioneer.
Each position has advantages and disadvantages, but they all complement each other, helping to meet the diverse demand for the product in the most effective way. One thing is important - to work in a segment in which competitive advantages are realized.
LLC "Mari Fruit Company" refers to the first type of positions of enterprises. The peculiarities of this position are the large size of the enterprise with low adaptability. Competitive advantages are high productivity and low unit costs.
In accordance with the characteristics of an enterprise belonging to one type or another, it has its own field of possible strategies.
Currently, scientists and practitioners have developed approaches and models that make it possible to reasonably approach the definition of an enterprise strategy.
We note the main factors on which the determination of the prospects for the development of enterprises depends:
enterprise goals;
the state of the market, the position of the enterprise on it;
competitor strategies;
production technology;
enterprise potential;
goods produced at the enterprise and its features;
competitive advantages;
market share, market attractiveness;
product life cycle stages;
costs of production and sale of goods, the claim of management, etc.
It is almost impossible to take into account all these factors when determining the direction of development of an enterprise. Therefore, approaches to the definition of strategic alternatives will differ primarily in what factors are taken into account and considered the main ones.
The core of any strategic plan of an enterprise is its basic strategy. In accordance with the development cycle of the enterprise, management can choose one of the following basic strategies:
Growth strategy - the main strategy of the enterprise, expressing the desire to increase sales, profits, capital, i.e. development strategy.
Stabilization strategy - the strategy of the enterprise in the conditions of instability of sales and income. Aimed at achieving early stabilization of income and subsequent increase in profitability.
A survival strategy is a purely defensive strategy used in a deep crisis in the economic activity of an enterprise. The management evaluates and analyzes the information obtained at the previous steps (external environment, internal capabilities) and makes the final decision.
At this time, the position of Mari Fruit Company LLC can be confidently called stable: production volumes are growing, profits are increasing, new capacities of the enterprise are being introduced every year, new areas of activity are developing, as a result of which the current activity of the enterprise is improving. Based on all of the above, we can conclude that today Mari Fruit Company LLC needs to use a growth strategy.
The company has already mastered the markets for its products, and now its strategy should be aimed at strengthening its position in the industry. In order to "keep up with the times", the company must improve the quality of products and expand its range by introducing new technologies. The plant is constantly developing its production capacities. In order to "keep the bar" in the market, the main direction of the development of the enterprise for the future should be the establishment of business cooperation and work with counterparties by developing a system of discounts, developing dealer activities, stimulating sales, and thus expanding sales channels. The task is also to gain a reputation and form the image of the company in the market.
A special place in the formation of a strategy is occupied by its type.
There are offensive, defensive, intermediate, absorbing and residual strategies.
For the Mari Fruit Company LLC, it is preferable to choose both an offensive strategy focused on winning the leading positions of the organization in certain areas of activity or the market, and an intermediate one, which boils down to reasonable competition, using the omissions and weaknesses of other enterprises and following the lead of the leading company . The success of the latter strategy is achieved through the independent implementation of an effective innovation policy that allows you to keep up with the leading firm.
To achieve the goal, based on the identified opportunities, the following marketing strategies of LLC "Mari Fruit Company" in the market can be proposed.
The strategy according to the matrix of the Boston Consultative Group allows you to evaluate the product of LLC Mari Fruit Company in terms of its activity and competitiveness in the market. On the basis of the BCG matrix, further strategic alternatives for the development of the enterprise are determined and developed.
The products of LLC "Mari Fruit Company" occupies an intermediate position between "Question Mark" and "Cash Cow". In accordance with what the strategy of the enterprise should be aimed at increasing the competitiveness and activity of goods in order to win the position of "Cash Cow".
To do this, Mariyskaya Fruit Company LLC needs to conduct more intensive advertising activities: post information about the product in the press, on radio and television, issue brochures and catalogs. The business is currently limited to placing advertisements in some local newspapers. In modern conditions, without a well-planned and well-organized system for promoting goods, it is almost impossible to succeed in the market.
To maintain and increase the sales of products of Mari Fruit Company LLC, it is advisable to use the following marketing strategies:
market penetration: a deeper study of the traditional market for the sale of old products is carried out, sales activities are improved in order to gain advantages over competitors;
product development: searching for "niches" for new products, as well as identifying new products for the old market. The strategy is also preferable in terms of cost and risk minimization;
Consequently, the growth of an enterprise is largely determined by the correct choice of a functioning option based on the development strategy that is being formed.
For a growing market, the approach proposed by Igor Ansoff is used. This approach is one of the tools for building a market strategy, its essence is illustrated by the Product-Market matrix. Using such a matrix, it is easier to link the developed strategy with the characteristics of the enterprise, with the characteristics of production and marketing, with the process of segmenting the consumer market.
There are several types of matrices, the simplest four-cell matrix gives a visual representation of the four possible options for an enterprise strategy (Fig. 3.8). There are two product classes (traditional and new) and two types of markets (established and new) in the matrix. Their combination forms four strategic fields, each of which represents one of the possible strategy options.
Rice. 3.8. Matrix "Product-Market"
Each of the 4 fields of the matrix represents a specific strategy and its elements.
Box 1 shows the focus of the organization's strategy on existing products and markets. The purpose of this strategy is to stabilize or expand the market. This strategy is used by organizations in an emerging or desaturated market. Possible ways to achieve the goals are to increase consumption and attract buyers of competing products. Such strategies are called "cost reduction" or "market processing" and involve increased marketing efforts.
Field 2 includes strategies aimed at developing the market. They provide for entering new markets with already produced goods. Possible avenues may be: marketing in new regional, national or international markets; new areas of use of the old product, introduction to new market segments.
Field 3 includes strategies aimed at developing new products (innovations) that will be sold in old markets. These strategies are applied by organizations with strong project services.
Box 4 represents diversification strategies, which refers to a change in directions and areas of activity, i.e. inclusion in the production program of products that do not have a direct resemblance to manufactured products. Reasons that encourage businesses to launch new products and enter markets with them can be: the desire to leave the stagnant markets of the industry and enter industries with high profit margins, risk reduction (“not all eggs in one basket”), as well as financial benefits.
These alternative strategies are not equivalent in terms of the required costs and the magnitude of the risk. As studies by some scientists have shown, if we assume that the cost of the "cost reduction" strategy is 100%, then product development will require eight times the cost; market development - fourfold expense; diversification - twelve to sixteen times the expense. In this case, the probability of success of various strategies will be approximately the following values: the product produced in the old market - 50%; new product on the old market - 33%; a product produced in a new market - 20%; new product in a new market - 5%.
The main disadvantage of this approach to generating alternative strategies is that they are determined depending on the state of two (albeit important) elements: the market and the product. Other important elements, for example, technology, the position of the enterprise in the industry are not taken into account.
The choice of the desired strategy is carried out on the basis of an assessment of the chances and risks corresponding to each of the strategies. Of the four possible strategies, Mari Fruit Company LLC prefers both the first strategy, which has the highest chances of success and the lowest risk, and the third one, as it corresponds to the goals of the enterprise, is characterized by considerable chances of success and medium risk compared to other strategies.
The choice of strategy can also be made using the matrix proposed by Thompson and Strickland, the axes of which are the growth dynamics of the product market and the competitive position of the enterprise.
For the main types of products sold by Mariyskaya Fruit Company LLC, the best business strategy is differentiation: market and product.
Market differentiation includes such areas as: brand loyalty; sale of high-demand goods.
To grocery: high quality; additional product features; work to order.
Growth opportunities for an enterprise can be realized by choosing products with a rapid increase in output or a new product. For growth, it is necessary to change the assortment, achieving greater potential for expanding output and securing a high share in the wholesale market.
Mari Fruit Company LLC can achieve competitive advantages and strengthen its position in the market not only by reducing the costs of selling goods, but also by ensuring the indispensability of the product through differentiation. The purpose of this strategy is to give the product distinctive features that are important to the buyer and that distinguish the product from the offer of competitors. The company plans to introduce a flexible system of discounts, which will attract buyers with different income levels. But quality improvement is a continuous process, as customer requirements are constantly changing, resulting in the need to improve the product, even if it is in demand.
This type of strategy is associated with higher costs, requires a variety of resources and marketing approaches, but allows the company to confidently exist and capture a leading position in the market.
The chosen strategies will allow Mari Fruit Company LLC to strengthen its position in the domestic market and outline the prospects for its further development.
The implementation of the chosen strategy of Mari Fruit Company LLC will be facilitated by:
- 1) Highly skilled workers
- 2) Orientation to the needs of consumers
- 3) Cost reduction
- 4) Competitiveness
To introduce this strategy, the enterprise has a sufficient number of opportunities and advantages.
After analyzing the current situation at the Mari Fruit Company LLC, we can conclude that in order to carry out effective marketing activities at the enterprise, first of all, it is necessary to create a marketing department. Of course, Mari Fruit Company LLC uses separate complexes (groups of interrelated methods and means) of marketing activities (development and production based on the study of demand), as well as individual elements of marketing (advertising, sales promotion, demand-based pricing), but this is not enough to carry out effective marketing activities.
The need to create a marketing department is due to the fact that the company needs to make an in-depth study of many factors that have a significant impact on the effectiveness of marketing activities.
To begin with, it is necessary to determine what market share is occupied by products sold by Mari Fruit Company LLC. To do this, you need to know exactly who is the consumer of each type of product, what is the need for these products, whether there are competitors on the market - sellers of similar products.
The employees of the existing sales department at the enterprise definitely know who their regular customer is, but due to a lack of labor and time resources, they do not study his needs. The main drawback in their work is the lack of a clear analysis of sales volumes. This is very important for determining the customers with the largest share in sales volume, the factors influencing sales volumes, and ways to influence these factors in order to increase sales volumes. An increase in sales leads to an increase in revenue, and, consequently, profit.
The key factors that distinguish Mari Fruit Company LLC in its industry are:
Production personnel with many years of experience.
Vision of the prospects for the development of the enterprise, which can be realized after achieving the goals of the project.
Orientation to the buyer, his requests and suggestions.
Competence in the economic field.
Focus on cost reduction.
Ability to adapt to changing market conditions.
The enterprise will sell products depending on the needs of the market, as well as increase production volumes at the expense of profits from current activities and sales of products.
So, the main task at the present stage of development for LLC "Mari Fruit Company" is to maintain the won positions in the wholesale market and further and more and more satisfy the needs of consumers in these products. At the same time, the promising directions for the development of the enterprise are:
- 1. Increase in trading capacity, and, consequently, growth in sales volumes
- 2. Product quality improvement
- 3. Expansion of the range of products sold
- 4. Organization of effective sales
- 5. Formation of the image and reputation of the enterprise, brand recognition
All of these possible directions for the development of the enterprise in the future will require the development of appropriate strategies that can be carried out in parallel.
The likelihood of implementing these strategies will be determined by the development of the situation in the country, the ability of the enterprise to correctly choose and evaluate its advantages and disadvantages.
At the same time, the promising directions for the development of the enterprise are: an increase in trading capacity, and, consequently, an increase in sales volumes of products, improvement in product quality, expansion of the product range, organization of effective sales, formation of the image and reputation of the enterprise.
Growth opportunities for an enterprise can be realized by choosing products with a rapid increase in output or a new product. For growth, it is necessary to change the assortment, achieving greater potential for expanding output and securing a high market share.
There are two groups of factors that provide organizations with competitive advantages - this is superiority in resources (better quality, low prices, etc.) and better craftsmanship (associated with the efficiency of all activities of the organization, the work of research, design, production services).
Superiority in resources and better craftsmanship will allow Mari Fruit Company LLC to offer consumers higher quality products at lower prices than competitors, achieving an advantage. The advantages achieved allow you to take a stronger position in the market, get profitability above the industry average, which in turn will further develop the strengths and eliminate the weaknesses of the organization.
The need for a permanent generalization of the organizational experience of mankind and the development of organization theory is recognized by many scientists, and above all by the followers of the school of A.A. Bogdanov - the founder of tectology (general organizational science). Moreover, the creator of this scientific school himself attached great importance to the category of “disorganization” - the process of disruption (destruction) of the organization: “The simplest definition of disorganization is that it is the opposite of organization: there the whole is practically a large sum of its parts, here it is less than this sum.”
Further, he, casting doubt on the interpretation of disorganization as a synonym for “destruction, decay, decomposition”, gives the following example: “A free-living cell has grown to a certain size and splits into two. Is it "disorganization"? No, this is “reproduction”, one of the processes by which life is organized in nature. By such a progressive cell division is the development of any complex organism. Therefore, it is not a matter of simply breaking ties.”
After that, A.A. Bogdanov speaks about the role of the external environment: the cell “grew at the expense of the environment, and daughter cells can continue to grow in the same environment. On the contrary, if the cell is surrounded by an unfavorable environment that destroys it, then division into two would only accelerate its death and would be disorganization. Further, he emphasizes that in reality the phenomena of disorganization are so closely intertwined with organizational ones that "both characteristics very often turn out to be equally applicable, depending on what activities of the studied complexes are taken into account."
These far-reaching conclusions of the creator of the Great Organizational Science are of particular importance in real practical life today, the problematic post-crisis period. No less interesting are the truly prophetic words of A.A. Bogdanov, which he said in his well-known work before the First World War (1912): “The more a society grows and develops, the stronger and more painful for it is its disorganization as a whole. The gigantic mass of living activities, continuously accumulated in it, keeps its balance more and more difficult, less and less perfectly. The acute and chronic ills of the social system - the calamities of fierce competition, crises local and world, the growing tension of the struggle between nations over markets, unemployment, merciless class conflicts - all this together creates a tremendous waste of social forces and creates an atmosphere of general uncertainty about the future. These are formidable manifestations of general disorganization processes, and the fight against them with the help of methods of a partial nature, which specialization has at its disposal, is, in essence, doomed to failure.
The fundamental principles of the modern theory of organization, based on the above and other conclusions of A.A. Bogdanov in tectology, allow her to claim one of the priority places in modern domestic and world science.
Until now, the question of whether it is necessary to limit the circle of objects in the theory of organization only to subject-material systems or to include non-material systems in their number is still debatable. No less difficult is the question of the purposefulness of systems. Many authors consider the "system of the sciences of organization" and include in it the economic and legal sciences, sociology, psychology, anthropology, computer science, etc. .
This indicates, on the one hand, the insufficient development and completeness of the theory of organization as a science, and on the other hand, its interdisciplinary nature, which gives it the role of a metatheory. The main methodological function of the theory of organization is to establish laws, principles, methods and mechanisms that reveal the processes of development of organizational or organizational-economic systems, the development of methodological approaches for their effective functioning.
If 30-40 years ago in domestic universities they mainly studied in detail the organization of industrial, machine-building and other enterprises (correlating this with their industry affiliation), then in the short and long term, in connection with the development of integration processes, it is required to study and improve knowledge in the theory of organization as sciences about the organization of organizations, the basic laws and principles of organizational activity, the design and development directions of the ECO, the strengthening of the role of international institutions and various factors of globalization.
As stated in the opening speech of K. Schwab at the World Economic Forum on January 28, 2009, “the formation of the post-crisis world lies, first of all, in the inclusion of global and intergenerational accounting and corresponding responsibility in everything that we do, both individually and collectively.”
The second half of the XX and the first decade of the XXI century. clearly revealed themselves “as a time of constant growth of complex problems that require for their solution not only more and more information and specialists, but new methods and forms of organization ... The organizational activity of mankind is a purposeful activity of people on a planetary scale to create the most favorable conditions for satisfying their needs. The world system turns into a single organism interacting with the biosphere. This is consistent with the logic of self-organization of complex systems. Ideas that can bring humanity to a new level of relationship with Nature begin to play a special role.
The recent climate cataclysms in Russia and in many countries of the world have shown that in the short term these relationships between human civilization and Nature (cosmic energies) become the most important motive for the activities of both individuals and governments of all countries of the world. Moreover, the main limiting factor in this activity is ecology and natural resources.
Indicators of comprehensive accounting of the combined impact of natural, socio-economic, environmental, political and other factors on the quality of life of people should be developed and implemented in the global socio-economic system.
As stated in the book by A.P. Fedotova and S.V. Plotnikova “Global Studies: Fundamentals of the Science of Earthly Controlled Civilization” (M., Profil-2C, 2009), “the world economic crisis can be tamed by the only way of a gigantic transition from the era of spontaneous civilization to the era of controlled civilization, by creating a worldview and systemically new Earthly controlled civilization ".
The modern values of the global market economy, on the one hand, activate the desire of systems for a single information Internet space, erasing existing national differences, and on the other hand, strengthen the institutional basis for ensuring sustainable economic development, without reducing the responsibility in this area on the part of the governments of each country as the main ones. system controllers.
It is necessary to create a set of institutional organizations that form interconnected mechanisms for self-regulation of the market economy at all levels - from global to local (local), which in the future will ensure the harmonious development of macro- and microsystems. And this is one of the most important tasks of the science of organization as a metatheory.
The book of the well-known economist A. Aganbegyan “Crisis: Trouble and Chance for Russia” (M., ACT: Astrel, 2009) emphasizes the need to develop a new Concept for the long-term development of Russia (instead of the one previously developed by the government for the period up to 2020) according to an innovative modernization scenario economy. With a 6% average annual GDP growth in the Russian Federation (correspondingly, 2.5% growth in the developed countries of the world), with the implementation of this strategy, Russia will be among the last in 25-30 years. At the same time, it is necessary “to build the structure of the national economy in such a way, to form such development institutions in order to best use the objective trends of globalization of world development to our advantage, while leveling out possible negative consequences, for example, from a possible outflow of foreign capital from the country, from the negative impact exchange rate changes, etc.”.
Using financial, social, organizational, economic and technical and technological tools based on the metatheory of organization in the long term, the domestic economy could solve in a relatively short period of time (in 5-7 years) the tasks of technical re-equipment of the national economy with the replacement of obsolete equipment “with modern systems of machines and equipment that implements the most advanced technologies in most industries and in the service sector”.
At the same time, it is necessary to significantly increase the interest of enterprises and organizations in the final results of their activities. At the first stage, it would be possible to stake on the development in Russia of industries for the deep processing of raw materials and materials, obtaining final products with high added value (for example, to become one of the world leaders in deep processing of wood, the production of finished products from wood and synthetic materials, the development of energy - and electrical engineering).
But along with them, in the near future, attention should be paid to priority innovative industries with high technology, a large share of science-intensive products (aviation, space industry, etc.).
As a result of the practical organization of these areas, the share of manufacturing industries and services in the country's exports should grow from the existing 10-20% to 50-60% (accordingly, the share of fuel and raw materials industries will sharply decrease).
According to A. Aganbegyan, with this approach, the foundation laid in the medium term (5-7 years) will allow on an updated technical and technological basis, taking into account the modernization and diversification of the national economy, eliminating the main imbalances and raising the standard of living, strengthening incentives to work and entrepreneurship among the population in the future (about a quarter) to solve the strategic task of scientifically organized long-term development of Russia with the achievement of socio-economic indicators of the most developed countries of the world.

 How to store porcini mushrooms after harvest and for the winter
How to store porcini mushrooms after harvest and for the winter Speed regulator for grinder - to make the machine more reliable and functional
Speed regulator for grinder - to make the machine more reliable and functional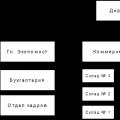 choice of strategic alternatives
choice of strategic alternatives