What is trapezoidal thread? Thread trapezoidal thread trapezoidal left
Trapezoidal carving is widely used for the manufacture of different screws that serve for various production equipment. For example, for machine tools, lifting devices, presses. Such a carving has a form of an equilibrium trapezium, while the profile angle may have different meanings: 15, 24, 30, 40 °. In the process of operating the screw on which the trapezoidal thread is cut, friction forces appear caused by naturally. That is, due to the presence of lubricant material, surface roughness, as well as the corner of the profile.
Types of thread
To date, there are such types:
- Metric. It serves to fix multiple elements. Cutting conditions are established in regulatory documentation. The profile is a triangle with equilateral corners. This indicator is 60 °. Metric thread screws are performed with small and large steps. The first species is used to fix the thin-leaf elements to create increased tightness. This type of access can be found in accurate optical devices.
- Conical. It is also made as the previous look, but the twist is made to a depth of 0.8 mm.
- Inch. To date, there is no regulatory document in which the thread sizes would be indicated. Inch thread is used when repairing various equipment. As a rule, these are old devices and devices. Its main indicators are the outer dimer and step.
- Pipe cylindrical. This species is an equifiable triangle, the upper angle of which is 55 °. Such internal thread is used to connect pipelines, as well as parts made of thin-leaf material. It is recommended when specific requirements for the tightness of the connection are presented.
- Pipe conical. Internal thread must comply with all the requirements of regulatory documents. Dimensions are fully standardized. It is used to attach various types of pipelines.
- Stubborn. This species represents a non-uniform trapezium, where one side is tilted by 3 °, and the other is 30 °. The first side is a worker. The form of the profile, as well as the diameter of the steps is determined by the regulatory documents. In accordance with them, the thread is performed with a diameter of 10 to 600 mm, and the maximum step value is 24 mm. They are used where elevated retention efforts are required.
- Round. Thread profile is various arcs related to straight lines. The profile angle is 30 °. This type of thread is used for those compounds that aggressive environments are affected.
- Rectangular. It is not fixed by any regulatory documents. Its main advantage is the high efficiency. Compared to the trapezoidal species, it is durable, and also causes many incomprehensible moments in its production. The main place of application is jacks and various types of screws.
- Trapezoidal. It has the shape of an equilibrium trapezion with an angle of a profile of 30 °. Trapezoidal thread, the dimensions of which are fixed in the documentation, is used to connect various elements of production equipment.
Production conditions
Compared to other types, the trapezoidal carving is much easier to manufacture.

That is why it is more often used in various spheres. The most popular is a trapezoidal screw having an angle of a profile of 30 °. The production technology is very similar to the one that is used to cut a rectangular thread. But still there are significant differences regarding the accuracy and purity of manufacture. Slicing the trapezoidal thread is no different from the same procedure with a rectangular view. At the moment there are several such ways.
Making a screw with one cutter
The thread trapezoidal one is manufactured in this way:
- prepared the workpiece and the channels for sharpening are supplied;
- the sharpening of the cutter is performed on a special prepared pattern;
- the installation and fixation of the sharpened element are manufactured. It should be located so that the centers coincide and there were parallel axes of cutting;
- equipment turns on and a billet on cutting threads is supplied;
- the finished item is checked according to the finished template.
Cutting with three rubber
This method is as follows:
- prepared the workpiece;
- the sharpening of three incisors is performed - direct, narrow and profile;
- installation and securing prepared elements are made. They can be located both perpendicular and parallel to the axis of the thread. It all depends on the angle of inclination.
Common production method
It is in production that the sliced \u200b\u200bof the trapezoidal thread is in such a way:
- work equipment is checked and configured;
- thanks to the slotted cutter, small recesses on the screw are made;
- with the help of a narrow slit element, cutting screws to a certain diameter;
- with the help of the profile slit element, the final production of trapezoidal thread is performed;
- the finished part is checked according to ready-made templates.
Trapezoidal thread: sizes
As mentioned earlier, this type of thread has a trapezoid form in which the angle between the parties may have different meanings. All major sizes are set in accordance with GOST.

For the one-income type, the trapezoidal thread (dimensions - GOST 9481-81) has dimensions and steps of various diameters - from 10 to 640 mm. In addition, it can be multisime, as well as twisted in the left or right side. These indicators are normalized by GOST 24738-81.
Where used
For the functioning of any element, such as a machine or mechanism, it is necessary to fulfill the mandatory condition: rotational movements must be transformed into progressive.

This principle is used to manufacture various machines, devices, regulatory systems used in the industrial sphere.
Advantages of thread
The efficiency of working on the conversion of rotational movements into the translational is carried out using a nut and screw. Despite the fact that these details look simple, they require care when making them. It is from these parts that the productivity and reliability of not only component elements, but also the entire work equipment depends on.
Features of multisope thread
To put the screw to the strength characteristics and increase its course use multi-turn trapezoidal threads. In this case, all parameters, such as the height of the thread, its diameter are absolutely the same, with a one-going specimen. The only difference is the number of moves one step. For example, three-point threads have three times more than their step. All this can be observed in the drawings.
Let us give an example so that this species becomes understandable to every person. All use conventional covers for canning vegetables and fruits. For their discovery, it is necessary to make a minimum effort. When using large diameter cylinders, to get into the sinking grooves is much more complicated. That is why they use multi-way.
This type of thread can be determined visually, just look at the drawing.

It can be seen how many turns go from the beginning of the screw. Multiple threads are manufactured by complex technologies, and accordingly cost more.
Other advantages
Trapezoidal compounds have many positive qualities. That is why they are used in various manufacturing industries. The most common area is mechanical engineering. So, their advantages include the following:
- the ability to collect and disassemble various devices an unlimited number of times;
- convenient process of parsing and assembly;
- reliability of the threaded connection;
- easy manufacturing process;
- self-regulation of compression force;
- production of parts in various versions.
Disadvantages of connections
Negative sides of this type of compounds are not so much. One of them is the emergence of a large voltage in the depression. In addition, they cannot be used in devices and mechanisms that have high vibrations, since the screws can unscheduled independently, which is not a good sign.

Therefore, it is necessary to follow this, and in the event of such a situation - to correct the position of the screws.
Such quality as cost can be attributed to both positive and negative parties.

One-way threads cost significantly lower than the multi-way. Here everyone chooses in accordance with personal preferences. Many design organizations use multiple threads, as they are distinguished by reliability and durability.
So, we found out that it represents such a type of compound as the trapezoidal thread, its size, advantages and disadvantages.
Profiles and threads
(GOST 9484-81)The standard applies to the trapezoidal thread and sets the profiles and the dimensions of its elements.
Main profile

An example of the conventional designation of the trapezidal one-row thread with a nominal diameter of 20 mm, step 4 mm and the tolerance of the mean diameter 7e:
TG 20 x 4 -7E
Nominal profiles
outdoor and internal thread

h 3 - the height of the external thread profile; H 4 - the height of the profile of the internal thread; D 3 - the inner diameter of the outer thread; D 4 - the outer diameter of the inner thread; R 1 - radius of roundings on top of the outer thread; R 2 is the radius of twisting in the depression of the outer and internal thread; A C is the clearance on top of the thread.
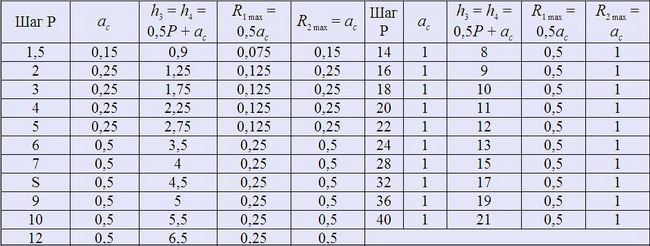
Diameters and steps
Trapezoidal Overcome Thread according to GOST 24737-81





Preferred diameters and steps are indicated in GOST 24738-81. Numerical values \u200b\u200bof tolerances of diameters and steps - according to GOST 9562-81
Diameters and steps
Trapezoidal multisope thread according to GOST 24739-81



Notes:
1. Steps isolated by the frame are preferred.
2. The steps specified in brackets, when developing new designs, it is not recommended.
3. Threads, in which the progress value is labeled *, have an angle of more than 10 o. For these threads, it is necessary to take into account when making a deviation of the profile form.
4. In technical and economically reasonable cases, it is allowed to apply other values \u200b\u200bof the nominal thread diameters according to GOST 24738-81.
5. When choosing a thread diameter, you should prefer the first row of the second.
An example of the conventional designation of the trapezoidal multi-step thread with a nominal diameter of 20 mm, a stroke value of 8 mm, a step of 4 mm and a tolerance field 8E:
TG 20-8 (P4) - 8E
The same left:
TG 20-8 (P4) LH - 8E
The length of swing, if it differs from the length of the thread, indicate in millimeters at the end of the thread designation, for example:
TG 20-8 (P4) LH - 8E - 180
Numerical values \u200b\u200bof swivel lengths related to groups N and L, according to GOST 9562-81.
Landing in the threaded connection denoted by the fraction
TG 20-8 (P4) LH - 8H / 8E - 180
The numeric values \u200b\u200bof the tolerances of diameters D and D 1 - according to GOST 9562-81.
Numeric values \u200b\u200bof diameters D 2, D 3 and D 2 - according to GOST 24739-81.
The use of trapezoidal threads

The trapezoidal thread of the screw is a chassis thread, which has a relatively big friction force, it is insegoing. The advantage for lifting technologies - at rest position does not require additional fixation.
Trapezoidal thread is used to convert the rotational movement to the translational and used, above all, for straight movement. It also finds its use as a driving screw in lathes or as a drive thread for the screw press of tables or vehicle bridges.
Examples of spindle trapezoidal threads:
Movement of feed on machines (for example, adjustment and running screws);
- movement on the manipulator;
- regulation of movement on lifting mechanisms and forklifts;
- the movement of the shutter when locking molding machines;
- movement of moving on assembly containers;
- Vertical movement when working with the press.
Similar documents:
GOST 3469-91 - microscopes. Thread for lenses. Dimensions
GOST 4608-81 - metric carving. Landing with tension
GOST 5359-77 - Thread Ocular for optical devices. Profile and sizes
GOST 6042-83 - Edison Round carving. Profiles, sizes and limit dimensions
GOST 6111-52 - carving conical inches with an angle of profile 60 degrees
GOST 6211-81 - Carving pipe conical
GOST 6357-81 - Cylindrical carving
GOST 8762-75 - a thread round with a diameter of 40 mm for gas masks and caliber to it. Main dimensions
GOST 9000-81 - Metric carving for diameters less than 1 mm. Tolerances
GOST 9484-81 - Trapezidal carving. Profiles
GOST 9562-81 - thread trapezoidal one-income. Tolerances
GOST 9909-81 - carving conical valves and gases for gases
GOST 10177-82 - thread stubborn. Profile and main sizes
GOST 11708-82 - thread. Terms and Definitions
GOST 11709-81 - metric carving for plastics details
GOST 13535-87 - thread resistant reinforced 45 degrees
GOST 13536-68 - Round thread for sanitary fittings. Profile, main dimensions, tolerances
GOST 16093-2004 - Metric carving. Tolerances Landing with a gap
GOST 16967-81 - Metric carving for instrument making. Diameters and steps
GOST 24737-81 - the thread of the trapezoidal one-income. Main dimensions
GOST 24739-81 - Trapezoidal multi-day thread
GOST 25096-82 - thread stubborn. Tolerances
GOST 25229-82 - Metric conical carving
GOST 28487-90 - carving conical cloth for elements of drill columns. Profile. Dimensions. Tolerances
In the mechanisms where it is necessary to convert rotation to the translational movement are used. In addition to its conversion function, this thread can withstand elevated loads. This is a sought-after thread type in important nodes of mechanisms, machines. You can observe the principle of operation of this thread when turning the screws when the rotation of the screw causes it to move in the linear direction. The force applied to convert the motion depends on the corner of the profile, the thread steps and the material material.
Title carving from similarity with a trapezium.
Telephone for communication: Whatsapp.
The main characteristics of the thread trapezoidal
The shape of the trapezium is formed by an angle of the thread profile. In this type, the profile angle may be within 15 - 40 degrees.
In the working process, the thread can cause excessive friction. This factor affect the profile angle, the type of lubricant and the material used. Radial gaps in trapezoidal threads can be revealed, having a thread in the middle of the diameter.
Trapezoidal carving is quite simple in the manufacture. In most cases, an angle of a profile of 30 degrees is exhibited. The quality of the thread depends largely on the accuracy of the used workpiece, as well as the material.


Ways to cut trapezoidal threads
The production of this type of thread can be divided into two categories - one cutter and three incisors.
As an example, consider such a designation: three × 4 LH - the thread of the trapezoidal, one-income, with a diameter 26 and step 4, left.
GOST 9484-81 is used as the main standard.
Thread profile is an equal trapezium with an angle of 30 ° between the sides (Figure 3, B). Trapezoidal thread can be overcome and multigrupp, right and left.
The diameters and steps of the one-income trapezoidal thread in the diameter range from 12 to 50 mm are shown in Table. 2. The same dimensions and the number of occasions for multi-day threads are shown in Table. 3.
Examples of thread designation:
the trapezidal wedding space with a nominal diameter of 36 mm and a pitch of 6 mm:
TGZBHB; The same thread left:
TG 36x6. LH;
trapezidal, three-way with a nominal diameter of 40 mm, step 3 mm and a move of 9 mm:
Tg.40 h.9 (RZ)
Examples of the thread designation in the drawing are shown in Fig. five. W.
Table 2. Diameters and steps of trapezoidal overcoming thread according to GOST 24738 81, mm
| Diameter D. | row | - | - | -" | - | - | ||||||
| - | - | - | - | - ■ | 30, | |||||||
| step | p. | |||||||||||
| r* | 3;8 | 3;8 | 3;8 | 3;8 | 3; 10 | |||||||
| Diameter D. | row | - | - | - - | ||||||||
| - | - | - | - | - | ||||||||
| step | R | 8, | ||||||||||
| R* | 3; 10 | 3;10 | 3;10 | 3;10 | 3;10 | 3;10 | 3;12 | 3;12 | 3;12 | 3; 12 |
Note:1. When choosing a thread, the first row should be preferred to the second;
2. Preferred steps are indicated *.
Tabelle 3. Main sizes of trapezoidal multi-speed threads in accordance with GOST 24739 81, mm
| d. | Pitch thread | Threading with the number of goals | ||||
| Row1 | Series 2. | R | R* | |||
| (8) | ||||||
| - | - | |||||
| - | - | |||||
| - | - | |||||
| ,-. - | - | (16) | (20) | |||
| - | - | |||||
| - | (20) | |||||
| _ | - | |||||
| - | (24) | |||||
| - | - | |||||
| - | (24) | |||||
| - | - | |||||
| - | (21) | (28) | ||||
| - | - | |||||
| _- | (28) | |||||
| ■ - | - | |||||
| - | (32) | |||||
| (24) | (36) | (48) | ||||
| - | - | |||||
| - | (32) | |||||
| - | (24) | (36) | (48) |
Note: Thread, the movement of which is enclosed in brackets, has an angle of lifting more than 10 °.
Thread stubborn.
The main purpose of the thread is the transfer by the axial load screw in one direction, for example, in jacks, presses, etc. Thread profile - non-uniform trapezium (Fig. 3, g).
:\u003e V diameters and steps of thrust threads in the diameter range from 16 to 42 mm are shown in Table. four.
Examples of thread designation: "
stubborn overcome right-hand diameter of 32 mm in 6 mm increments:
the same thread left:
S32X6LH.In the drawing, the thread is indicated as shown in Fig. 6.
Fig. 6.
Table 4. Diameters and steps of thrust thread according to GOST 10177 82, mm.
| Diameter d. | Step | ||
| Row1 | Series 2. | R* | R |
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | 3;8 | ||
| - | 3;8 | ||
| - | 3;8 | ||
| - | 3;8 | ||
| - | 3;10 | ||
| - | 3;10 | ||
| - | 3;10 | ||
| - | 3;10 | ||
| - | 3;10 | ||
| - | 3;10 |
Note ^. When choosing a thread diameter, the first row should be preferred to the second.
Steps that are preferred in the development of new designs.
Pipe cylindrical carving.
This thread is used in cylindrical compounds of pipes and connections of internal cylindrical threads with an outer conical carvings.
Profile (Fig. 3, b) and the main dimensions are set to GOST 6357 81. The values \u200b\u200bof the main sizes of the tubular cylindrical thread are given in Table. five.
The designation of the pipe thread (Fig. 7, a, b) consists of the letter G and the size of the thread in inches, for example:
Designation is conditional, because Indicates the diameter is not a thread, but holes in the pipe (conditional passage DN.with a certain wall thickness). The outer diameter of the tubular thread will be greater than the designated in the drawing. For example, the designation G1.corresponds to a pipe thread having an outer diameter d \u003d 33.25mmi intended for pipes with inner diameter 1 "(25.4 mm).
Pipe cylindrical thread of the same diameter (conditional passage DN)it can be performed on pipes with different wall thickness and even on a solid rod.
Fig. 7. Conventions of pipe cylindrical and conical threads: a) pipe cylindrical thread G 1 1/2;
b) thread of the same size internal, left; c) outer pipe conical carving; d) inner pipe conical
Table 5. Main sizes of pipe cylindrical thread
Details in machines, mechanisms, devices, as well as devices and structures in any way are connected to each other. These compounds perform various functions, and are separated, first of all, into two types: movable and fixed.
Connection is fixed - the connection of parts that ensures the invariance of their mutual position when working. For example, welded, compounds using fasteners, etc. Compound is movable - a compound in which parts have the possibility of relative movement in working condition. For example, a toothed connection.
Fixed and movable connections, in turn, are divided into detachable and dear depending on the possibility of dismantling the connection.
The connection is inconphigible - a compound that cannot be disconnected without disturbing the form of parts or their connecting element. For example, the compound is welded, soldering, riveting, etc.
Connection connection is a compound that can be repeatedly disconnected and uninstalled without deforming neither connected nor fasteners. For example, a threaded connection with a bolt, screw, wedge, key, gear, and others.
This article is devoted to the review of threaded compounds, with a variety of which have to face quite often in everyday life.
Threaded connection - connection of parts with a thread. Everyone knows what carving is all seen it. Many are also known that threads differ among themselves, as they have different sizes, step, and so on. However, not many represent than it is regulated, as well as that there is not only the metric carving of the cylindrical form for us, but also many other types of it.
1. Concept of thread
The thread is called the surface formed during the screw movement of a flat circuit along a cylindrical or conical surface, in other words, a spiral with a constant step, formed on this surface.
Figure 1 - Carving
For the purpose of the threads are divided into fastening (in a fixed connection) and running or kinematic (in the moving connection). Often fastening threads carry second function - seals a threaded connection, ensuring its tightness, such threads are called fastening. There are still special threads that have a special purpose.
Depending on the surface shape, according to which the thread is cut, it can be cylindrical or conical.
Depending on the location of the surface, the thread can be outer (sliced \u200b\u200bon the rod) or inner (sliced \u200b\u200bin the hole).
Depending on the profile form, the thread is triangular, trapezoidal, rectangular, round, special.
Triangular thread is divided into a metric, tubular, conical inches, trapezoid carving - on trapezoidal, stubborn, stubborn reinforced.
The magnitude of the step distinguishes the threads large, small and special.
In terms of the number of kids, the threads are divided into one-going and multisope.
In the direction of the screw line, the thread is the right (thread thread rolls clockwise) and the left (thread thread cuts against a clockwise).
Figure 2, the entire classification of threads is presented in the form of a chart:

Figure 2 - Classification of threads
In addition to the above classification, all threads are divided into two groups: standard and non-standard; In standard threads, all of their parameters are determined by gtos. The main parameters of the thread are defined by GOST 11708-82. These are the so-called standard overall threads. In addition to them, there is a concept of special thread. Special threads are a thread with a standard profile, but differ from the standard diameter sizes or a thread step, and a thread with a non-standard profile. Non-standard threads - square and rectangular - manufactured by individual drawings on which all thread parameters are specified. (More in section 5. Operational purpose of the thread and its application).
3. Profiles and thread parameters
Thread profiles are characterized by the following features:
. Metric carving It has a profile in the form of an equilateral triangle with an angle at the top of 60 °. The protrusions and depressions of the threads dulled (GOST 9150-2002).
Metric carving is cylindrical and conical.

. pipe thread It has a profile in the form of an equally chained triangle with an angle at the top of 55 °. Pipe thread may also be cylindrical and conical.


. conical Inch Thread It has a profile in the form of an equilateral triangle.

Thread inch conical
. Round thread It has a profile in the form of a semicircle.

. Trapezoidal thread It has a profile in the form of an equally trapezium with an angle of 30 ° between the sides.

. Stubborn thread It has a profile not an equally trapezium with an angle of inclination of the working side of 3 ° and non-working - 30 °.

. Rectangular thread It has a profile in the form of a rectangle. Carving is not standardized.

Cutting rectangular non-standard
Thread Parameters
The main parameters of the thread are considered:
Diameter of thread (d) - The diameter of the surface on which the thread will be formed.

Figure 3 - Outer diameter
Pitch thread (P) - distance along the line parallel to the thread axis between the average points of the nearest same side of the sides of the thread profile lying in one axial plane on one side of the rotation axis (GOST 11708-82).
Threaded (PH) - Relative axial movement of a detail with a thread for one turnover (360 °), equal to the product of NP, where N is the number of thread drives. The same thread has a step equal to step. The thread formed by the movement of one profile is called the one-income, formed by the movement of two, three and more identical profiles, is called multisope (two-, three-way, etc.). In other words, on the bolt and the nut simultaneously cut down not one spiral, and two or three. Multi-turn threads are often used in high-precision equipment, for example, in photographic equipment, to uniquely position the position of the parts with mutual rotation. Such a thread can be distinguished from the usual two or three beginnings of turns on the end.

Figure 4 - Thread step and thread
Threads are characterized by three diameters: outer D (D), internal D1 (D1) and medium D2 (D2). The outer thread diameters are denoted by D, D1 and D2, and internal threads in the hole - D, D1 and D2.

Figure 5 - Thread diameters
- the outer (nominal) diameter D (D) is the diameter of the imaginary cylinder, described around the vertices of the outer (D) or inner thread (D). This diameter for most threads is determining and enters the conventional thread designation;
- the average diameter d2 (d2) is the diameter of the cylinder forming which it crosses the thread profile in such a way that its segments formed when crossing the groove is equal to half the nominal thread step;
- the inner diameter D1 (D1,), the diameter of the cylinder included in the depression of the outer (d1) or the vertices of the internal thread (D1).
The construction of the screw surface in the drawing is a long and complex process, therefore, the thread shows conditionally, in accordance with GOST 2.311-68. In accordance with GOST 2.311-68. The thread rod is depicted with solid main lines along the outer diameter and solid thin lines - by internal diameter.

Figure 6 - Example of a thread image on the rod and in the hole
4. Marking thread
The designation of the thread usually includes an alphabetic designation type of thread and the nominal diameter. Additionally, a thread step (or TPI - Threads Per Inch - the number of turns per inch may be given, the number of openings for multi-surcharge, the diameter of the thread hole, the direction (left, right).
Metric carving - with a step and major thread parameters in millimeters. It has widespread use with a nominal diameter of 1 to 600 mm and a pitch of 0.25 to 6 mm. Metric carving is the main fastener thread. This thread is overcome, mainly the right, with a large or small step. The designation of the metric thread includes the letter M and the nominal diameter of the thread, and the major step does not indicate: M5; M56. For threads with a small step, the thread step M5 × 0.5 is additionally indicated; M56 × 2. At the end of the legend, the left threads put letters LH, for example: M5LH; M56 × 2 LH. The thread designation also indicates the accuracy class: M5-6G.

An example of the designation:
M 30 - metric carving with an outer diameter of 30 mm and a large thread rate;
M 30 × 1.5 - metric thread with an outer diameter of 30 mm, a small step of 1.5 mm.
Although metric threads and did not find wide use in compacted compounds, but this possibility is laid in standards. This is a thread metric conical and cylindrical.
Metric conical carving It is performed with a taper 1:16 and a nominal diameter of from 6 to 60 mm according to GOST 25229-82 (ST SEV 304-76). It is intended for self-adequate conical threaded compounds, as well as for compounds of external conical carving with internal cylindrical carvings having a nominal profile according to GOST 9150-2002. The designation of metric conical thread includes the type of thread (the letters of the MK), the nominal diameter of the thread, the thread step. At the end of the conditional designation of the left thread put letters LH.
An example of the designation:
MK 30 × 2 LN - Left metric conical carving with an outer diameter of 30 mm, a pitch of a thread is 2 mm.
Metric Cylindrical Thread (with Profile) Based on metric thread (m) with a nominal diameter of 1.6 to 200 mm and an angle of profile at a top of 60 °. Its main difference in the screw, which has an increased radius of the threads on the thread (from 0.15011p to 0.180424p), which gives a threaded compound based on cylindrical metric threads. Higher heat-resistant and fatigue qualities. The metric cylindrical thread letters MJ is denoted, then the numeric value of the nominal diameter of the thread in millimeters, the numeric value of the step, the tolerance field of the average diameter and the tolerance of the protrusion diameter is.
Internal thread MJ is compatible with external thread M with the coincidence of the nominal diameter and step, i.e., a normal metric screw can be twisted into a nut with such thread.
An example of the designation:
MJ6 × 1-4H6H - Outer thread on the surface of the shaft with a nominal diameter of 6 mm, 1 mm pitch, the tolerance field of the mean diameter 4H and the tolerance of the diameter of the protrusions 6H.
Differences inch thread From the metric in the fact that the angle at the top of the thread is 55 degrees for the BSW British standards (WW) and BSF or 60 degrees (as in the metric) in the American system (UNC and UNF), and the thread step is calculated as the ratio of the number of turns Threads per inch thread length. Compatible metric and inch threads are not possible, therefore, in countries with a metric system, only pipe inch threads are used.
In an inch thread, all the parameters of the thread are expressed in inches (most often indicated by a double stroke per numerical value, for example, 3 "\u003d 3 inches), a thread step in inches (inches \u003d 2.54 cm). For pipe inch thread, the size in inches means not the amount of thread, but the conditional lumen in the pipe, while the outer diameter is actually significantly more. The penette feature is the fact that it takes into account the thickness of the pipe walls, which may be thicker or thinner depending on the material of manufacturing and working pressure on which the pipes are calculated. Therefore, the inch tube thread standard is clear and accepted worldwide as an exception from metric rules.
The diameters of inches threads are not the only parameter that is important when choosing pipes. It must be considered: the depth of the thread, the thread step, the outer and inner diameter, the angle of the thread profile. It is worth noting that the step of the thread in this case is not calculated in inches and not even in millimeters, but in threads. Under the thread is the sliced \u200b\u200bgroove. Therefore, the calculation is based on how many grooves are cut on one inches dimly cut pipe. Let's say, ordinary water pipers have only two types of thread steps: by 14 threads, which corresponds to the metric step by 1.8 mm, and by 11 threads - the metric step in 2.31 mm.
Table 2 shows the main differences in "inch" and "tubular" cylindrical threads with respect to the "metric" thread for the most common sizes of the above-mentioned threads.

Threads, designated * if possible not to apply.
Naturally, such peculiar standards for calculating the diameter and step only make a task in determining the desired values. Therefore, tables were developed to determine the number of threads and pipe diameters if inch threads. In addition, its value and standard always indicate on any packaging. But all the same, the data is approximate in nature, and should never be eliminated by a possible error.

* When determining the size, preference must be given to the values \u200b\u200bof the row 1.
It has a profile in the form of an equally chained triangle with an angle at the top of 55 °, the vertices and the depressions are rounded (GOST 6357-81).

The symbol of the thread consists of the letter G, denoting the nominal diameter of the thread in inches, and the accuracy class of the average diameter. For the left thread, the designation is complemented by LH letters.
An example of the designation:
G 1 1/2-A - pipe cylindrical thread with size 1 1/2 ", accuracy class A;
1 / 4-20 BSP - Pipe cylindrical carving of the cake according to B. S.93 (England).
It has a profile similar to a pipe cylindrical threads. It is possible to connect pipes having a conical thread (taper 1:16), with products having pipe cylindrical threads GOST 6211-81.

The conditional designation of the thread consists of the letters R, the size of the nominal diameter in inches. The designation RC is used for pipe conical internal threads. The legend of the left thread is complemented by LH letters.
An example of the designation:
R 1 1/2 - Carving pipe conical outdoor with size 1/2 ";
R 1 1/2 LH - Carving pipe conical outer left;
RC 1/2 - carving pipe conical internal;
BSPT 1 1/2-Prev Conical Pipe Domestic according to B. S.93 (England).
With an angle of the profile of 60 ° GOST 6111-52, cutting into a conical surface with a taper 1:16.

The designation consists of the letter to the size of the thread in inches with the indication of the dimension, applied on the shelf of the lifting line, as in pipe threads. An example of the designation:
By 3/4 "according to GOST 6111-52. 3/8-18 NPT AnSI / ASME B 1.20.1 (USA) designation.
It serves to transfer movement and effort. The trapezoidal thread profile is an equilibrium trapezium with an angle between the side of 30 °. For each diameter, the thread can be one-going and multiser, right and left GOST 9484-81.
The main dimensions, diameters, steps, the tolerances of the one-time thread are standardized, respectively, GOST 24737-81, 24738-81, 9562-81. For multisope thread, these parameters are located in GOST 24739-81.
The conventional designation of the uniform thread consists of letters that the nominal thread diameter, step, tolerance fields.
An example of the designation:
TH 40 × 6-8E - trapezoidal uniform outdoor thread with a diameter of 40 mm with a pitch of 6 mm; TH 40 × 6-8E-85 - the same twist length of 85 mm;
It is 40 × 6LH-7N - the same for the inner left.
The numerical value of the progress is added to the conventional designation of the multidigar thread:
TR 20 × 8 (P4) -8E - trapezoidal multi-turn outdoor thread with a diameter of 20 mm with a course of 8 mm and a pitch of 4 mm.
It has a non-equal trapezium profile. Profile depressions are rounded, for each diameter there are three different steps. It serves to transmit movement with large axial loads GOST 10177-82.
Stubborn threads are denoted by the letters s, then indicate the nominal diameter of the thread in millimeters, the thread step (stroke and step, if this thread is multi-way), the direction of the thread (for the right thread does not indicate for the left letters LH), and the thread accuracy class.
An example of the designation:
S 80 × 10 - a stubborn thread one-income with an outer diameter of 80 mm and 10 mm pitch;
S 80 × 20 (P10) - a thrust thread two-way with an outer diameter of 80 mm, a course of 20 mm and a 10 mm pitch.
Special thread With a standard profile, but non-standard steps or diameter, designate: SP M40 × 1.5 - 6G.
Rectangular thread (square). Thread with a rectangular (or square) non-standard profile, so all its dimensions are indicated in the drawing. It is used to transmit the movement of severe loaded moving threaded connections. Usually performed on cargo and running screws.
It has a profile obtained by pairing two arcs of one radius. GOST 13536- 68 Determines the profile, the main dimensions and tolerances of the circular thread. This thread is used for spindles of the valves of mixers and toilet cranes GOST 19681-94 and water cranes. There is only one diameter d \u003d 7 mm and step p \u003d 2.54 mm.
An example of the designation:
Cr 7 × 2.54 GOST 13536-68, where 2,54 is a thread step in mm, 12 - a nominal diameter of the thread in mm.
A similar profile has a round thread (but for diameters 8 ... 200 mm) under ST SEV 3293-81, entered into action directly as a state standard. The thread is used for hooks of cranes, as well as under the impact of the aggressive environment.
An example of the designation:
RD 16 - Round thread with an outer diameter of 16 mm; RD 16LH - Round thread with a diameter of 16 mm, left.
5. Operational assignment of the thread and its application
Threaded compounds are widespread in mechanical engineering (in most modern machines, over 60% of all parts have threads). In operating purposes, threads are distinguished general and special, intended for connecting one type of details of a particular mechanism. The first group includes threads:
1.) Fastening - metric, inch used to connect machine parts connected. Their main purpose is to provide a complete and reliable connection of parts at various loads and with different temperature conditions during long-term operation.
2.) Hango or kinematic - trapezoidal and rectangular applied to the running screws, screws of calipers of machine tools and tables of measuring instruments, etc. The main purpose is to ensure accurate movement with the smallest friction, and for rectangular threads also excluding self-evidence under the action of the applied force; Stubborn (in presses and jacks) and round, intended for transformation of rotational motion into straight movement. They perceive great efforts at relatively low movement speeds. Their main purpose is to ensure the smoothness of rotation and high load capacity (for accurate micrometer devices, metric threads of increased accuracy are used). Round thread is widely used for water taps according to GOST 20275-74 and in such elements as mixers, cranes, valves, spindles according to GOST 19681-94 (fittings sanitary and technical water treatment).
3.) Fastening-sealing (pipe and reinforcement) - pipe cylindrical and conical metric inch and conical, used for pipelines and reinforcements, their main purpose is to ensure the tightness of the compounds (excluding shock loads) at low pressures.
Pipe cylindrical threads according to GOST 6357-81 are used on water-gas pipes, parts for their compound (couplings, coolers, crosses, etc.), pipeline fittings (valves, valves, etc.).
The pipe conical thread according to GOST 6211-81 is used in pipe compounds at high pressures and temperatures (in valves and gas cylinders) when an increased tightness of the compound is required.
Referred to the second group, special thread It has a special purpose and applied in separate specialized industries. These include the following:
1.) metric tight thread - thread made on the rod (on the heel) and in the hole (in the nest) at the largest limit sizes; Designed to form threaded connections with tension.
2.) metric carving with gaps - The thread required to ensure the light screwability and the dysfunction of the threaded compounds of parts operating at high temperatures when conditions for setting (splicing) of oxide films are created, which are covered with the thread surface.
3.) hour carving (metric) - thread used in the clock industry (diameters from 0.25 to 0.9 mm).
4.) carving for microscopes - thread, designed to connect a tube with lens; It has two sizes:
4.1) inch - diameter 4/5 "" (20,270 mm) and step 0.705 mm (36 threads per 1 "");
4.2) metric - diameter 27 mm, step 0.75 mm;
5) ocular multisope thread - recommended for optical devices; Thread profile is an equal trapezium with an angle of 60 °.
Operating requirements for threads depend on the purpose of the threaded connection. General for all threads are the requirements of durability and screws without fitting independently made threaded parts while maintaining the operational qualities of the compounds. Summarizing briefly, the main used operational threads can be displayed in the form of the following table:

6. Determination of the size of the thread
As a rule, the carving on different fittings looks like it makes it difficult to visually determine the type of thread. Fitting threads are determined by measuring the basic parameters with a threaded and caliper and comparison of the results obtained with the thread table.

Figure 7 - Measuring Thread Parameters
There are two types of threaders: with brand M 60O - for metric threads with an angle of profile 60o and with brand d 55o - for inch and tube threads with an angle of profile 55o. On each comb of a threader for metric threads, the digit indicates the thread step in mm for inches and pipe threads - the number of steps at a length of 25.4 mm (1 "\u003d 25.4 mm).
7. Signs of threading
The main methods of making threads are:
- cutting them with cutters and combs on lathes;
- cutting with tanks with dies with thread-cutting heads;
- cold and hot rolling with flat or round rolling dies;
- milling with special thread cutters;
- grinding abrasive circles.
The choice of the method of obtaining a thread depends on the type of production of the threads of its accuracy of the workpiece material, etc.

Figure 8 - Thread-cutting tools
1. Cutting threads with cutters. With threaded cutters and comb on tokar-screwing The machines are cut by the threads as an outer and inner (internal thread starting with a diameter of 12 mm and above). The method of cutting threads with cutters is characterized by relatively low performance. Therefore, it is currently used mainly in small-sector and individual production as well as the creation of accurate screws of running screws and so on. The advantage of this method is the simplicity of the cutting tool and the relatively high accuracy of the resulting thread.
2. Carving the threads with dies and ties. Dies in their constructive features are divided into round and sliding. Round dies applied on mounting blanks and other works are designed to cut the outer thread with a diameter of up to 52 mm in one pass. For a larger thread, the dies are used for a special design that actually serve only for stripping the thread after pre-cutting it with other tools. Sliding dies consist of two halves gradually converge in the cutting process. The tap is a steel rod with threads separated by longitudinal straight or screw grooves forming cutting edges. The same grooves serve to exit chips. By the method of use, the taps are divided into manual and machine.
3. Accounting thread. The main industrial method of making threads is currently pumping on special thread-car machines. Detail is clamped in vice. In this case, with great performance, it provides high quality products (sizes and surface roughness). The process of rolling the thread is to create a thread on the surface of the part without removing the chips due to the plastic deformation of the surface of the processed part. Schematically, it looks like this. The part is rolled between two flat dies or cylindrical rollers having a thread profile and a thread of the same profile is squeezed on the rod. The largest diameter of the rolling thread 25 mm is the smallest of 1 mm; The length of the rolling thread is 60 ... 80 mm.
4. Driving a thread. Milling outdoor and internal threads are performed on special threaded machines. In this case, the rotating comb milling cutter during radial feed is crashed into the body of the part and milling the thread on its surface. Periodically, there is an axial movement of the part or cutters from a special copier by an equal thread rate during one parts of the part.
5. Grinding accurate threads. Grinding as a way to create a thread is used mainly to obtain accurate threads on relatively short threaded parts for example, threaded plugs - carbar calibers, etc. The essence of the process is that the grinding circle is located to the part at the angle of lifting the thread with rapid rotation and at the same time Slow rotation of the part with the feed along the axis on the amount of the thread step in one turn is cut (above) part of the surface of the part. Depending on the design of the machine and a number of other factors, the carving is polished for two or four and more passage.
8. Types of foreign threads
The world uses several well-deserved respected standards of countries such as United Kingdom (BS), Germany (DIN), France (NF), Japan (JIS), USA (UNC). The main reasons for their differences between themselves are traditionally different systems of measures and ways to set the size of the threads in different countries as well as special scope of thread. However, over the past century, the Metric Standard ISO - International Organization for Standardization (International Organization for Standardization) has strongly approved its position in the world, which in turn contributed to the mutual understanding of technical specialists.
The most common types of foreign thread include:
- Metric ISO.
- Cork thread (Whitword Thread)
- Trapecledal thread
- Round thread
- Stubborn thread
The presented summary table describes the correspondence of more than twenty types of threads (general-barred oil and gas sorting), and refers to regulatory and technical documents by domestic and foreign regulatory documents this sphere. 




Since the above table 8 gives only a general idea of \u200b\u200bthe abundance of different types of threads and regulating their documents and a large amount of data does not allow to fully compare and compare the threads of domestic and foreign standards. Consider the compliance of various types of triangular threads that are more often found in general engineering.

and couplings to them. Technical conditions »
OST NKTP 1260 "Thread inch with an angle of 55 degrees profile"
 How to return the love of her husband to his wife - Tips of the psychologist
How to return the love of her husband to his wife - Tips of the psychologist Why you can not give icons
Why you can not give icons