Nutrition of a pregnant woman. What should be the diet during pregnancy? Oral face-to-face interview
Since these goals are the normal physiological tasks of the human reproduction process, the changes in the woman's body during pregnancy should be considered as natural and physiological. According to this concept, pregnancy reveals weak links in a woman's body, which can lead to the development of pregnancy pathology. During pregnancy, a woman's body undergoes profound transformations. With the normal development of pregnancy, all the changes that take place in the body of a woman are aimed at creating harmonious ...
Share work on social networks
If this work does not suit you, there is a list of similar works at the bottom of the page. You can also use the search button
State budgetary professional educational institution
Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous Okrug
"Yamal multidisciplinary college"
Department of Natural Science
_______________________
Admitted (a) to the defense
APPROVED
at a meeting of the scientific and methodological council
Protocol No. dated ".."____201.. g
Chairman _______________________
/ G.A. Preobrazhenskaya /
Deputy Director
for academic work
______________________ / V.N. Sarycheva/
Course work
on an interdisciplinary course, a professional module
_______ __________________________________________
_________________________________________________
(the topic of the course work (project)
Speciality ____________________
Student (ka) group No. _____ ________ (full name of the student)
Teacher head _______ (full name of the teacher)
Introduction
Structural and functional changes in the body of a pregnant woman are aimed at achieving the following main goals: - ensuring an adequate supply of the growing body of the fetus with oxygen, nutrients and the evacuation of the products of its vital activity from the body of the fetus; - preparation of the mother's body for the process of childbirth and breastfeeding. Since these goals are normal physiological tasks of the human reproduction process, the changes in the woman's body during pregnancy should be considered as natural and physiological. On the other hand, since all the systems of a woman's body work during this period in a more intense mode, a point of view has recently appeared that considers pregnancy as a kind of "strength test" of the mother's body. According to this concept, pregnancy reveals "weak links" in a woman's body, which can lead to the development of pregnancy pathology. Let's consider these changes in the systems of the body. At the same time, this will make it possible to formulate some preventive measures that prevent the development of pathology in the event that such a system is a “weak link”. Pregnancy is a normal (physiological) process that occurs in a woman's body during fetal development. During pregnancy, a woman's body undergoes profound transformations. With the normal development of pregnancy, all the changes that take place in the body of a woman are aimed at creating a harmonious relationship between the mother's body and the body of the developing fetus. Also, from the very first days of pregnancy, the body of a pregnant woman begins to prepare for future childbirth and breastfeeding.
The role of the nurse in organizing the nutrition of a pregnant woman
Goals:
1. Improve the nutrition system of a pregnant woman.
2. Provision of professional fulfillment of the obligations of a midwife in the nutrition of a pregnant woman.
Tasks:
1. Identify the main causes of malnutrition in a pregnant woman
2. Increase the role of the nurse in organizing the nutrition of a pregnant woman
Relevance:
1. The threat of miscarriage and the peculiarities of nursing premature babies is very relevant today due to the unfavorable demographic and environmental situation in the Russian Federation and the adoption of the presidential program "Children of Russia"
2. The subject of the course work meets the objectives of the national project "Health", aimed at preventing the adverse effects of this pathology in pregnant women
MAIN PART
Chapter I : Changes in a woman's body during pregnancy. Daily routine, nutrition and hygiene of a pregnant woman
- Body systems that undergo changes during pregnancy
From the very first days of pregnancy, the body of a pregnant woman undergoes profound transformations. These transformations are the result of the coordinated work of almost all body systems, as well as the result of the interaction of the mother's body with the child's body.
1.2 Changes in body weight
Undoubtedly, one of the most noticeable changes in a pregnant woman is a change in body weight. By the end of pregnancy, a woman's weight increases by about 10-12 kg. This value is distributed as follows: fetus, placenta, membranes and amniotic fluid approximately 4.0 4.5 kg, uterus and mammary glands 1.0 kg, blood 1.5 kg, intercellular (tissue) fluid 1 kg , increase in the mass of adipose tissue of the mother's body 4 kg. Obviously, such an increase in the weight of the woman herself, as well as the process of development and growth of the body of the fetus, place increased demands on the nutrition of the pregnant woman. Along with an adequate intake of proteins, fats and carbohydrates, it is usually recommended to supplement the woman's diet with iron preparations (necessary for the synthesis of maternal and fetal red blood cells), vitamins and calcium preparations (building the fetal bone skeleton). The question often arises - what weight gain should be considered normal, and what is excessive? It all depends on the initial weight of the woman before pregnancy. And not so much on weight, but on the ratio of weight and height, expressed by the so-called body mass index (BMI). BMI is calculated using the formula: BMI \u003d Weight (kg) / Height2 (m 2) So, for example, for a woman weighing 60 kg and 1.6 m tall, this index will be 60 / 1.62 = 23.4 kg / m2. Women with an index from 20.0 to 26.0 are considered proportionately built. If the index exceeds 26.0, then these are women with signs of obesity, and if the BMI is less than 20.0, then they are women. 5
there is a nutritional deficiency. Approach to weight gain in pregnancy
depending on BMI following. Significantly greater weight gain is allowed in undernourished women than in normal-nourished women (eg, weight gain of 15-18 kg should not be considered pathological in them). The approximate estimated value of weight gain during pregnancy for women with a normal physique is 10-12 kg. And for women with signs of obesity, weight gain should be less than for women in the two previous groups and not exceed 10 kg. Women who smoke during pregnancy have less overall weight gain than non-smokers. This weight deficit is mainly formed due to a smaller increase in the weight of the fetus, placenta and amniotic fluid. Children born to smoking mothers weigh 250 g less than non-smoking women, which directly indicates the obvious negative effect of smoking on intrauterine development of the fetus.
1.3 Respiratory system
An increase in the concentration of the pregnancy hormone progesterone in the blood leads to additional relaxation of the smooth muscles of the bronchial wall and an increase in the airway lumen. Increasing requirements for the supply of oxygen to a growing fetus is expressed in an increase in tidal volume (the amount of air inhaled in one respiratory movement) and respiratory rate per minute. This leads to an increase in the so-called "minute ventilation" indicator by 30-40%, which significantly covers the oxygen demand of the pregnant woman's body increased to 15-20%. The fetal requirement is approximately 30% of the total increase in oxygen consumption of the body of a pregnant woman. An additional 10% falls on the needs of the placenta, and the rest goes to cover the increased work of the woman's body systems due to pregnancy.
1.4 A few words about diet
Taking into account the changes in motility mentioned above and the direct mechanical pressure on the digestive organs by the growing uterus, frequent fractional meals are considered the most rational for a pregnant woman. It is advisable to have approximately 6 meals per day. Given that the body of the fetus is formed mainly from proteins, these food components play a special role in the diet of a pregnant woman. In the gastrointestinal tract of a pregnant woman, proteins are broken down, digested and absorbed. It should be noted that amino acids, the elementary components that make up proteins, are absorbed. The source of amino acids in the body of the mother and fetus can be proteins of a very different nature. These are primarily proteins of animal origin: lean meat (beef, pork), poultry meat. Fish is very useful, especially fatty varieties of sea fish containing omega-3 fatty acids, which play a positive role in the prevention of preeclampsia. An important source of protein is eggs, milk and dairy products. Proteins of plant origin (nuts, soy) are very useful for the mother and the unborn child. In addition to significant nutritional value, proteins have another important property. It has been shown that proteins somewhat slow down the absorption of carbohydrates from food, the main energy substrate for a growing organism. Due to this property, proteins smooth out sharp peaks in the increase in the concentration of glucose in the mother's blood after a meal and make the concentration of carbohydrates in the blood of a pregnant woman more stable,
1.5 Nutrition during pregnancy: by week and trimester
Happiness, agonizing expectation, anticipation and even fear all these feelings inevitably accompany pregnant women. And it is very important during this period not to surrender to emotions, but to remember the responsibility, which is also an integral part of it. It is at this time that the most important is the observance of the basics of a healthy lifestyle. Almost all of them apply to pregnancy, although some require minor changes.
Pregnant woman: proper nutrition
Proper nutrition during pregnancy is most relevant, since it is on what a woman eats that largely depends on how her child will develop. For example, whether a pregnant woman receives enough protein depends on whether the child will have enough building material. Protein nutrition for pregnant women this is very, very important.
In addition, many products have the most detrimental effect on the condition and development of the child, and on the well-being of the mother. Of course, such products must be abandoned. It makes sense to take into account one important feature: proper nutrition in early pregnancy will be somewhat different from the diet of a pregnant woman in the last weeks.
Not everyone understands where such differences come from, but understanding the topic will be quite simple. Judge for yourself, important systems of the body are laid in the early stages, but the size of the fetus increases
slightly. Therefore, in the early stages, a healthy diet for pregnant women
women is based on sufficient intake of minerals, vitamins and the like.
In the second trimester of pregnancy, nutrition should focus on increased protein intake, since it is now that the active growth of the child and its internal organs begins. All this requires a building material, that is, protein.
Nutrition in the third trimester of pregnancy is, first of all, vitamins and minerals that are necessary for the development of the internal systems of the child's body, especially calcium for bone growth and the development of the nervous system.
When planning a pregnancy, proper nutrition is also very important. The more healthy, hardy, strong the woman's body at the time of conception, the greater the chance of successfully fixing the fetal egg in the uterus. And a certain set of vitamins in the body contributes to the proper development of the embryo.
As you can see, the difference in recommendations for proper nutrition of pregnant women by months, and sometimes even by weeks, is quite justified. However, there are, of course, general rules for proper nutrition during pregnancy, so they will be discussed further.
General principles of proper nutrition during pregnancy
First of all, it is worth remembering one simple thing: it is better to get up from the table slightly hungry than with a heaviness in the stomach from overeating. In this regard, it is better to adhere to the principles of fractional nutrition altogether: eat less, but more often. The ideal option would be to eat 5-6 times a day. You need to eat the last time 3 hours before bedtime. Later, eating is highly discouraged, if the feeling of hunger is unbearable, you can drink a glass of milk or kefir, eat an apple or a pear. It is this diet for pregnant women that will be most optimal.
A pregnant woman eats an apple: fruits are part of proper nutrition during pregnancy
Proper nutrition during pregnancy, like, in fact, any proper nutrition, involves the rejection of junk food.
Food for pregnant women should be as fresh as possible, should not contain preservatives, excess salt and the like.
Obviously, canned foods, various sausages and other long-term storage products, if they are not banned, then require strict control of their use.
Of course, it is recommended to give up fast food. However, it is worth noting that if the choice arises to remain hungry or eat something not very healthy, it is better to choose the latter. A pregnant woman should not starve. Another thing is, if you get suspiciously often before such a choice, then you should think about carrying fruit or sandwiches with you.
Of great importance is the balance between such important components of nutrition as proteins, fats, carbohydrates, as well as vitamins and minerals. Of course, a balanced diet for pregnant women at different times implies a different balance of these components, the fact itself remains unchanged.
Meals by week
1-3 weeks of pregnancy
Gynecologists count pregnancy not from the day of conception, since it is almost impossible to calculate it, but from the first day of the last menstruation. Therefore, the first 2 weeks of the obstetric gestation period falls on the time before conception.
Pregnancy planning is an extremely important period, on which, whatever one may say, the health of the unborn child and the absence of any complications during pregnancy depend. And so it turns out that
Proper nutrition before pregnancy is of paramount importance.
At this stage, it is very important to increase the amount of folic acid. Often doctors recommend drinking it in capsule form, but it is much better to get all the vitamins from normal food. Folic acid is found in leafy greens, lettuce, and grains.
It is equally useful to consume yellow fruits and vegetables. But it is better to refuse fatty and sweet foods. This will avoid problems with obesity, as well as reduce the risk of early toxicosis.
Pregnant woman prepares fruit smoothie for proper nutrition
Approximately on the 10-14th day of the cycle, fertilization occurs and the movement of the fetal egg begins towards the uterus. From this time on, we can talk about the onset of pregnancy.
3 week
Nutrition at the beginning of pregnancy is a very complicated topic, since literally every week new organs and systems appear in the fetus, which means that the need for vitamins and nutrients is constantly changing.
In the third week of pregnancy, the egg is implanted and the placenta begins to develop, as well as the fetal membrane. For their full development, calcium is needed, which is found in milk and dairy products, broccoli, green vegetables and fruit juices; and manganese, it can be obtained from turkey and pork, almonds, oatmeal, eggs, raisins, bananas, carrots and spinach.
4 week
For 4 weeks, the nutrition remains the same as for 3, but at this time it is especially important to give up coffee. However, drinking this, of course, tasty, but not very healthy drink during pregnancy is with extreme caution. Especially coffee is contraindicated in the evening. As you can see, proper nutrition in the first month of pregnancy is not too difficult. Further it will be a little more difficult.
5 week
As a rule, at about this time, toxicosis of pregnant women begins. To alleviate this condition, you can slightly change your daily menu. So, meat and eggs, as well as other animal proteins, can be replaced with nuts, soy and other legumes. Instead of milk, you can eat yogurt and cheese. It will not be superfluous to introduce carrots, mangoes, apricots into the diet.
6 week
Toxicosis is in full swing, so the morning should start with crackers or unsweetened crackers. It is better to eat them immediately after waking up, without getting out of bed. At this stage, it is better to drink plenty of fluids, at least 8 glasses a day. At night, you can eat a handful of raisins.
7 week
At this time, problems with the intestines may arise. Therefore, you should avoid foods that promote gas formation, including cabbage. It will not be superfluous to refuse those products that are attached. It is better to introduce prunes, fresh kefir and the like into the diet.
Kefir: an element of proper nutrition during pregnancy
8 week
Ginger tea will help to cope with toxicosis, and do not forget about nuts.
9-10 weeks
Opt for whole grain cereals and whole grain breads. Brown rice is better than white. In general, the body of a pregnant woman at this stage requires quite a lot of fiber.
11-12 weeks
The first trimester of pregnancy is coming to an end, and nutrition at this time should be special. This is the most difficult time, and it is very important to listen to yourself, to your body. If you want to eat a particular dish, then it is precisely those substances that are contained in it that your baby is lacking. Of course, you shouldn't go to extremes.
13-16 weeks
Nutrition in the 2nd trimester during pregnancy is characterized, as already mentioned, by abundant protein intake. In addition, it is necessary to increase the total daily caloric intake of food. If in the first trimester it will be enough to eat 2400-2700 kcal, then from now on you need to eat 2700-2900 kcal.
16-24 weeks
Nutrition at 6 months of pregnancy should contribute to the development of the child's vision and hearing. That is, you need vitamin A and betacarotene. At this time, it is better to eat cabbage, yellow peppers, carrots. Keep in mind that vitamin A is absorbed only with fats.
24-28 weeks
It is at this time that fractional nutrition becomes especially relevant. The uterus is actively growing, taking up more and more space in the abdominal cavity, and begins to put pressure on the stomach. Accordingly, the stomach becomes smaller, and it is difficult for him to accommodate a large amount of food. Even when eating small meals, a pregnant woman may be bothered by heartburn. It is better to give up carbonated drinks and coffee, they also provoke heartburn. In general, the nutrition of a pregnant woman in the third trimester should be as diverse as possible, as the needs of the baby grow.
Food: nutrition during pregnancy by week
29-34 weeks
At 8 months, bones are actively growing and teeth are being laid, therefore, it is very important to eat as many calcium-containing foods as possible. For brain development, fatty acids are simply necessary, and it is they that contribute to the absorption of calcium. Iron deficiency at this time can lead to the development of anemia, both in the mother and in the child. Fatty fish, nuts, red meat, dark green vegetables and seeds are the foods to eat during this period of pregnancy.
35-40 week
Nutrition at the 9th, last month of pregnancy should contribute to the overall strengthening of the mother's body. After all, she has a very difficult and time-consuming job ahead of her - childbirth. The main source of energy in the body are carbohydrates, and it is their consumption that should become the basis of the nutrition of a pregnant woman before childbirth. Cereals and vegetables these are the foods that you should eat during this period.
That's all that can be said about trimester nutrition. An example of dinner, breakfast or lunch for pregnant women may also be useful.
A sample menu for the day might look like this:
The first meal: black bread toast, a small piece of butter, a chicken egg, a glass of kefir;
Second meal: Green salad, a glass of tea;
Third meal: Chicken fillet, boiled potatoes, one pear, a glass of kefir or drinking yogurt;
Fourth meal: Toast with jam or butter, a glass of juice;
Fifth meal: Brown rice, boiled fish, vegetable salad, tea;
Sixth meal: a glass of kefir or a small fruit.
Special nutrition for pregnant women
But this is not all the nutritional features of pregnant women. In some cases, women develop pathologies during pregnancy that require special nutrition. So, with anemia in pregnant women, special nutrition is simply necessary. With such a disease, it is very important to increase the intake of foods containing iron.
In addition, it is important not only to know which foods to use, but also in what combinations, as this affects the absorption of iron in the human body. A woman experiencing pregnancy anemia should consult a doctor not only about medication, but also about an appropriate diet.
1.6 Nutrition for pregnant women
What are the basic principles of rational nutrition of a pregnant woman?
Rational nutrition contributes to the normal development of pregnancy, the fetus, and is also a prevention of the development of large fetuses, which significantly complicate the course of pregnancy, childbirth, the postpartum period, neonatal and postnatal development of newborns.
In the first half of pregnancy, a special diet is not required. Food should be varied, containing a sufficient amount of proteins, carbohydrates, fats, salts and vitamins. In the first months of pregnancy, spicy and salty dishes are not excluded, if necessary, in the second half, mainly dairy and vegetable food is recommended. Meat and fish should be consumed 3-4 times a week. Spicy and spicy foods are prohibited, carbohydrates, flour products, starch and liquid are limited within reasonable limits.
What amount of proteins, fats, carbohydrates and trace elements should be in the daily diet of a pregnant woman?
The amount of proteins and fats is introduced into the daily diet at the rate of 1.52 g per 1 kg of a woman's body weight. Carbohydrates, as the main energy material and source of fat formation, should be no more than 500 g per day (in case of obesity, the amount of carbohydrates decreases to 300-400 g per day). For the prevention of late toxicosis of pregnant women, salt in the second half of pregnancy should be limited to 5 g per day, liquid to 11.2 lavas in the last weeks to 0.8 liters per day. The number of trace elements, the sources of which are milk, cottage cheese, eggs, liver, meat, bread, nuts, buckwheat and barley groats, beets, peas, in the second half of pregnancy should be: calcium 1.52 g, phosphorus 2 g, magnesium 0.5 g, iron 15 20 mg per day.
What is the importance of vitamins for a pregnant woman?
In the diet of a pregnant woman, vitamins are especially necessary, which are part of a number of enzymes and perform the function of catalysts for metabolic processes in the body. With a lack of vitamins entering the body of a pregnant woman with products of dairy and vegetable origin, ready-made dosage forms should be prescribed.
What is the significance and daily requirement of vitamins A, PP, C, E for a pregnant woman?
Vitamin A (carotene) affects the uterine mucosa, promotes its regeneration, which is especially important in the postpartum period. Daily dose 5000 ME, in the last months of pregnancy 1000020000 ME.
Vitamin PP (nicotinic acid) is involved in the metabolism of sex hormones, in small concentrations it has a depressing effect on the contractile function of the pregnant uterus. Daily dose 1825 mg.
Vitamin C (ascorbic acid) a powerful catalyst for redox processes in the body, potentiates the action of estrogens, enhances the effect of pituitrin and mammophysin on uterine contraction. Daily dose 100200 mg.
Vitamin C is involved in the regulation of calcium and phosphorus metabolism, is used in obstetric practice to prevent rickets in the fetus. Daily dose 1000 ME.
Vitamin E (tocopherol) plays an important role in the normal course of pregnancy (fertility vitamin), its deficiency leads to dysfunction of the genital organs, sometimes to fetal death and miscarriage. Daily dose 2025 mg.
What is the importance and daily requirement of B vitamins for a pregnant woman?
Vitamin Bj (thiamine) is involved in the regulation of estrogen hormone metabolism, the synthesis of acetylcholine, promotes proper metabolism in the nervous system, liver, and regulates water-salt metabolism. Daily dose 1020 mg.
Vitamin B2 (riboflavin) contributes to the normal course of pregnancy and childbirth, is used to prevent threatening abortion, enhances redox processes in the body. Daily dose 23 mg.
Vitamin B6 (pyridoxine) is essential for the metabolism of essential amino acids (histamine and tryptophan). Daily dose 5 mg.
Vitamin B12 (cyanocobalamin) is effective in anemia caused by diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and liver, enhances the release of growth hormone. It is used for fetal hypotrophy. Daily dose 0.003 mg
1.7 Rational nutrition of pregnant women
Pregnancy is the most crucial period of a woman's life, and childbirth is a kind of test of the functional and physical state of her body. During pregnancy, a number of physiological functions change due to the restructuring of the activity of the entire woman's body.
The body of the mother and fetus in the early stages of pregnancy is sensitive to the influence of various factors of the external and internal environment. There is a restructuring of metabolic processes, the body's need for plastic and energy material increases. This is due to the fact that the body of the future mother should provide the best conditions for the life of the fetus.
Early pregnancy (up to 12 weeks) may be accompanied by various disorders in the digestive organs (nausea, vomiting, salivation, dermatoses). These are toxicoses (gestoses) that occur during pregnancy and are associated with the development of the fetal egg.
There are also several forms of late toxicosis of pregnant women: dropsy, hypertension, hypotension, nephropathy of pregnant women, preeclampsia and eclampsia. Sometimes pregnancy occurs against the background of concomitant diseases, i.e. those diseases that a woman had before
pregnancy. These are various cardiovascular diseases,
respiratory systems, liver, kidneys, etc. In addition, in the second half of pregnancy, when the uterus increases in size and raises the diaphragm, displacing the abdominal organs, there is an additional burden on the cardiovascular, respiratory, digestive and other systems.
So, from the second half of pregnancy, the stomach turns around its axis and shifts upwards and backwards, its ability to stretch decreases, the muscles of the walls relax, which leads to a violation of the ability to move food into the intestines. The function of the digestive glands is often reduced; the amount of gastric juice and hydrochloric acid decreases, lethargy of the intestinal walls, weakness of peristalsis develops. Constipation, hemorrhoids, swelling of the rectum appear, gases can accumulate, which causes discomfort and disruption of the digestion process, mainly carbohydrates, and the exchange of individual vitamins.
All this requires careful monitoring of the course of pregnancy and the development of the fetus, the appointment of a woman with a balanced diet and timely treatment of concomitant diseases and possible complications.
Rational nutrition is one of the main conditions for a favorable course and outcome of pregnancy and childbirth, ensuring the normal development of the fetus and newborn.
Rational nutrition is a properly organized and timely supply of the body with well-cooked and tasty food containing the optimal amount of various nutrients necessary for its development and functioning. Food in the body of a pregnant woman performs both building (plastic) and energy functions. In the process of digestion, the complex components of food are broken down and absorbed into the blood through the walls of the intestine, the blood delivers nutrition to all cells of the body of the mother and fetus. As the fetus grows, the need for
nutrients increases, at the same time the body of pregnant women
can absorb far from all food, due to the above features of the function of the digestive system. It has been proven that malnutrition at different stages of pregnancy has a different effect on the condition of the fetus. Thus, starvation and an insufficient amount of protein and vitamins in the pre-implantation period causes the death of the embryo, during the period of organogenesis it can contribute to deformities in the development of the fetus.
Violation of the qualitative composition of the diet, in particular, a change in the content of proteins, fats, carbohydrates in it towards the predominance of carbohydrates and fats, can lead to overweight women. With an excess of body weight above 15 kg, in 15% of cases, there is a weakness in labor activity, prolonged pregnancy and a large fetus, which complicates childbirth and the postpartum period, since there is a higher percentage of childbirth operations, birth traumatism of the mother and fetus.
Rational nutrition during pregnancy will also contribute to normal lactation and to ensure the sufficient quantity and quality of breast milk necessary for the child.
One of the most important indicators of rational nutrition of a pregnant woman is the increase in body weight. By the 40th week of pregnancy, body weight gain consists of fetal weight (approximately 3200 g), placenta weight (650 g), amniotic fluid (800 g), enlarged uterus (900 g). Body weight increases during pregnancy by an average of 910 kg (with tolerances of + 3.0 kg). An increase in body weight over 2 kg per month is undesirable, because it indicates the possibility of edema or metabolic disorders.
During pregnancy, the expenditure of muscle energy is significantly reduced, women are transferred to lighter work, are on maternity leave, that is, they belong to groups I and II of labor intensity, in some cases, to group III (medium physical labor).
The general principles of preparing a diet for pregnant women are that the nutrition of a pregnant woman should be differentiated in
depending on body weight, geographical conditions, time of year, term
pregnancy and household habits, as well as the nature of work. The diet for women of average height (155165 cm) and average weight (5565 kg) should be from 2700 to 2900 kcal per day. The calorie content of the required diet can be calculated individually. To maintain weight during an average work activity, 50 kcal is required for every kilogram of body weight. So, with a height of 155 cm, a normal weight of 53 kg, 50 kcal x 53 kg = 2650 kcal is required per day. In the second half of pregnancy, the woman's body's need for energy rises to 2900 kcal, and in working conditions - up to 3300 kcal.
In the first half of pregnancy, a woman's diet should not differ significantly from her usual diet, she can eat everything that suits her tastes, but foods that irritate the kidneys (smoked meats, garlic, horseradish, pepper) should be avoided. It should be remembered that in the first trimester the fetal organs are laid down, therefore during this period it is especially important to ensure sufficient intake of complete proteins, vitamins and microelements in the optimal amount and ratio.
The chemical composition of food
Squirrels. This is the main plastic material for building fetal tissues, the synthesis of hormones and enzymes in the mother's body. Not only the quantity but also the quality of proteins matters. The usefulness of a protein is determined by the content of essential amino acids in it, that is, those that are not produced in the human body, but come only with food. All the amino acids necessary for a person are part of the proteins contained mainly in animal products (meat, fish, eggs, milk, etc.). And these products should make up at least 60% of the diet of pregnant women. The main amount of protein is consumed in the form of milk protein casein with the addition of meat and fish proteins.
From the 4th month of pregnancy, you need 1.3 g of protein per 1 kg of body weight per day (average 110120 g). Especially recommended are cottage cheese, kefir, milk, boiled meat and fish, mild cheeses. These products contain not only easily digestible proteins, but also essential amino acids and calcium salts.
Protein for pregnant women is also necessary for the growth of the uterus, placenta, increase in blood mass and mammary glands. Insufficient protein nutrition leads to a change in the biochemical composition of the blood and can contribute to a delay in the development of the fetus, a decrease in the weight of its body, brain, liver and heart, spontaneous abortions, and premature births.
Fats. Like proteins, they are involved in the structure of body cells, are a source of energy and carriers of a number of vitamins. They are necessary for the normal absorption of certain vitamins (A, D, E) and mineral salts (calcium, magnesium) by the body. Part of the fat is deposited in the liver, placenta, in the mammary glands. Fat intake during pregnancy should be somewhat limited (no more than 90 g, or 1.5 g per 1 kg of weight per day). The main type of animal fat during pregnancy is fresh butter, cream, sour cream, cheeses. It is also necessary to consume daily 2530 g of vegetable oils (sunflower, olive, corn), which contain a number of vitamins. It must be remembered that overweight women also need fat, but in a smaller amount (7080 g).
Carbohydrates. These are organic compounds made up of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. They are part of plant products vegetables, cereals, fruits in the form of sugars, starch, fiber. Over half of the energy necessary for the life of the body, a person receives in the form of carbohydrates. An increase in carbohydrate intake, especially sucrose, is one of the factors leading to female obesity and an increase in fetal weight. With food, a woman should consume 350400 g of carbohydrates per day, and with an excess of body weight - 250300 g. The source of carbohydrates should be: wholemeal bread, potatoes, vegetables, fruits, buckwheat, oatmeal.
In winter, you can use apple, plum, tomato juices, frozen fruits. Juices prepared at home are not recommended, because if they are not prepared correctly, alcohol is formed in them, which is categorically contraindicated for a pregnant woman. The total amount of sugar should not exceed 45 g per day, and in the second half of pregnancy, the consumption of confectionery, jams, sweets should be limited, because they cause increased fermentation in the intestines, peristalsis. This is especially important for women with recurrent miscarriages, because they often have high blood sugar, and glucose easily crosses the placental barrier and enters the fetus.
Liquid. Water, together with minerals dissolved in it, makes up the internal environment of the body, being the main part of plasma, lymph, and tissue fluid. Water exchange at pregnant has a number of features.
The body's daily need for fluid is about 35 g per 1 kg of body weight, i.e., about 2 liters. The amount of fluid consumed by pregnant women ranges from 23 liters per day. It must be remembered that a significant part of the water is contained in food. Therefore, with a rational diet, liquid in the form of tea, milk, soups, etc. should be no more than 1.2 liters.
Excessive fluid intake leads to its retention (the average amount can be 8 liters, and about 6 liters fall on the share of the fetus, placenta, uterus, increased amount of blood), and in the last months of pregnancy increases the load on the cardiovascular system, causes swelling of pregnant women, therefore, it is advisable to limit its use to 0.8 liters, in combination with a low-salt diet.
Vitamins. With a lack of vitamins, various complications of pregnancy occur (miscarriages, premature births). Without vitamins, enzymes are not formed, and therefore, normal metabolism is disrupted, blood formation suffers, and the body's resistance to infections decreases.
During pregnancy, the need for vitamins almost doubles.
In winter, it is very important to use carrots (preferably raw with sour cream or butter).
Synthetic preparations can be used as an additional source of vitamins in the winter-spring period.
Vitamins are found more in plant products: vegetables, fruits, root crops, berries. Some vitamins (B, PP, K and D) are formed in the human body under the influence of intestinal microflora, D in the skin under the influence of ultraviolet radiation.
Long-term use of antimicrobials, as well as diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, can lead to hypovitaminosis, despite their rational introduction with the diet.
Vitamin A (retinol) promotes the growth of all cells and tissues of the body, ensures normal growth of the skin, hair, skeleton, takes part in fat metabolism, in the act of night vision. Vitamin A is heat stable and is better absorbed with fats. It is important in the prevention of abnormal development of the placenta and postpartum infections. In the last 2 months of pregnancy, it should be included in the diet in an increased amount. The richest in vitamin A: the liver of fish and animals, eggs, butter, milk, carrots, pumpkins and other vegetables. But for better absorption, vegetables should be consumed in a slightly stewed form with vegetable oil. Its daily dose is 1.25 mg, and at the end of pregnancy 1.5 mg.
Vitamins of group B take part in the processes of growth and metabolism, especially protein and carbohydrate, contribute to normal hematopoiesis. With a lack of one of the vitamins of this group or the entire complex, the activity of the nervous system and the gastrointestinal tract is disrupted. The main source of vitamins of this group are almost all vegetable and dairy products. There are many of them in brewer's and baker's yeast, meat, liver, especially in the germs and shells of grains, in wholemeal flour, cereals (except barley and polished rice).
B1 (thiamine) its deficiency is accompanied by increased fatigue, loss of appetite, damage to peripheral nerves, a sufficient amount improves the secretory and motor function of the stomach. Source liver, meat, yeast, wholemeal bread.
B2 (riboflavin) affects the function of the liver, vision, is involved in the metabolism of carbohydrates, fats, proteins. With its lack, dysfunction of capillaries and blood flow is possible.
B5 (calcium pantothenate) is involved in metabolism. A rich source of it are yeast, bran, liver.
Bg (pyridoxine) is involved in the cellular metabolism of amino acids, carbohydrates, fats. Found in bread, beans, yeast, beef, egg yolk.
B12 (cyanocobalamin) is involved in the formation of a number of amino acids (methionine, etc.) and ribonucleic acids. Its source is the liver, kidneys, heart, egg yolk, buckwheat. A lack of vitamin B13 contributes to the development of anemia.
B15 (calcium pangamate) increases the absorption of oxygen by tissues, the content of glycogen in muscles and liver, reduces the effects of hypoxia in the body. More of it is found in the seeds of plants, the liver.
B (folic acid, folacin) anti-anemic vitamin. Its source is beans, yeast, leafy vegetables, beef liver.
Vitamin C (ascorbic acid) activates the activity of enzymes and hormones, the growth of bones, cartilage, increases blood clotting, prevents swelling, increases the body's resistance to infections, strengthens the walls of capillaries. Vitamin C is found in black currants, rose hips, citrus fruits, greens, fruits, potatoes, cabbage, tomatoes and other foods. In the winter-spring period, its dosage increases, and the amount in food decreases by the end of their storage, therefore, during this period, it is advisable to take additional vitamin C in tablet forms.
Vitamin P has a lot in common with vitamin C.
In plant nature, a large number of substances with P-vitamin activity have been identified, all of which have received the general name of bioflavonoids. Their main role is capillary-strengthening action and reducing the permeability of the vascular wall. They enhance the effect of vitamin C. Vitamin P is found in chokeberry, rose hips, black currants, carrots, beets, salads, sweet peppers, etc.
Vitamin PP (nicotinic acid) participates in the reactions of cellular respiration, improves the function of the pancreas and liver. Nicotinic acid, a participant in the tissue metabolism of the brain, normalizes inhibitory-excitatory processes in the central nervous system. Partial deficiency of vitamin PP in the body can be due to diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and with prolonged use of antibiotics, sulfanilamide. This can cause headaches, insomnia, impaired attention, memory. Contains nicotinic acid in yeast, nuts, beans and grain products, veal, beef, potatoes.
Vitamin E (tocopherol) reproduction vitamin, affects the normal course of pregnancy, prevents miscarriages, premature births. A close relationship of vitamin E with the function of the gonads, pituitary gland and other endocrine glands has been established. If there is no vitamin E in the body of a pregnant woman, the metabolism is disturbed and the resulting poisonous products can cause fetal death and spontaneous abortion. Tocopherol is found in butter and vegetable oils, egg yolk, wheat germ, corn, buckwheat and oatmeal. Its daily dose during pregnancy increases from 10 mg to 20 mg.
Vitamin D D2 (calciferol) antirachitic vitamin. It plays an important role in phosphorus-calcium metabolism, in the osteoplastic processes of the fetus, in the function of the reproductive system, and contributes to the maturation of full-fledged germ cells. Vitamin D is found in egg yolk, caviar, cod liver, fish oil, milk, butter. But, mainly, it is formed in the skin when exposed to solar radiation. In the last months of pregnancy, especially with a lack of sunny days, the dose should be 600800 units (ME).
An overdose of this vitamin is also harmful, because it has a toxic effect: body weight decreases, early ossification of the fetal skull occurs, calcium is deposited in a number of organs and vessel walls.
Vitamin K contributes to normal blood clotting, strengthens the walls of blood vessels, and prevents hemorrhages. Contained in lettuce, spinach, milk, eggs.
Table 14.1 Vitamin requirements of pregnant women
Vitamins, units rev. Need
Thiamine, mg 1.7
Folacin, mcg 600
Riboflavin, mg 2.0
Niacin 19 mg
Pyridoxine, mg 2.0
Ascorbic acid, mg 70
Cyanocobalamin, mg 4.0
Tocopherol, ME 15
Retenol, mg 1.25
Calciferol, ME 500
Equally important is the provision of a woman's body with the necessary amount of macro- and microelements. Excess and lack of them adversely affects the body of the mother and fetus. Salts are necessary for building the skeleton of the fetus, blood and other tissues. The most important are salts of sodium, calcium, potassium, phosphorus, iron, magnesium, copper, cobalt, zinc.
Calcium is important for building bone and cartilage tissues of the fetus. The need of the female body for calcium during pregnancy increases to 1100 mg per day.
If the increased need for calcium is not covered by its content in the diet, then the fetus provides for itself at the expense of the mother's body, which leads to its deficiency in the pregnant woman and can cause osteoporosis of the pubic bones (during childbirth, the threat of symphysitis and divergence of the pubic joint), teeth are affected etc.
A valuable source of calcium are milk, cottage cheese, lactic acid products, egg yolk. The absorption of calcium salts depends on the provision of the body with vitamin D and phosphorus.
Phosphorus is involved in the formation of fetal bone tissue. During pregnancy, the need for phosphorus (1500 mg per day) increases by 5060%, and the ratio of calcium and phosphorus in the diet should be 1:1.5; 1:2. A pregnant woman needs a daily intake of 1.52.0 g of phosphorus (in the composition of dairy, meat and fish products). There is a lot of phosphorus in nuts, beans, oatmeal and buckwheat.
Iron. A woman's need for iron increases and amounts to 20 mg per day. Iron, copper, cobalt take part in hematopoiesis and oxidative processes. Pregnant women are prone to developing iron deficiency anemia. You can prevent it or reduce its severity with the help of a balanced diet, including the liver, kidneys, tongue, apples, apricots, plums, lettuce in the diet.
Cobalt, which is included in vitamin B12, in combination with copper and iron, is involved in oxidative processes and in hematopoiesis.
Copper, zinc. With their deficiency, protein deficiency occurs, the weight of the fetus may decrease, newborns are born with edema.
Magnesium is contained in bone tissue, the exchange of magnesium and phosphorus in the body are interconnected. Lack of magnesium salts in food disrupts the excitability of the nervous system, muscle contraction. The need for it is 450 mg.
The main source of these trace elements are buckwheat, oatmeal, beans, peas, prunes, dried apricots, nuts, rye bread. Cobalt is also found in black and red currants, strawberries, and liver.
Potassium (and its salts) is especially important for the normal functioning of the cardiovascular system, takes part in plastic processes and energy metabolism. Apples, plums, apricots, raisins, peaches, mulberries, gooseberries, baked potatoes, oatmeal, etc. are rich in potassium salts. The need for potassium is at least 5 g per day.
Sodium salts (table salt) are involved in the regulation of water metabolism. Particular attention should be paid to their content in the diet of a pregnant woman: in the 2nd half of pregnancy, it should not exceed 68 g per day. In the last month, you can use dietary salt (sanasol) instead of table salt.
Thus, nutrition containing the optimal amount of macro- and microelements ensures the normal course of metabolic processes in the mother and fetus and is an important therapeutic agent.
The diet of pregnant women
Of exceptional importance for the physiological course of pregnancy is the diet. Violations of it harm not only the mother's body, but also the normal development of the fetus. Nutrition should be not only rational, but largely individual. When compiling a diet for a pregnant woman, one must proceed from the fact that proteins make up an average of 2030%, fats 2025% and carbohydrates 45 50% of the total energy value of the diet. All products should be assimilated and used as much as possible. One of the prerequisites for this is to limit the amount of food taken at a time. Physiologically justified in the first half of pregnancy 45 meals a day: first breakfast at 89 o'clock, second breakfast at 1112 o'clock, lunch at 1415 o'clock, dinner at 1819 o'clock and at 21 o'clock a glass of kefir. After eating, it is not advisable to rest lying down, rest should be active.
In the second half of pregnancy, you must first five, and in the last two months, six meals a day.
Meat and fish dishes should be consumed mainly during breakfast and lunch.
It is advisable for pregnant women to consume the meat of young animals and it is better in boiled form in order to avoid harmful
influence of extractives. In the last three months of pregnancy, it is desirable to exclude broths, meat borscht, soups from the diet. During this period, meat consumption should be limited to 3-4 times a week, and in the last month 1-2 times a week (to facilitate the work of the kidneys). In the first half of pregnancy, fish should occupy no less place in the diet than meat. In the second half of pregnancy, it is desirable to eat dishes prepared from fresh fish. Milk and dairy products are recommended throughout pregnancy (if well tolerated). On average, a pregnant woman needs to consume 0.50.6 liters of milk per day. Vegetables, fruits and berries are mandatory for a woman throughout pregnancy. From cereals, preference should be given to buckwheat, oatmeal and rice. Bread more include rye. At the end of pregnancy, exclude oatmeal and semolina, especially with excessive body weight.
It is most favorable to combine animal and vegetable products in the diet so that the former make up 6070%. The menu is recommended to take into account the time of year and diversify food more.
The food consumed should be fresh, well cooked and not very hot. If food is stored for a long time and then heated, it loses not only taste, but also a large amount of vitamins.
Basic principles of cooking
Food is prepared from fresh, good-quality products, well washed in running water and cleaned. The main task of culinary processing of products is to preserve their nutritional value (proteins, fats, carbohydrates and vitamins) and promote better absorption of nutrients.
In cooking, they use boiling in water and steaming, roasting; it is better to stew vegetables with the addition of water and fat over low heat in a sealed container.
Under the influence of culinary processing, physico-chemical changes occur in food substances and food becomes suitable for digestion. For example, when meat is cooked at a temperature of 100°C, the insoluble collagen protein, which is part of the connective tissue, is converted into soluble glutin, suitable for digestion.
During the cooking of meat, some of the nutrients and extractive substances pass into the water. If the meat is immersed in boiling water, then the broth will be of low concentration, but more extractive substances will remain in the meat, which are not advisable for pregnant women to take. It is better to cook meat for the diet during pregnancy in a different way: cut it into small pieces and immerse it in cold water, gradually bring to a boil and cook for 1.5 2 hours. smaller quantity.
During the preparation of plant products, significant structural changes in protein and carbohydrates also occur. Protein coagulates, starch gelatinizes. In the preparation of vegetables, in addition to heat treatment, mechanical (fine shredding) and chemical processing (fermentation, treatment with acetic or citric acid) are used. Vegetables are then better digested and absorbed. Do not soak vegetables in water for a long time, as this destroys vitamins and other nutrients. From 50 to 75% of minerals pass into the water in which vegetables were boiled, so vegetable broth can be used for cooking first courses. Vitamins of group B during cooking pass into the water. For example, when stewing meat, only 40 60% of vitamin B1 is preserved? up to 75% vitamin B2, up to 7090% nicotinic acid. The activity of vitamin A and carotene does not decrease during heat treatment. Vitamin C is very destroyed when vegetables are cleaned and stored in water. This also applies to dairy products. It is known that lactic acid products lose their nutritional value when heated above 60 °. Less destruction of vitamins and enzymes can be achieved by pasteurizing milk (heating it for 30-40 minutes at a temperature of 60 °) than by boiling it. It is better to take cottage cheese fresh or after heat treatment in the form of curd dishes (syrniki,
casseroles, cheesecakes). Kefir is stored in the refrigerator for no more than 48 hours. Butter is stored in a sealed container in the refrigerator for no more than 7 days.
Brief description of individual food products
Meat. This is a food product rich in proteins, it also contains mineral salts, vitamins of group B. Lean meats (beef, veal) are introduced into the diet of pregnant women. Meat by-products are valuable; liver, brain, rich in phosphorus compounds, tongue.
Fish. Fish contains easily digestible proteins. Cod, hake, perch, pike perch, saffron cod, catfish are used to feed pregnant women. The fish should be fresh, preferably boiled or in the form of steam cutlets, you can cook fish soup.
Eggs, a valuable food product, contains proteins, fats and vitamins (A, B, D and E). Eggs are best consumed boiled, as raw eggs can provoke allergies or be infected. Women during pregnancy should consume only fresh eggs.
Oil. In the diet of pregnant women, it is better to use butter. When preparing salads and vegetable dishes, vegetable oil is recommended. Fat can be used in small quantities and only fresh. It is better not to use beef, mutton fats for the nutrition of pregnant women, because they are refractory, contain almost no vitamins and are poorly digested.
Sour cream. It should only be fresh, better to add it to vegetables.
Milk and dairy products. The composition of milk includes high-quality proteins, fats, carbohydrates, minerals, vitamins. It is recommended to take up to 500600 ml of dairy products per day (kefir, acidophilus milk), which improve digestion. Milk is best used in pasteurized form (or fresh only from healthy cows, with full compliance with hygiene standards during milking). To preserve the value of milk, it must be boiled for no more than 1 2 minutes or pasteurized. Repeated boiling dramatically reduces the amount of vitamins in it and the value of proteins. In the diet of pregnant women, lactic acid products have an advantage, with a tendency to constipation.
only one-day kefir is appropriate.
Cottage cheese. Nutritious protein product essential for women during pregnancy. It is better to use freshly prepared cottage cheese at home. The recipe is as follows: mix 3 liters of fresh cold milk with 12 g of calcium lactate and heat slowly, bringing to a boil (12 min), then cool to room temperature and squeeze through a sterile gauze. Transfer curd to a glass jar. Yield 500 g. Store in the refrigerator for no more than 2 days. Recipe for sour cottage cheese: 3 liters of sour pasteurized milk are placed in a water bath for 1 hour at a temperature of up to 75 ° (cannot be brought to a boil). When the transparent whey has separated, the jar is removed from the water bath, cooled, filtered and squeezed.
Cereals, flour. The most valuable in terms of chemical composition are buckwheat and oatmeal. Cereals are used for making porridges of different consistency and soups. Use with butter, milk and other seasonings to taste.
Vegetables and fruits. They contain vitamins, carbohydrates, minerals and organic acids. The diet includes: carrots, cabbage, pumpkin, zucchini, tomatoes, cucumbers, beets, onions, dill, parsley, lettuce, etc. Greens are rich in vitamins and trace elements, it is better to use it fresh. Onions, radishes, garlic contain essential oils that irritate the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract, so they are included in the diet to a limited extent. Vegetables, fruits and berries are consumed both raw and after appropriate cooking. Vegetables, especially potatoes, peeled before cooking, cannot be soaked and stored for a long time, because their nutritional value is lost (vitamins, starch and trace elements pass into water). It is better to boil potatoes and other vegetables like this: the cooked vegetables are placed immediately in boiling water and boiled in a pot with a closed lid over low heat. Vitamin C is better preserved in baked potatoes or boiled in "uniforms".
Of great importance is the variety of food, which largely depends on the ability to correctly compose the menu. About the right
selection of food products in the organization of rational nutrition, you can
judged by the normal course of pregnancy
weight gain in the second half should not exceed 300350 g per week. With a more intense increase, you should find out the cause and adjust the diet. We give an example of a set of products for one day, their chemical composition and energy value.
Table 14.2. A set of products for one day for a woman in the second half of pregnancy
Quantity, g Chemical composition Energy
Foods proteins, g fat, g carbohydrates, g gia, kcal
Meat products 120 16.2 9.12 147.6
Fish products 100 16.0 0.4 68.0
Cottage cheese (low-fat) 170 23.8 0.85 5.9 129.6
Kefir (ryazhenka) 200 6.0 7.4 9.4 136.6
Milk 250 9.0 10.5 13.5 186.0
Sour cream 30 0.6 8.4 0.9 85.5
Butter 15 0.06 11.7 0.09 110.1
Oil 25 23, 2 215.7 vegetable
Sugar 50 48.0 196.0
Rye bread 100 7.0 1.0 45.0 223.0
Wheat bread 100 7.1 1.0 47.5 230.0
Eggs 1 pc. 9.2 5.4 0.5 100.5
Bun, biscuit 100 5.7 11.8 55.7 361.3
Cereals, pasta 60.0 7.4 1.5 40.0 208.0
Potatoes 200 3.7 42.1 189.0
Cabbage 100 1.4 5.2 62.0
Beetroot 100 1D 10.3 47.0
Carrot 100 1.3 7.6 36.0
Tomatoes 200 1.3 4.0 21.3 and other vegetables
Bulb onion 35 1.0 3.1 16.1
Fruit, berries 200 1.2 46.0 193.4 or fruit juice
TOTAL 119.2 92.27 384.7 2962.7
If a pregnant woman is on bed rest for any reason, the caloric content of the diet is reduced by 2030%.
One day menu for pregnant women in the second half of pregnancy
1st breakfast
Boiled meat 120 g with mashed potatoes 200 g, fresh cabbage salad 100 g Cottage cheese 150 g, tea 200 g, sugar 25 g Rye bread 50 g
2nd breakfast
Buckwheat porridge 200 g, milk 200 g Wheat bread 50 g
Dinner
Ukrainian borscht with minced meat and sour cream 300 g Rye bread 50 g Vegetable stew 80 g with boiled fish 100 g Fruits, berries 300 g
afternoon tea
Egg 1 pc. hard-boiled, rosehip infusion or apple juice 200 g, biscuits 50 g.
Dinner
Protein omelette 60 g with sour cream 15 g Bun 75 g Tea 200 g,
sugar 25 g.
Before bedtime
Fresh kefir 200 g
Diets for pregnant women were developed at the Kiev Institute of Pediatrics, Obstetrics and Gynecology. The effect of these diets on a large number of observed women has been studied. Women who were on such a diet were less likely to develop complications (anemia, toxicosis), such nutrition favorably affects the course of pregnancy and childbirth, the development and condition of the fetus and newborn.
In addition to diet, an important therapeutic and prophylactic agent that contributes to the normal course of pregnancy and the development of the fetus for a pregnant woman is regular exercise in a special complex. Information on this issue can be obtained from the antenatal clinic.
Approximate weekly menu in the second half of pregnancy with its normal course
MONDAY
First breakfast (8 9 h)
Butter. Egg. Salad. Tea with lemon. Bun.
Second breakfast (11 12 h)
Pancakes with rice and sour cream. Milk. Bun.
Lunch (14 15 h)
Shchi vegetarian, with grows, butter. Meatballs with vermicelli. Baked apples. Black bread.
Afternoon snack (17 h) Berries with honey.
Dinner (19h)
Tea with a bun.
Cottage cheese with sour cream.
At night (2122 h) Kefir.
TUESDAY
First breakfast (8 9 h)
Butter. Cottage cheese with sour cream. Tea with milk. The bread is white.
Second breakfast (11 12 h)
Vinaigrette with vegetable oil. Pancakes with meat. Rosehip decoction.
Lunch (1415 h)
Rice milk soup. Beef stroganoff from boiled meat with boiled potatoes. Dried fruits compote. Black bread.
Afternoon snack (5 p.m.) Fresh apples.
Dinner (19h)
The fish is boiled. Tea. Bun.
For the night (2122) Ryazhenka.
WEDNESDAY
First breakfast (8-9 h) Butter, nom, biscuits. The fish is boiled. Salad. tea with lemon
Second breakfast (11 12 h)
Boiled potatoes with salad. Protein omelet. Milk, cookies.
Lunch (1314 h)
Ukrainian borscht. Stewed meat, with vegetable oil salad. Fruits or berries with honey. Black bread.
Afternoon snack (5 p.m.) Apple juice.
Dinner (19h)
Vegetable stew. Tea with milk, cookies.
At night (2122 h) Kefir.
THURSDAY
First breakfast (8 9 h)
Butter. Salad with sour cream. Cheese. Tea with lemon. The bread is white.
Second breakfast (11 12 h)
Rice porridge with milk. Cheese. Rosehip decoction.
Lunch (1314 h)
Buckwheat soup with potatoes. Pike perch boiled. Salad with vegetable oil. Compote. Black bread.
Afternoon snack (17 h) Fruits.
Dinner (19h)
Boiled meat with vegetable salad. Milk.
At night (2122 h) Kefir.
FRIDAY
First breakfast (8 9 h)
Butter. Protein omelet. Tea with milk.
The bread is white. Second breakfast (11 12 h)
Semolina pudding with raisins. Rosehip decoction. Lunch (1314 h)
Vegetarian pickle. Boiled meat with rice
porridge. Dried fruits compote. The bread is black.
Afternoon snack (17h)
Peppers stuffed with carrots. Fruit juice. Overnight (2122 h)
Ryazhenka.
SATURDAY
First breakfast (8 9 h)
Butter. Cottage cheese with sour cream. Tea with milk.
Bun. Second breakfast (11 12 h)
Potato fritters. Milk, biscuits Lunch (1314 h)
Vegetarian cabbage soup with vegetable oil. Chicken
boiled with vegetable salad. Berry compote. Bread
black. Afternoon snack (17h)
Rosehip infusion. Cookie. Dinner (19h)
The fish is boiled. Vegetable stew. Tea. Overnight (2122 h)
Kefir.
SUNDAY
First breakfast (8 9 h)
Butter. Vinaigrette with vegetable oil.
Tea with lemon. Cookie. Second breakfast (11 12 h)
Buckwheat porridge with butter. Milk. Lunch (1314 h)
Fish soup. Meat zrazy with buckwheat porridge. Fruit. Rosehip decoction. The bread is black. Afternoon snack (17h)
The cheese is non-greasy. Milk. Dinner (19h)
Boiled meat or egg. Vegetable salad. Tea. Overnight (2122 h)
Kefir.
The amount of products depends on their chemical composition.
It is necessary to monitor the amount of fluid taken, which should be no more than 1.2 liters per day (together with soups, milk, tea, etc.). With the appearance of edema and the last 2 months no more than 0.8 liters.
Features of nutrition of women with toxicosis of pregnancy
Toxicosis of pregnant women are early - up to 3 months of pregnancy and late, which develop in the last 23 months of pregnancy.
The early ones manifest themselves in the form of nausea (especially in the morning), vomiting of pregnant women, salivation and allergic skin reactions (dermatoses). Early toxicosis occurs in 5060% of women. According to the severity of the disease, mild, moderate and severe degrees of toxicosis are distinguished. With a mild form, vomiting of pregnant women occurs from 1 to 5 times a day, sometimes only on an empty stomach, but the woman's health remains satisfactory.
The nutrition of pregnant women with a mild degree of toxicosis corresponds in chemical composition to the nutrition of a healthy woman. Food should be easily digestible and rich in vitamins. Vomiting may appear on an empty stomach, during a meal or after a meal, sometimes on individual odors. If vomiting appears on an empty stomach, pregnant women are advised to take a small sandwich before getting out of bed - bread with butter or cheese, you can eat a few pieces of small crackers from black bread, lightly salted. All pregnant women with a mild form of toxicosis should take food in small portions every 2 3 hours, warm, but not hot, and when reacting to odors, chilled. Liquid and solid food should not be taken at the same time, that is, it is not recommended to drink 0.51 hours before meals and after (water, milk, compote, etc.). It is useful to include cottage cheese, hard-boiled eggs, baked potatoes, vegetable puree, a small amount of pickles (cucumber, tomato) or a piece of herring in the diet. If possible, satisfy the food whims that appeared during pregnancy.
With salivation, a number of trace elements and fluid are lost. In these cases, the woman is asked to recommend liver and herring pates, freshly pickled cucumbers, sauerkraut and an additional intake.
liquids or juices.
With vomiting of pregnant women of the 2nd degree (up to 10 times a day) and the 3rd degree (1520 or more times), treatment should be carried out in a hospital, because it is necessary to replenish the lost trace elements, proteins and fluid through parenteral nutrition (through tube, intravenously).
With repeated vomiting, the body undergoes profound biochemical changes, the content of residual nitrogen in the blood increases, ketoacidosis and dehydration increase.
The period of fasting in pregnant women should not exceed 23 days, since after 1218 hours of fasting, fats and proteins of the pregnant woman herself become the main source of nutrition. There is a drop in body weight, the woman's condition deteriorates sharply, dry skin and mucous membranes appear, the smell of acetone from the mouth, an aversion to food, the pulse quickens, and violations of the central nervous system are observed. All this negatively affects the state of the intrauterine fetus up to its death.
In this regard, all pregnant women who vomit up to 10 times a day (and even less than 10 times) should see a doctor within 12 days and start treatment as soon as possible. The task of parenteral (intravenous) nutrition is to replenish the loss of energy and plastic materials, as well as normalize violations of the water-salt and vitamin balance.
Late toxicosis of pregnant women is accompanied by various disorders of the metabolism of proteins, fats, carbohydrates, vitamins and microelements. Functions of a number of organs and systems are disturbed: liver, kidneys, cardiovascular and nervous. There are such forms of late toxicosis of pregnant women: dropsy, hypertension, nephropathy of pregnant women, preeclampsia and eclampsia.
The diet of pregnant women with late forms of toxicosis should include: vegetables, fruits, honey, wholemeal bread. Strawberries, strawberries, blackcurrants, apples, pumpkins, watermelons, beets, carrots are especially useful. These products provide sufficient intake in the body
vitamins and minerals and are a source of carbohydrates.
The amount of free fluid should not be sharply limited, because with late toxicosis, the volume of circulating blood and plasma decreases and uteroplacental blood flow decreases. The amount of liquid should be at least 800 ml and it is advisable to include in the diet products that increase diuresis; rosehip broth, beet juice, parsley, blackberry, viburnum, chokeberry, cool milk, dried apricots.
With an excessive increase in body weight and the development of edema, women are transferred to a salt-free diet, in which the salt content should not exceed 34 g per day. The complete exclusion of salt is impractical, as this can lead to a decrease in urine output and the retention of nitrogenous waste in the body.
Pregnant women with severe forms of late toxicosis should have fasting days once a week, for example:
1) curd-kefir 200 g of cottage cheese and 500 g of kefir per day (45 doses);
2) apple and cottage cheese 1 kg of apples and 250 g of cottage cheese per day;
3) apple 1.5 kg of apples per day;
4) potato 500 g baked potatoes, 20 g butter, 500 g milk per day.
The chemical composition and energy value of the diet for toxicosis: proteins 100 110 g, fats 80 g, carbohydrates 40 g, caloric content 2600 3000 kcal. They use the most complete proteins - cottage cheese, milk, meat, fish. Exclude from the diet meat, mushroom broths, spices, pickles, smoked meats, fried foods, sauces, seasonings, chocolate, coffee.
Culinary food processing. Cook the first courses only on vegetable broths (shchi, beetroot soups, soups, milk soups). Second courses boiled. Meals 5 times a day, before going to bed kefir.
Sample menu for one day for pregnant women with a late
toxicosis
1st breakfast
Boiled fish 150 g or 120 g meat with potatoes 180 g or stewed liver 75 g with carrots 200 g Vegetable salad with sour cream 15 g or 1 boiled egg and fresh cabbage salad 200 g with vegetable oil 15 d. Butter 10 g. Tea or tea with milk 200 g.
2nd breakfast
Cottage cheese 150 g or millet milk porridge 300 g Apples 300 g or fruit juice 200 g
Dinner
Beetroot 300 g with sour cream 15 g or rice soup with minced meat 50 g. Boiled meat 50 g with pasta 200 g; or steam cutlet 60 g with buckwheat porridge 200 g; or vegetable stew 100 g with boiled fish 75 g. Compote or rosehip broth 200 g.
afternoon tea
Fat-free cottage cheese 50 g with milk 200 g; or fruits and berries up to 300 g; or cottage cheese 50 g with honey 40 g.
Dinner
Milk rice porridge 300 g; or low-fat cottage cheese 150 g with rosehip broth 100 g; or boiled fish 100 g with vinaigrette 200 g.
Before bedtime
Kefir 200 g
For a day
Rye bread 200 g or wheat bread 100 g.
Complex therapy of late toxicosis of pregnant women, including the medical nutrition developed by the Kyiv Research Institute of Pediatrics, Obstetrics and Gynecology, helps to reduce high blood pressure, normalize metabolic processes, increase diuresis,
normal development of the fetus, the course of pregnancy and childbirth.
Therapeutic nutrition for anemia in pregnant women
In recent years, there has been an increase in the number of anemia in pregnant women up to 2037%. Iron deficiency anemia is most often noted, in most cases it is attributed to one of the types of toxicosis of pregnant women. More often it appears after 1822 weeks of pregnancy. A pregnant woman develops fatigue, weakness, dizziness, headache, drowsiness. In the blood, a decrease in hemoglobin, a color index, the number of erythrocytes and iron content in the blood serum is determined.
The main reasons for the development of iron deficiency anemia in pregnant women are an increase in the need for iron in the developing fetus, its insufficient intake or absorption in the alimentary canal. When the balance of iron is disturbed, when the consumption exceeds the intake, anemia develops with iron deficiency of varying degrees. The biosynthesis of hemoglobin is disturbed with a lack of cobalt (the main component of vitamin B2) and vitamins B2, B6, E, C, D, as well as glutamic acid.
A decrease in the level of hemoglobin in the blood of the mother causes changes in tissue metabolism in the fetus, leads to disruption of oxidative processes and the appearance of oxygen deficiency, and intrauterine fetal hypoxia develops. With anemia in pregnant women, a number of complications of pregnancy (miscarriage, late toxicosis, fetal death) and childbirth (untimely discharge of amniotic fluid, weakness of labor, high stillbirth) occur. All pregnant women with iron deficiency anemia are at high risk and should be monitored and treated.
Rational nutrition is of great importance in the prevention and treatment of anemia.
The purpose of the diet is to replenish the deficiency of protein, iron, trace elements and vitamins.
The chemical composition and energy value of the diet: in the 1st half of pregnancy for women of average height (155165 cm) and average body weight (5565 kg) proteins 120 g; fat 80 g; carbohydrates 300400 g; energy 3200 3300 kcal.
It is necessary to consume more proteins of animal origin, as they contribute to the absorption of iron. Foods rich in amino acids (meat, fish, cottage cheese, chum caviar), foods rich in iron (tongue, liver, eggs, fruits - peaches, apricots, apricots, Antonov apples, pumpkin, tomatoes, beets) are introduced into the diet. Berries are also valuable - strawberries, strawberries, raspberries. B vitamins are replenished with vegetables, fruits, buckwheat and oatmeal. In winter, with a lack of vitamins in foods, a complex of vitamins is prescribed in the form of medications. Vitamin C plays an important role, it activates the absorption of iron in the stomach and intestines and is involved in the metabolism of folic acid and vitamin B12. Women with anemia are also allowed to take extractive substances (meat broths), as their secretory function of the stomach is often disturbed.
Sample menu for one day for pregnant women with iron deficiency anemia
1st breakfast
Stewed liver 75 g with carrots 200 g or liver pate 100 g, butter 15 g Tea with lemon 200 g, oatmeal cookies 50 g
2nd breakfast
Cottage cheese casserole 150 g or boiled fish 120 g with mashed potatoes 100 g, vegetable salad 100 g Apple juice 200 g
Dinner
Ukrainian borsch with meat and sour cream 300 g, meat 80 g Boiled tongue 80 g with oatmeal 200 g or sausages 100 g with buckwheat porridge 200 g Rosehip infusion 200 g
afternoon tea
Milk 200 g, bun 100 g.
Before bedtime
Kefir 200 g, baked apples 100 g.
Culinary processing. To preserve vitamins, it is necessary to lower the chopped vegetables into boiling water and cook until tender under a closed lid. Prepare raw vegetable dishes before eating. Do not store cooked food for a long time, as when it is reheated, the content of trace elements decreases.
Conclusion
Nursing staff plays a huge role in organizing the nutrition of a pregnant woman, performing a significant amount of care work, medical manipulations, and preventing nosocomial infections.
The problem in the organization of nutrition for pregnant women, and the fight against it, is relevant for the entire health care system of the country and St. Petersburg, in particular. The incidence of GSI is determined, along with violations of the rules of asepsis and antisepsis and the anti-epidemic regime, by the presence of objective factors, such as: a significant technical complication of diagnostic and therapeutic manipulations, an increase in the number of operations, as well as their complication and often carried out against the background of immunosuppression and in the early period.
The introduction of modern, effective infection control methods improves the quality of medical care for pregnant women, and also reduces the cost of their treatment. In addition, the results of the work carried out allowed the administration of other departments to demonstrate their effectiveness of treatment.
A reserve for improving the effectiveness of epidemiological surveillance is the active involvement of nursing specialists in the implementation of its individual areas. The proposed model of activities of the nursing service for the supervision of nosocomial infections will improve it and will contribute to a more complete and timely
information about infectious diseases in the hospital and
the factors that cause it.
Bibliography:
1. Grekov I.G. The attitude of nurses to their professional activities. // Nurse. 2000. №1.
2. Deev A.N. Socio-hygienic characteristics of the health and living conditions of paramedical workers and members of their families: Diss. cand. honey. Sciences. M., 1987.
3. Dubrovina Z.V. et al. Health status of nurses
4. Kanishchev V.V. Disinfection in neonatology. Complex processing of couveuses and instruments. // Nurse, 2007, No. 7.
5. Korchagin V.P., Naigovizina N.B. Organizational and economic aspects of the implementation of the concept of development of health care and medical science in the Russian Federation. // Economics of health care. 1998.
6. Marchuk N.P., E.N. Fomicheva Professional training of nurses and midwives of obstetric institutions and the formation of symptoms of "emotional" burnout / / Nurse, 2007, No. 7.
7. Monisov A.A., Lazikova G.F., Frolochnikina T.N., Korshunova G.S. The state of the incidence of nosocomial infections in the Russian Federation. // Epidemiol. and infectious Bol. 2000. No. 5.
8. Fundamentals of infection control: A practical guide. / Ed. E.A. Burganskoy. 1997.
9. Perfil'eva G.M. Nursing process. // Med. sister. 1999. №3
10. Ponomareva G.A., Uspenskaya I.V., Voronkov D.V., Kineleva T.A. Planning the number of medical personnel of round-the-clock posts. // Healthcare. 1999. No. 4.
11. Romashova T.I. Evaluation by health workers of their work activity. // Sociology in medicine. Issue. 3. Tbilisi, 1990
12. Semina N.A. Scientific and organizational principles for the prevention of nosocomial infections. // Epidemiol. and infectious Bol. 2001. №5.
13. Smirnova L.M., Saidova R.A., Braginskaya S.G. Obstetrics and gynecology: Textbook. M.: Medicine, 1999. 368 p.
14. Ugarov V.A. Social and hygienic characteristics of secondary medical workers in rural areas and ways to improve work with medical personnel in the Tula region: Diss. cand. honey. Sciences. M., 2000.
15. Cherkassky B.L. Guide to General Epidemiology. M .: Medicine, 2001.
16.Kratz C.R. The Nursing Process.London: Bailliere Tindall, 1979.
17.McFarland G.K., McFarlane E.A. Nursing Diagnosis and Intervention: Planning for Patient Care.3rd Ed. St. Louis: Mosby-Year Book, 1997.
Other related works that may interest you.vshm> |
|||
| 7673. | Accounting for operations in public catering | 32.09KB | |
| Accounting for products in minibars. There is the following classification of types of public catering establishments: a restaurant is a public catering establishment with a wide range of complex dishes, including custom-made and branded ones; wine-vodka tobacco and confectionery products with a high level of service in combination with recreation; bar catering company with a bar counter selling mixed strong alcoholic low-alcohol and non-alcoholic drinks snacks desserts flour confectionery and... | |||
| 18803. | Organization of improvement of commercial activities to improve the quality of service in public catering | 184.51KB | |
| Theoretical foundations of commercial activities to ensure the quality of service in public catering establishments; features of the formation of a service quality management system; the level of quality of service in the dining room of the Criminal Procedure Code; | |||
| 1492. | The constitutional foundations of the position of women in the Russian Federation | 18.14KB | |
| On the biological and psychological traits of her personality, behavior and a whole system of values, the models of which are taken from the social group in which they live. The responsibilities of any mother stem from the prevailing society and culture. | |||
| 13578. | Untouchables in the social and political life of India. The role of women in Indian society | 60.54KB | |
| Untouchables in the social and political life of India. Untouchables in the political life of India in the second half of the 20th century. Social stratification in India did not lead to the formation of classes of slave owners and slaves, but to the emergence of special class groups - varnas: brahmins, priests, kshatriyas, rulers, warriors, vaishyas, farmers, artisans and sudra servants. for civil and political rights took on the character of anti-caste movements that unfolded in the West and South of India against caste oppression. | |||
| 11185. | The set of psychological characteristics of a woman's personal qualities that affect her success in professional activities | 230.59KB | |
| Many people often ask themselves the question: What is success What does it consist of. In order to achieve them, it is useful to set larger goals. The second necessary condition is the ability to interact with others so that others support her in her aspirations, goals and efforts. Each person needs to be understood, loved, so that a person feels comfortable and safe in society, so that his values \u200b\u200bare respected by others. | |||
| 19570. | RESEARCH OF A WOMAN IN A MANAGEMENT POSITION OF A MUNICIPAL BUDGETARY PRESCHOOL EDUCATIONAL INSTITUTION - CHILD DEVELOPMENT CENTER - KINDERGARTEN №7 "SOLNYSHKO" | 42.3KB | |
| The study of trends, problems, and prospects for women in leadership positions in modern Russian gender culture makes it possible to explain many social problems and give recommendations for their solution; will serve to form new relations between the sexes in society; for an individual, research can help to reassess one's personal strategy. | |||
| 11607. | Comprehensive development of the organization. The main directions of the integrated development of the organization | 1.58MB | |
| To achieve the goal, the following research methods were used in the work: analysis of publication material on the topic of a systematic approach; structural-functional approach; comparison and analysis. To select one general strategy, consider general strategies as a whole. As a result, an increase in price or an increase in sales is achieved, buyers become committed to the chosen brand, barriers arise for the appearance of substitute products and newcomers. Production risk is that the firm's efforts to... | |||
| 11699. | Statistical study of the financial stability and solvency of the organization (on the example of the limited liability company "Slavic Bitumen Plant") | 74.1KB | |
| In the process of operational investment and financial activities, there is a continuous process of capital circulation, the structure of funds and sources of their formation, the presence and need for financial resources, and, as a result, the financial condition of the enterprise, the external manifestation of which is solvency, change. A stable financial condition is achieved with equity capital adequacy, good asset quality, sufficient level of profitability, taking into account the operational and financial risk of liquidity adequacy... | |||
| 18962. | Ways to increase labor motivation in a first-class restaurant at the Chocolate Hotel when organizing a coffee break and its importance in organizing customer service | 5.43MB | |
| Personal preparation of waiters for a coffee break. Classification of public catering establishments A public catering enterprise is an enterprise intended for the production of culinary products, flour and confectionery products, drinks, their sale and organization of consumption. Restaurants at the hotel are designed to simultaneously serve all residents of the hotel and to serve the population of the city. Banquet hall Chocolate can accommodate up to 300 people and is designed for weddings, anniversaries and special events. | |||
| 9234. | Participants in the securities market. State control over the market. Self-regulation as a form of market organization. Specific forms of structural organization in the Russian securities market | 65.46KB | |
| Specific forms of structural organization in the Russian securities market. Participants in the securities market. Specific forms of structural organization in the Russian securities market. | |||
Moscow region
FINAL QUALIFICATION WORK
student (s) IV course 31 M group
specialty 34.02.01 Nursing (basic training)
KHATANOVA MILANA DZHAMILYEVNA
Orekhovo-Zuevo - 2016
INTRODUCTION 3
CHAPTER 1. NURSING CARE OF A PREGNANT WOMEN DURING NORMAL PREGNANCY.. 5
1.1 Changes in the body of a pregnant woman .. 5
1.2 Determining the timing of childbirth or the timing of pregnancy. ten
1.3 Maslow's pyramid of needs. 12
1.4 The main problems of a pregnant woman and their solution. 13
1.5 Features of the organization of the nursing process. eighteen
Conclusions on chapter 1. 27
CHAPTER 2. NURSING PROCESS IN NORMAL PREGNANCY.. 29
Conclusions on chapter 2. 39
CONCLUSION. 40
LIST OF USED SOURCES.. 43
INTRODUCTION
The period of expectation of a child is one of the happiest in a woman's life. However, this is a time of great responsibility. A new stage has begun - caring not for yourself, but for the child. What happens after birth is a continuation and undoubtedly depends on what happens before and during it. Understanding this fact explains why the newborn is so perfectly functioning. His ability to respond to maternal caresses, hugs, looks and voice is based on a long intrauterine acquaintance with her. Every mother dreams of happiness for her child, and every mother strives to give him something without which a full life is impossible - health and strength. The foundations of his future health are laid in his mother, therefore, taking care of health, and therefore the future of your baby, must be started even before birth, especially in the most important period for him - intrauterine. A successful pregnancy should become a strong foundation for further health and a happy life for both the mother and her child.
Pregnancy- this is a normal (physiological) process that occurs in a woman's body during fetal development.
During pregnancy, a woman's body undergoes profound transformations. With the normal development of pregnancy, all the changes that take place in the body of a woman are aimed at creating a harmonious relationship between the mother's body and the body of the developing fetus. Also, from the very first days of pregnancy, the body of a pregnant woman begins to prepare for future childbirth and breastfeeding.
Pregnancy begins at the moment of conception or fertilization and ends with childbirth. The average duration of a normal pregnancy is 280 days (40 weeks), counting from the first day of the last menstruation.
The period of fetal development is divided into three stages or trimesters:
1st trimester - up to 12 weeks
2nd trimester - 13-28 weeks
3rd trimester - 29-40 weeks
From the very first days of pregnancy, the body of a pregnant woman undergoes profound transformations. These transformations are the result of the coordinated work of almost all body systems, as well as the result of the interaction of the mother's body with the child's body.
Purpose of the study: the study of nursing care for a pregnant woman during the normal course of pregnancy
Research objectives:
· To study the activities that provide nursing care for a pregnant woman during the normal course of pregnancy.
Study of nursing care for a pregnant woman during the normal course of pregnancy.
Practical significance is that the results of the study can be used in the professional activities of a nurse.
Object of study: Nursing care of a pregnant woman in the normal course of pregnancy.
Subject of study: nursing care.
Research base: GBUZ MO "Davydovskaya district hospital".
Respondents: patients undergoing treatment at the Davydov Regional Hospital.
Research methods:
1. Work with literary sources.
2. Working with Internet resources.
3. Drawing up memos.
CHAPTER 1
Changes in the body of a pregnant woman
Changes in the reproductive system.
The most significant changes, however, occur in genitals pregnant woman. These changes prepare the female reproductive system for childbirth and breastfeeding:
The uterus of a pregnant woman increases significantly in size. Its mass increases from 50 g - at the beginning of pregnancy to 1200 g - at the end of pregnancy.
The volume of the uterine cavity by the end of pregnancy increases by more than 500 times.
The blood supply to the uterus is greatly increased.
The number of muscle fibers in the walls of the uterus increases.
The cervix is filled with thick mucus that clogs the cavity of the cervical canal.
The fallopian tubes and ovaries also increase in size.
In one of the ovaries there is a "yellow body of pregnancy" - a place of synthesis of hormones that support pregnancy.
The walls of the vagina loosen up, become more elastic.
· External genital organs (small and large labia), also increase in size and become more elastic.
· Perineal tissues are loosened.
There is an increase in mobility in the joints of the pelvis and a divergence of the pubic bones.
The changes in the genital tract described above are of extremely important physiological significance for childbirth. Loosening the walls, increasing the mobility and elasticity of the genital tract increases their throughput and facilitates the movement of the fetus through them during childbirth.
Milk glands increase in size, become more elastic, tense. When pressing on the nipple, colostrum (first milk) is released.
Changes in the CNS.
1. Changes in the cortex and subcortex:
o Drowsiness,
o Tearfulness,
o Irritability,
o Insomnia,
o Nausea and vomiting.
2. Changes in smell (to smells that were pleasant).
3. Changes in touch - changes in taste sensations (chalk).
4. Changes in auditory perception - sharp sounds irritate.
External changes in the skin and mucous membranes.
1. Pigmentation on the skin:
On the face according to the type of mask "pregnant - the bridge of the nose, cheeks, around the eyes,
Nipples and areola,
· Along the white line of the abdomen.
2. Sometimes pregnancy scars (“stretch marks”, striae gravidarum) form on the skin of the lateral parts of the abdomen. In connection with the violation of the extensibility of the elastic fibers of the skin, they break, a connective tissue scar is formed. A fresh scar is purple-blue, and then it becomes whitish.
3. Acrocyanosis - blue chin, tip of the nose, ears.
4. Acromegaly - an increase in the protruding parts of the body (arms, legs, nose, ears).
5. Changes in the navel:
At 32 weeks, the navel is retracted,
At 40 weeks, the navel is convex or flattened.
Changes in the cardiovascular system.
The mother's circulatory system during pregnancy is forced to pump more blood to ensure an adequate supply of nutrients and oxygen to the fetus.
Changes:
Increases the thickness and strength of the heart muscles
the pulse and the amount of blood pumped by the heart in one minute become more frequent,
Increases the volume of circulating blood
in some cases, increased blood pressure,
The tone of blood vessels during pregnancy decreases, which creates favorable conditions for increased supply of tissues with nutrients and oxygen.
All of the above changes in the cardiovascular system completely disappear after childbirth.
Changes in the urinary system.
kidneys work hard during pregnancy. They secrete decay products of substances from the body of the mother and fetus (the waste products of the fetus pass through the placenta into the mother's blood). There may be frequent urge to urinate due to compression of the bladder by the enlarging uterus.
Changes in body weight.
In the first 2 months of pregnancy, while the baby and mother are only adapting to mutual coexistence, a woman usually does not gain weight. In addition, at this time, she may be disturbed by toxicosis, which often leads to weight loss.
So, in the 1st trimester of pregnancy, there is no intensive increase, the expectant mother usually gains 1-2 kg. The main events occur later, because the body weight of the expectant mother increases mainly in the 2nd half of pregnancy, when the weekly weight gain averages 250-300 g. If the process goes faster, this may mean the appearance of a problem - hidden, and then obvious edema (dropsy of pregnancy).
For 40 weeks of pregnancy, the expectant mother should gain 10-12 kg. It is believed that, starting from 30 weeks of pregnancy, a woman's weight increases by about 50 g per day, by 300-400 g per week and no more than 2 kg per month.
They are distributed like this:
child - 3300g;
uterus - 900 g;
afterbirth - 400 g;
amniotic fluid - 900 g;
increase in the volume of circulating blood - 1200 g;
mammary glands - 500 g;
adipose tissue - 2200 g;
tissue fluid - 2700 g.
Total: 12 100
Chapter 1 Conclusions
The nurse should also remember to ensure the safety of the conditions for the course of pregnancy, giving recommendations on sexual and physical activity, the right choice of clothing, shoes.
Optimal for the expectant mother is loose, non-constricting clothing made from natural materials. During pregnancy, low-heeled shoes should be worn; in late pregnancy, the center of gravity changes, the risk of falls increases, and the likelihood of varicose veins in the legs is high.
Maintaining the safety of pregnancy may also include the active intervention of a nurse (paramedic) in a woman's work activities, monitoring compliance with labor protection requirements, which may require interaction with the administration and medical services of the enterprise where the expectant mother works. During pregnancy, contact with aggressive chemicals, heavy lifting, prolonged standing on your feet, work associated with vibration, training, overheating or hypothermia are completely unacceptable. The woman's legitimate demands to change the nature of her work during pregnancy should certainly be supported by all those responsible for her health and antenatal care of the fetus. This can be done by a nurse (paramedic), and a midwife, and a doctor observing a pregnant woman.
An equally important activity of the family nurse (paramedic) for antenatal fetal protection is work with the environment of the pregnant woman. In particular, it is necessary to convince her family members of the harmful effects of smoking in her presence, since passive smoking is just as dangerous as active smoking, and no less leads to chronic fetal hypoxia, and ultimately to the birth of a weakened child. Of course, it is quite difficult to achieve a positive result in just words, specific actions are needed (using various methods of treating nicotine addiction, attending smoking cessation courses, etc.).
A pregnant woman should be freed from some household chores, especially those associated with lifting weights (a small child, bags of groceries), moving objects, standing for a long time (ironing clothes, hand washing), contact with detergents, disinfectants, pesticides.
Chapter 2 Conclusions
Pregnancy care is very important. Proper manipulation, observance of asepsis and antisepsis, control over the duration of pregnancy, timely examinations guarantee pregnancy and childbirth without pathologies.
CONCLUSION
Our lives are rapidly changing. Science is constantly moving forward, and thanks to technological progress, many of the problems that existed earlier have disappeared. It is impossible to list all the changes that are happening around us. The main thing remains unchanged - people continue to love, hope, give birth and raise children. And the birth of a person will always be one of the most amazing and significant events taking place in our world.
The hormones secreted by the placenta during pregnancy cause numerous physiological changes in the mother's body that ensure the proper development of the fetus, prepare the body for the upcoming birth and feeding. The nervous system of a pregnant woman is rebuilt in such a way that it subordinates the entire body to one goal - bearing a fetus. In accordance with this, physiological changes occur in its main systems. The cardiovascular system during pregnancy performs more intense work, since a "second" heart actually appears in the body - this is the placental circle of blood circulation. Here the blood flow is so great that every minute 500 ml of blood passes through the placenta. Blood pressure during pregnancy practically does not change. On the contrary, in women who have an increase before or in early pregnancy, it usually decreases. in mid-pregnancy, which is due to a decrease in the tone of peripheral blood vessels under the action of the hormone progesterone. The kidneys during pregnancy function with great stress, as they remove the metabolic products of the pregnant woman herself and her growing fetus from the body. The amount of urine excreted varies depending on the amount of liquid drunk.
During pregnancy, you need to reasonably treat the regime of work and rest. In our country, much attention is paid to the protection of labor of pregnant women. The legislation provides for their release from the moment pregnancy is established from overtime work, night shifts, business trips, work on weekends. Moderate work during pregnancy is necessary - it trains muscles, improves the activity of internal organs and thereby increases overall tone. Good sleep is very useful, so its duration should be at least 8-9 hours, preferably from 22 to 7 hours.
The upcoming birth will require a lot of physical stress from the woman. To better prepare for them, we recommend a special set of exercises that will increase the efficiency and defenses of the body to perform physical exertion during childbirth.
The diet of a pregnant woman should include food enriched with plant fiber to ensure normal bowel activity, which is often disrupted during pregnancy. A healthy diet for a pregnant woman involves excluding confectionery from the diet, in particular, sweets, jams, and sugar. Margarine and refractory animal fats are highly undesirable. They should be replaced with vegetable fats and butter. Syrups, compotes, juices, jelly, decoctions of dried fruits, fresh and frozen fruits, berries, vegetables are very useful. Proper nutrition of pregnant women should contain plant products, flour, cereals, legumes, root crops (excluding root crops with a high content of essential oils - radish, radish).
The main requirement for the hygiene of a pregnant woman is the cleanliness of the body. The skin, along with the lungs, is involved in respiration, excretes some metabolic products with sweat, which facilitates the work of the kidneys, and protects the body from the penetration of pathogenic microbes. Finally, clean skin, fresh underwear contribute to good health and cheerful mood. It is useful to take a warm shower, wipe the whole body with room temperature water daily, followed by rubbing with a hard towel. It strengthens the nervous system, improves circulation and respiration. A pregnant woman should not bathe in a hot bath, from the 32nd week of pregnancy it is forbidden to take a bath, while a shower until the very birth is considered a very useful procedure. Particular attention should be paid to the care of the mammary glands. It is also important to take care of the external genitalia. During pregnancy, you need to be in the fresh air for at least 3 hours a day. It is necessary to maintain cleanliness in the room, systematically ventilate it and do wet cleaning. The air temperature in the room should be no higher than 18-20°C.
MINISTRY OF HEALTH OF THE MOSCOW REGION
State budgetary professional educational institution
Moscow region
"Moscow Regional Medical College No. 3"
NURSING CARE OF A PREGNANT WOMEN IN NORMAL PREGNANCY
n1.docx
CARE OF PREGNANT WOMEN AND PARTNERS.BASICS OF OBSTETRIC PHYSIOLOGY AND
PATHOLOGIES
ECTOPIC PREGNANCY
MISSION OF PREGNANCY
PREGNANT HYGIENE
OBSERVATION OF A PREGNANT WOMAN
NUTRITION FOR PREGNANT WOMEN
TOXICOSIS OF PREGNANT WOMEN
PARTNERSHIPS
POSTPARTUM THROMBOPHLEBITIS
THERAPEUTIC-PROTECTIVE AND SANITARY REGIME OF THE OBSTETRIC HOSPITAL
DETERMINATION OF THE DATE OF PREGNANCY AND DELIVERY
What is the duration of a normal pregnancy?
Pregnancy in a woman lasts an average of 280 days, i.e. 40 weeks, or 10
obstetric months. Pregnancy often lasts less than this period
(230-240 days).
How is the estimated due date calculated?
To calculate the due date, add 280 to the 1st day of the last menstruation.
days, i.e. 10 obstetric (or 9 calendar) months, and 7 days. Usually calculation
produce easier - from the date of the 1st day of the last menstruation count back 3
calendar months and add 7 days. For example, if the last menstrual period
started on 11.12, then, counting 3 months ago (11.11, 11.10, 11.09) and adding 7 days,
determine that the due date should be 18.09.
What are the signs of pregnancy?
When determining the duration of pregnancy and childbirth, the time of the first movement is taken into account
fetus. In primigravidas, this happens at 20 weeks, in multiparous - at 18
weeks. To the date of the first fetal movement in primigravidas, 5 obstetric
months (20 weeks), in multiparous - 5 and a half obstetric months (22
weeks). Fetal movement is a subjective sign, which is taken into account as
auxiliary.
To determine the duration of pregnancy, objective data are of great importance.
examinations: the size and shape of the uterus, the volume of the abdomen, the length of the fetus, its dimensions
heads. In the first 3 months of pregnancy, its term is determined by the size of the uterus,
after 4 months - according to the height of the uterine fundus. Later, the volume of the abdomen is measured and
dimensions of the fetus.
How does the size of the uterus change during a normal pregnancy?
At the end of the first obstetric month, the size of the uterus corresponds to approximately
chicken egg, at the end of the second month - a goose egg, at the end of the third month, the uterus reaches
newborn head size. Starting from the fourth month, the size of the uterus is judged by
the height of the fundus of the uterus. At the end of the fourth month (16 weeks), the fundus of the uterus is located on
the middle between the pubis and the navel (4 transverse fingers above the symphysis); towards the end of V
months (20 weeks) - located 2 transverse fingers below the navel; by the end of VI
months (24 weeks) - at the level of the navel, at the end of the VH month (28 weeks) - for 2-3
finger above the navel, at the end of the Vni month (32 weeks) - in the middle between the navel and
xiphoid process. The navel begins to smooth out, the circumference of the abdomen is at the level
the navel is 80-85 cm. At the end of the 9th month (36 weeks), the bottom of the uterus stands at the xiphoid
process (the highest level of standing of the uterus), abdominal circumference 90 cm, navel
smoothed. By the end of the X month (40 weeks), the uterine fundus is determined at the VIU level of the month
(midway between the umbilicus and the xiphoid process). The navel is bulging
abdominal circumference 95-98 cm.
With the same standing of the uterine fundus in VHI and X obstetric months, the abdominal circumference
different, the position of the head is different: in the 8th month, the head stands high above the entrance
in the small pelvis; in the X month, as a rule, it is lowered, and in primigravida it is pressed
or a small segment is located at the entrance to the small pelvis.
How is the length and head of the fetus measured?
The length of the fetus is measured with a tazomer: one button of the tazomer is placed on the lower pole
heads, the other - to the bottom of the uterus, the resulting value is multiplied by 2 and from it
subtract 2-3 cm (depending on the thickness of the abdominal wall). By setting the length
fetus, divide this number by 5 and get the gestational age (in the second half).
The fetal head is measured with a tazometer: the buttons of the tazomer are set to the most
protruding points of the head (usually the forehead and back of the head). Fronto-occipital size
head in the VIII month is on average 9.5 cm, at the end of the IX month - 11 cm, at the end of the X
months - 11.5-12 cm.
ECTOPIC PREGNANCY
What are the causes of an ectopic pregnancy?
An ectopic pregnancy develops when the fertilized
the egg is implanted outside the uterine cavity. Depending on the site of implantation
distinguish between tubal, ovarian and abdominal pregnancy (very rare).
The main cause of ectopic pregnancy is changes associated with
inflammation of the tubes, preventing the normal progression of the egg into the uterus:
the egg settles in the tube and implants in its wall. Usually ectopic
pregnancy is interrupted at the 5-6th week, less often at the 8th or at the beginning of the 12th
weeks.
What are the signs of an ectopic pregnancy?
Until an ectopic pregnancy is terminated, it is characterized by a delay
menstruation, nausea and other signs of normal pregnancy.
Kvass signs of spontaneous termination of an ectopic pregnancy?
Termination of pregnancy occurs according to the type of tubal abortion and according to the type of rupture
pipes. When a pipe breaks, its entire wall is destroyed, a strong
bleeding, quickly leading to severe anemia, life-threatening.
When a pipe breaks suddenly or after a slight physical strain
there is an attack of severe pain in the lower abdomen, accompanied by fainting or
semi-conscious state. The pain radiates to the shoulder, shoulder blade, anus. In connection with
profuse bleeding into the abdominal cavity, anemia rapidly increases: skin and
visible mucous membranes turn pale, breathing quickens, blood pressure
falls, the pulse becomes frequent, soft. The abdomen may be swollen, painful,
palpation is determined by the positive symptom of Blumberg-Shchetkin.
What is emergency care?
If an ectopic pregnancy is suspected, the woman should be immediately
hospitalized by the most convenient mode of transport accompanied by
medical personnel. When the diagnosis is established, immediate
operation. With a large blood loss, blood and blood-substituting fluids are transfused,
use cardiac drugs.
MISSION OF PREGNANCY
What forms of miscarriage are distinguished in clinical practice?
Pregnancy can spontaneously terminate at any time. Interrupt
pregnancy up to 28 weeks is called a miscarriage, or abortion, and at 28-38
weeks - premature birth. Abortions are divided into early (up to 16 weeks) and
late (16-27 weeks). If miscarriage recurs more than 2 times,
this indicates habitual miscarriage.
What are the reasons for miscarriage?
The causes of miscarriage are numerous, complex and may not always be
be clarified. Etiological factors include infectious and
non-communicable diseases of the mother, infantilism, neuroendocrine disorders,
artificial abortions, intoxication of the body, complications of pregnancy,
chromosomal and gene anomalies, diseases and abnormal development of sexual
organs, immunological incompatibility of maternal and fetal blood, injuries,
spermatogenesis disorders. Currently the main cause of miscarriage
consider hormonal disorders, primarily functional
insufficiency of the ovaries and placenta, as well as an infectious factor, in particular
inflammatory processes of the genitals.
What are the common symptoms of an abortion?
In case of premature termination of pregnancy in terms of early abortion, fetal
the egg gradually exfoliates from the walls of the uterus, dies and under the influence of contractions
the musculature of the uterus is expelled from its cavity in whole or in part. At the same time, as
as a rule, spotting appears and intensifies. late abortion and
preterm labor proceeds according to the type of conventional labor: smoothing occurs
and opening of the cervix, rupture of amniotic fluid, birth of the fetus and placenta.
At the beginning of an abortion, there is a feeling of heaviness or dullness, and in a number
cases of cramping pain in the lower abdomen and lower back. This is the most
frequent symptoms of miscarriage. The sensation of pain may be intermittent.
relative rest. Pain indicates irritation of the neuromuscular apparatus
uterus as a result of an increase in its tone or the occurrence of contractions. Second
symptom - bloody discharge from the genital tract, indicating
the detachment of the implant that has begun - it usually happens with early abortions, with
late abortions and premature births are noted in cases of pre-lying
placenta. The amount of discharge depends on the degree of placental abruption.
How is the threat of premature termination of pregnancy treated?
Treatment of the threat of premature termination of pregnancy is carried out in
hospital. The patient is prescribed bed rest, suppositories with papaverine 0.02-
0.03 g 2 times a day, no-shpa, vitamin B. If placental abruption continues,
bleeding intensifies, then, as a rule, curettage of the cavity is performed
uterus to remove the remnants of the fetal egg, pieces of the placenta.
PREGNANT HYGIENE
What is pregnancy hygiene?
Hygiene of pregnant women should include activities aimed at
preservation and strengthening of the health of a woman whose body is experiencing
increased loads, antenatal protection of the fetus, preparation of the woman's body
to the normal course of childbirth and the postpartum period, to lactation and breastfeeding
feeding.
What personal hygiene rules should a pregnant woman follow?
A pregnant woman should take a shower 1-2 times a week, wipe daily
body with a towel soaked in water at room temperature, wash 2 times a day
external genitalia with warm water and soap (vaginal douching is not
sunbathing. Air baths are taken at an air temperature of 20-22
° С, starting from 5-10 minutes - and gradually increasing their duration to
20-30 minutes. In summer, short-term sunbathing is useful, and in winter and autumn -
ultraviolet irradiation. Swimming is allowed in warm weather,
for a short time if the pregnancy is proceeding normally.
What is prohibited during pregnancy?
Smoking and drinking alcohol are strictly prohibited, as poisonous
tobacco smoke products and wine alcohol pass through the plantar barrier and
can cause irreparable harm to the fetus, up to the development of deformities. .
In the first 3 and in the last 2 months of pregnancy, sexual activity is prohibited in order to
prevent infections, miscarriage and premature birth.
What does breast hygiene in pregnant women include?
A pregnant woman needs to systematically prepare the nipples of the mammary glands for
future feeding to prevent their cracks and mastitis. Bras must be
comfortable, made of natural fabrics, match the size and shape of the glands. glands and
nipples are washed daily with soap and water at room temperature and wiped
hard towel. If nipples are flat or inverted, in the last 2 months
pregnancy, they are massaged: daily after lubrication with boron
vaseline, the nipple is captured by the index and thumb and pulled into
for 3-4 minutes (2-3 times).
What are the basic requirements for maternity clothes?
Pregnant women's clothing should be comfortable and free, not restrict the chest.
cage, stomach, do not squeeze the lower limbs. For varicose veins
Elastic sanitary stockings must be worn or placed over the thighs and
shin elastic bandage. From the 7th-8th month of pregnancy for prophylaxis
bandage. Shoes should be in size, with wide heels.
What are the features of the labor regime during pregnancy?
The mode of operation during the normal course of pregnancy is normal with alternation
physical, mental labor and recreation. Pregnant women shouldn't lift weights
make sudden movements, experience psycho-emotional trauma. At home and
work around it, it is necessary to create an atmosphere of attention, care and respect.
Before going to bed, the duration of which should be at least 8 hours,
walks in the fresh air, airing the room, air baths are required.
OBSERVATION OF A PREGNANT WOMAN
What is the role of clinical blood tests during pregnancy?
A clinical blood test during pregnancy is performed several times,
especially in the second half of pregnancy; repeated blood tests give
the ability to timely identify diseases that require special treatment.
All pregnant women take blood twice (in the first and second half of pregnancy)
from the cubital vein for serological examination (Wasserman reaction,
Sachs-George). Treatment of identified patients is carried out in the venereological
dispensary with mandatory involvement in the treatment of the father of the unborn child.
All patients must determine the blood type and Rh affiliation; at
Rh-negative mother often has hemolytic disease
newborn. If a pregnant woman has Rh-negative blood
need to test the blood
and the husband. Leucorrhea in the father is Rh-positive blood and the fetus has inherited
Rh-affiliation of the father, then with such a pregnancy between the mother and the fetus
there is a Rh conflict: the fetus may die in utero, be born
prematurely or with signs of hemolytic disease.
What measures are taken when there is a threat of Rh-conflict between the mother and
fruit?
To increase the resistance of the fetus to the harmful effects of Rh antibodies and
improvement of placental circulation in all pregnant women with Rh-negative
desensitizing treatment is carried out with blood (in the period of 12-14, 22-24, 32-34
week of pregnancy). Therapeutic and preventive measures are designed to
creation of the most favorable conditions for the development of the fetus: food should be
rich in proteins, vitamin C (up to 1 g per day during pregnancy with
short breaks).
What is the role of clinical urine tests during pregnancy?
The kidneys during pregnancy function with great stress, as they
remove metabolic products from the body of both the pregnant woman herself and
growing fetus. Therefore, the urine of a pregnant woman must be examined at every
attending a antenatal clinic. If protein appears in the urine, a pregnant woman
take on a special account, and with an increase in protein, they must be hospitalized.
How is the weight gain of a pregnant woman monitored?
Weighing a pregnant woman is carried out at each visit to the antenatal clinic, not
less than once a month in the first half of pregnancy and every 2 weeks in the second
half of pregnancy. Weigh a pregnant woman without clothes, after urinating
and bowel movements.
What is the rate of weight gain during pregnancy?
In the first weeks of pregnancy, body weight should not increase. From the 16th week
pregnancy is weight gain; from the 23-24th week, the increase is 200 g per
week, and from the 29th week does not exceed 300-350 g. A week before delivery, the weight is usually
decreases by 1 kg, which is associated with fluid loss by tissues. throughout the pregnancy
body weight should increase by about 10 kg (due to the weight of the fetus, amniotic
water and placenta).
NUTRITION FOR PREGNANT WOMEN
What are the basic principles of rational nutrition of a pregnant woman?
Rational nutrition contributes to the normal development of pregnancy, fetus, and
It is also a prevention of the development of large fetuses, which significantly complicate
during pregnancy, childbirth, the postpartum period, neonatal and
postnatal development of newborns.
In the first half of pregnancy, a special diet is not required. The food must be
varied, containing a sufficient amount of proteins, carbohydrates, fats, salts
and vitamins. In the first months of pregnancy are not excluded, if necessary,
spicy and salty dishes, in the second half it is recommended mainly
dairy and vegetable food. Meat and fish should be consumed 3-4 times a week.
Spicy and spicy foods are prohibited, within reasonable limits
carbohydrates, flour products, starch and liquid.
What amount of proteins, fats, carbohydrates and trace elements should be in
daily diet of a pregnant woman?
The amount of proteins and fats is introduced into the daily diet at the rate of 1.5-2 g per 1 kg
woman's body weight. Carbohydrates as the main energy material and source
formation of fats, should be no more than 500 g per day (for obesity
the amount of carbohydrates is reduced to 300-400 g per day). For prevention
late toxicosis of pregnant women table salt in the second half of pregnancy
it is necessary to limit to 5 g per day, liquid to 1-1.2 lava last weeks -
up to 0.8 liters per day. The amount of trace elements, the sources of which are milk,
cottage cheese, eggs, liver, meat, bread, nuts, buckwheat and barley groats, beets, peas,
the second half of pregnancy should be: calcium - 1.5-2 g, phosphorus - 2 g,
magnesium - 0.5 g, iron - 15-20 mg per day.
What is the importance of vitamins for a pregnant woman?
In the diet of a pregnant woman, the vitamins that are part of
a number of enzymes and performing in the body the function of catalysts for processes
metabolism. With a lack of vitamins entering the body of a pregnant woman with
products of dairy and vegetable origin, ready-made
dosage forms.
What is the significance and daily requirement of vitamins A, PP, C, E for a pregnant woman?
Vitamin A (carotene) has an effect on the uterine mucosa, promotes
its regeneration, which is especially important in the postpartum period. Daily dose - 5000
ME, in the last months of pregnancy - 10000-20000 ME.
Vitamin PP (nicotinic acid) is involved in the metabolism of sexual
hormones, in low concentrations has a depressing effect on the contractile
function of the pregnant uterus. The daily dose is 18-25 mg.
Vitamin C (ascorbic acid) - a powerful catalyst
redox processes in the body, potentiates the action
estrogens, enhances the effect of pituitrin and mammophysin on uterine contraction.
The daily dose is 100-200 mg.
Vitamin C is involved in the regulation of calcium and phosphorus metabolism, is used in
obstetric practice for the prevention of rickets in the fetus. Daily dose - 1000 ME.
Vitamin E (tocopherol) plays an important role in the normal course of pregnancy
(fertility vitamin), its deficiency leads to dysfunction of the genital
organs, sometimes to fetal death and miscarriage. The daily dose is 20-25 mg.
What is the importance and daily requirement of B vitamins for a pregnant woman?
Vitamin Bj (thiamine) is involved in the regulation of estrogen hormone metabolism, synthesis
acetylcholine, promotes proper metabolism in the nervous system, liver,
regulates water-salt metabolism. The daily dose is 10-20 mg.
Vitamin B2 (riboflavin) contributes to the normal course of pregnancy and childbirth,
used to prevent threatened abortion, enhances
redox processes in the body. The daily dose is 2-3 mg.
Vitamin B6 (pyridoxine) is essential for the metabolism of essential amino acids
(histamine and tryptophan). The daily dose is 5 mg.
Vitamin B12 (cyanocobalamin) is effective in anemia caused by diseases
gastrointestinal tract and liver, enhances the release of growth hormone.
It is used for fetal hypotrophy. The daily dose is 0.003 mg.
TOXICOSIS OF PREGNANT WOMEN
What are the main symptoms and causes of toxicosis in pregnant women?
Toxicosis of pregnant women is a multi-symptomatic condition that occurs when
violation of the processes of adaptation of the woman's body to pregnancy. Wherein
there may be significant changes in metabolism, gland function
internal secretion, cardiovascular and other systems, in the content
electrolytes, hormones.
Predispose to the occurrence of toxicosis various diseases transferred
before pregnancy or during it, malnutrition, nervous strain,
fatigue, lack of sleep.
The development of late toxicosis is based on changes in capillary
circulation and vascular tissue permeability, i.e. the main disorders
occur in the vascular system. Distinguish toxicosis of pregnant women first
half of pregnancy, or early, and second half of pregnancy, or
later.
What refers to early toxicosis of pregnant women?
Vomiting, salivation, jaundice, dermatoses.
What is pregnancy vomiting?
Vomiting of pregnant women - the most common form of early toxicosis - is repeated
several times a day, most often after meals, accompanied by nausea,
decrease in appetite. There are mild, moderate (or moderate) and
excessive (or severe) vomiting. With a mild form, vomiting is repeated 3-5 times a day.
day, usually after eating, does not affect the general condition of the pregnant woman, it is easy
treatable and resolves on its own after 2-3 months
pregnancy. The moderate form is characterized by an increase in vomiting that occurs
regardless of food intake, up to 10-12 times a day and is accompanied by a decrease
body weight, general weakness, tachycardia, dry skin, decreased diuresis. At
excessive form of vomiting is repeated up to 20 or more times a day and causes severe
the condition of the patients. Hunger and dehydration lead to exhaustion, falling
body weight, loss of strength.
How does salivation occur in pregnant women?
Salivation may accompany vomiting and occur as an independent early
toxicosis of pregnant women. Daily salivation varies, sometimes reaching 1 liter and
more. Salivation depresses the psyche of the patient, causes maceration of the skin and
mucous membrane of the lips. Significant salivation causes symptoms
body dehydration.
What is the treatment for vomiting and salivation in pregnant women?
With vomiting and salivation of pregnant women, psychotherapy is carried out,
therapeutic and protective regimen, physiotherapy (ultraviolet irradiation,
electrosleep), drug treatment (bromine with caffeine, vitamins A, group B). AT
in severe cases, hospitalization is indicated.
What is pregnancy jaundice?
Jaundice of pregnancy is rare, manifested by icteric staining of the skin,
her itching, while the liver is affected. Pregnant women with jaundice urgently
hospitalized to determine its cause.
What are dermatoses of pregnancy?
Dermatoses of pregnancy include a group of skin diseases that appear during
pregnancy and disappearing after its termination. The most common itching
pregnant women, which captures the whole body (more often localized in the area of external
genital organs), causes insomnia, irritability. Less common eczema
pregnant, affecting the skin of the mammary glands or abdomen, thighs, arms. Sometimes
dermatoses of pregnant women can occur in the form of scarlatina-like rashes
skin or hives.
What conditions are related to pretoxicosis of pregnant women?
Expressed forms of late toxicosis of pregnant women are usually preceded by
conditions called pre-toxicoses. Doctor of women's consultation together with
a nurse identifies such conditions and takes measures to treat them,
to prevent more severe forms of toxicosis.
Pretoxicoses of pregnant women include such conditions in which there are:
1) increase in maximum blood pressure by 10-20 mm Hg. Art.,
minimum - by 5-10 mm Hg. Art. compared to baseline before pregnancy or
in the first 9-10 weeks of pregnancy; 2) pastosity of the shins or feet; 3) traces of protein
in urine. The state preceding toxicosis is indicated by a decrease in the daily
diuresis up to 500 ml, the presence of negative diuresis, an increase in the circumference of the lower leg,
measured at the level of 10 cm above the outer ankle, 8-10% in relation to its
size in the first half of pregnancy.
How is pretoxicosis treated?
For the treatment of pretoxicosis of pregnant women, a rational daily regimen is recommended,
appropriate diet, medications. Requires maximum
eliminate stressful situations, provide daytime rest and night sleep
lasting more than 8 hours. The amount of liquid is limited to 1 liter,
table salt up to 3-5 g. Unloading is carried out once or twice a week
g and glucose 1.0 g orally 3 times a day, oxygen cocktails or oxygen
tent. Light diuretics are used for 3-4 days.
What refers to late toxicosis of pregnant women?
Edema, nephropathy, preeclampsia, eclampsia.
What are pregnancy edema?
Water and sodium retention in tissues during pregnancy is clinically manifested by edema,
which are initially localized on the legs and feet, then can spread to
thighs, external genitalia, abdominal wall, face, upper limbs
(often observed simultaneously on the lower extremities and face). Sometimes
latent edema is formed, which is evidenced by an increase in body weight over
300-400 g per week. In 20-24% of cases, edema of pregnant women turns into nephropathy.
What is Nephropathy of Pregnancy?
Nephropathy of pregnancy is characterized by a triad of symptoms: edema, increased
blood pressure, the appearance of protein in the urine.
Pregnancy nephropathy often occurs against the background of extragenital diseases.
(hypertension, chronic nephritis, heart defects, diabetes mellitus).
Nephropathy most often develops at 32-36 weeks of gestation, although associated
its forms can be observed as early as 24-25 weeks.
What are the basic principles for the treatment of nephropathy?
Treatment of all forms of nephropathy in pregnant women, including medical and protective
regimen, a rational diet, the use of antihypertensive, diuretic,
antihistamines, improvement of microcirculation, carried out only in
hospital.
What is preeclampsia in pregnancy?
Preeclampsia is characterized by the addition of signs to nephropathy
functional disorders of the central nervous system that occur in
the result of increased intracranial pressure due to cerebral edema. Main
symptoms of preeclampsia: headache, blurred vision (flickering or "fog" in
eyes), pain in the epigastric region. Patients are usually agitated, restless or,
on the contrary, they are inhibited. Sometimes there is nausea or vomiting, the face is hyperemic
with cyanosis of the lips and wings of the nose. Most often, preeclampsia occurs against a background of severe
forms of nephropathy. Preeclampsia can be complicated by cerebral hemorrhage and
other vital organs, as well as go, sometimes quite quickly, into
eclampsia. Preeclampsia must be differentiated from acute
gastrointestinal disease and hypertensive encephalopathy. At
diagnosing preeclampsia in the antenatal clinic, the patient should be delivered
to the hospital under anesthesia for treatment. Often shown early
abortion.
What are the symptoms of eclampsia in pregnancy?
Eclampsia is the final stage in the development of late toxicosis and
characterized by seizures. Usually occurs against the background of preeclampsia. For
provocation of a seizure is sufficiently sharp light, noise, painful stimuli.
The seizure lasts 1-2 minutes and develops in a certain
sequences. In the first period (20-30 seconds) - preconvulsive -
small fibrillar twitches of facial muscles appear, spreading to
upper limb muscles. In the second period (20-30 seconds) occurs
tonic contraction of all skeletal muscles, the body stretches and tenses,
the spine is bent. Breathing and consciousness are absent, pupils are dilated,
increasing cyanosis of the skin and mucous membranes. In the third period (30-60 seconds)
clonic muscle spasms continuously following each other
trunk and limbs, the face becomes purple-blue. By the end of the attack
hoarse breathing appears, foam with an admixture of blood is released from the mouth
(biting the tongue). In the fourth period, the seizure resolves: convulsions
stop, breathing is restored, the face turns pink. The patient is in
coma, which can be of different duration, sometimes up to
next seizure. Consciousness is restored slowly. About what happened
the patient does not remember.
How is eclampsia pregnant treated and cared for?
Treatment is inpatient only. During a seizure, the nurse should
be near the patient, as it is necessary to prevent biting of the tongue and
fall injuries. To prevent biting the tongue into the patient's mouth from the side
a spoon wrapped in gauze is inserted between the molars. If appears
breathing, short-term oxygen supply is shown to eliminate hypoxia and
general anesthesia.
How is the prevention of toxicosis of pregnant women carried out?
Prevention of toxicosis of pregnant women includes the whole complex of necessary
hygiene measures, which in some cases must be carried out even before
pregnancy. For the prevention of early toxicosis,
the fight against abortion, the treatment of chronic diseases, the creation of a pregnant
emotional peace. In the prevention of late toxicosis, compliance with
rational nutrition in the second half of pregnancy, especially abstinence from
abundant intake of liquid and salt, the correct mode of work and rest,
elimination of mental and physical overload.
PHYSIOPSYCHOPROPHYLACTIC PREPARATION FOR BIRTH
What does physiopsychoprophylaxis of childbirth include?
Preparation of pregnant women for childbirth is a set of activities,
including physiotherapy exercises, ultraviolet irradiation and special
lessons.
What is the essence of psychoprophylactic preparation for childbirth?
The method of psychoprophylactic preparation of pregnant women for childbirth is based on the doctrine of
labor pain, in the formation of which not only irritation of the nervous
endings from the uterus and other genital organs, but also conditioned reflex
component associated with the effects on the second signal system. Wherein
It is recognized that the leading role in the occurrence of pain belongs to the cortex
brain.
The essence of the method is to create by means of verbal influence
more correct functional relationship between the cerebral cortex and
subcortical formations, reduce excitation in the subcortical centers and
balance the processes of excitation and inhibition in the cerebral cortex.
What is the purpose of psychoprophylactic preparation for childbirth?
The goal of psychoprophylactic preparation is to eliminate the fear of childbirth and other
negative emotions that arise during pregnancy, develop and consolidate
ideas about the birth act as a physiological and non-painful process,
bring up a new positive feeling associated with the upcoming motherhood.
How is psychoprophylactic preparation for childbirth carried out?
Psychoprophylactic preparation of pregnant women for childbirth begins with the first
visits to the antenatal clinic.
For classes on psychoprophylactic preparation of pregnant women for childbirth, which
carried out by a doctor or a specially trained midwife, a special room is allocated,
equipped with couches and teaching aids (drawings, posters, dummies). Total
5 lessons are held.
What is the role of exercise in the normal development of pregnancy?
Systematic physical education increases the body's resistance,
create a feeling of cheerfulness, strengthen the nervous system, improve the general condition,
appetite, sleep, work of the cardiovascular system, respiration, gastrointestinal
tract. Physical exercise strengthens the muscles of the abdominal wall, pelvic floor,
eliminate congestion in the pelvis and lower extremities, contribute to
the correct location of the fetus in the uterine cavity, the normal course of childbirth and
postpartum period. Physically trained women know how to manage their
breathing, which allows you to quickly and more fully saturate the body with oxygen.
How are physical education classes conducted?
Physical education classes are carried out mainly in a group way in the women's
consultations under the guidance of a physiotherapy instructor or
specially trained midwife with constant medical supervision. Allowed
performing physical exercises after appropriate training
individually at home with the condition of visiting a antenatal clinic every 10
days to check the correctness of the exercises.
Physical activity should be changed depending on the duration of pregnancy.
The duration of classes should not exceed 15-20 minutes. Study
well-ventilated and lit room in a special, unobstructed
clothes movement. If exercise makes you feel tired,
shortness of breath, increased heart rate - it is necessary to alleviate them and
consult a doctor. Jumps should be excluded from the complex of exercises,
significant straining, sudden movements.
Physical education can only be recommended to healthy women with
normal course of pregnancy.
PARTNERSHIPS
How is childcare provided?
The postpartum period lasts 6-8 weeks. Postpartum cleansing, or
lochia, the first 4 days are bloody in nature, and then turn pale, their number
gradually decreases; they have a characteristic smell of dampness. Appearance
a fetid odor indicates an incorrectly current postpartum period and
the need for appropriate remedial measures. Postpartum uterine contractions
are often painful, especially during breastfeeding. If a
they are very painful, you can give the puerperal as an analgesic
analgin, antipyrine or apply a candle with papaverine. External genitalia
the organs are washed, then dried with a dry sterile tupfer on a forceps, in
further (at home) drained with a special towel. If urination is
the first days after childbirth are somewhat difficult, hexamethyleptetramine is prescribed and
bearberry decoction. If the mother is unable to urinate on her own,
apply a heating pad to the bladder area, give a warm vessel, subcutaneously
enter magnesium sulfate, pituitrin. If these measures are unsuccessful within 7-8 hours
after childbirth, catheterization is performed as prescribed by the doctor.
In the first postpartum days, independent bowel function is difficult. On the 3rd
the day after childbirth, they put an enema or cleanse the intestines with a laxative.
Underwear and bedding should be changed every 4-5 days. If a woman is strong
sweating, linen should be changed more often. It is also necessary to change the bedding frequently (4-5
once a day), especially if the discharge is plentiful.
You can sit on the bed of the puerperal from the 2nd day of normal postpartum
period, and walking - from the 3rd day. Recently, healthy puerperas have to walk
allowed from the 2nd day after birth.
What are the characteristics of nutrition in the postpartum period?
On the first day, the puerperal receives liquid food, and on the following days passes
on a regular table. Food should be well cooked, tasty, rich
vitamins. From liquids, you can give tea, weak coffee, mineral water, fruit drink,
boiled water in a cool or warm form at the request of a woman.
Products passed by relatives must be strictly controlled
nurse. The number of products transferred and the assortment are usually
indicated in the rules of the obstetric hospital. Products must be in new
cellophane bag or wrapped in a clean napkin (clean paper).
How is the gymnastics of puerperas carried out?
In the postpartum period, gymnastics is carried out by a nurse collectively in
ward with all healthy puerperas. Gymnastic exercises haunt
the goal is to teach the puerperal to breathe correctly and deeply, to strengthen the muscles of the abdominal
press and pelvic floor, activate the muscular system and along with early
getting up to promote more brisk blood circulation. Gymnastics
is carried out daily in the morning, starting from the 2nd day after childbirth, after breakfast,
in summer - with open windows, in winter - after thorough ventilation of the ward.
Duration of classes - from 5 to 15 minutes, depending on well-being
(pulse, respiratory rate) of the puerperal. It is important that every postpartum woman continues
and regularly do gymnastics at home.
What regimen should the puerperal follow after discharge from the maternity
hospital?
In the maternity hospital, the puerperal is instructed about the rules of home regimen,
the implementation of which is checked by a nurse during patronage
home visits.
Sexual life with a normal postpartum period can be
resume no earlier than 8 weeks after birth, preliminarily
after consulting with a doctor.
The puerperal should observe the correct mode of work and rest: at home
work to be included gradually; sleep at least 8 hours a day and be sure to rest
afternoon; avoid heavy lifting and work that involves a lot of physical
load; to carry out gymnastics at first according to the scheme obtained in the maternity hospital, and
belts with water at room temperature with soap (for children), while washing and
milk glands; wash every other day in the shower with warm water and soap and a washcloth.
You can visit the bath or use the bath no earlier than 7-8 weeks after
childbirth. Mothers should wash their hands thoroughly before every feeding.
child and before eating, after cleaning the room, using the restroom, etc.
Nails should be cut short and not varnished. Morning and evening should
wash with warm water with baby soap or a solution of calendula (1 teaspoon
a spoonful of calendula tincture per 1 liter of boiled water); dry the genitals
washing with a special towel. It is necessary to observe the hygiene of linen and clothing;
change underwear every 3-4 days and bedding at least once a week; on the
put on a nightgown at night; wear a bra that is well supported and not too tight
squeezing the mammary glands, often change it; wear a bandage for 4
months after childbirth, and in some cases (with a very stretched, sagging abdomen)
Constantly. At least 3-4 hours daily should be in the fresh air,
thoroughly ventilate the room and bedding.
What diet should be followed by the puerperal after discharge
from a maternity hospital?
You need to eat fresh food. Especially useful are buckwheat and
oatmeal with milk, kefir, curdled milk, varenets, cottage cheese, honey, jam, tea with
milk, fruit and vegetable juices, berries, boiled and raw fruits after
washing them with boiled water. Do not eat spicy food, alcohol
beverages. It is important to monitor daily bowel movements.
How many days after childbirth does the puerperal visit the antenatal clinic?
The puerperal should visit the district doctor of the antenatal clinic approximately
7-10 days after discharge from the maternity hospital. In case of occurrence of any
complications (fever, bleeding, excessive engorgement
mammary glands, the appearance of painful nipple cracks, etc.) should be immediately
go to a women's clinic.
MASTITIS
What causes mastitis in the postpartum period?
In the postpartum period, acute mastitis (inflammation of the breast) is most often
It is caused by Staphylococcus aureus, which is resistant to many antibiotics.
The causative agents of infection enter the mammary gland mainly through
cracks in the nipples (lymphogenous) or through the milk ducts.
What forms of mastitis are isolated in clinical practice?
The inflammatory process captures individual lobules of the gland, and often whole
lobe (serous mastitis). If the infiltrate does not resolve, then it occurs
suppuration (purulent mastitis). In severe cases, it comes to phlegmonous
mastitis.
What are the main symptoms of mastitis?
Symptoms of the disease depend on the stage of the process. characteristic feature
mastitis in modern conditions is its late onset, mainly
after discharge of the puerperal from the hospital (at the 2-3rd week after childbirth). Mastitis
begins acutely with the appearance of pain in the affected mammary gland, a sharp rise
temperatures up to 38-39 "C. Characterized by chills and poor general health. Pain in
mammary gland gradually increases, especially when feeding a child. Gland
increases in volume, the skin in the affected area is somewhat hyperemic. At
palpation in the thickness of the gland, areas of densely elastic tissue are determined
painful textures. After 1-3 days, serous mastitis turns into
infiltrative. Under the changed area of the skin begins to palpate
dense sedentary infiltrate, painful on palpation; often
there is an increase and soreness of the axillary lymph nodes.
With suppuration of the infiltrate, the general condition worsens significantly, high
temperature becomes constant, there is severe pain in
affected mammary gland, chills.
What is emergency care and treatment for mastitis?
With serous and infiltrative forms of mastitis, it is necessary to empty the milk
gland (expressing milk with hands or a breast pump). To improve outflow
milk is injected intramuscularly with 1 ml of oxytocin solution. In the initial stage
disease, short-term use of a local ice pack is acceptable - on
20-30 minutes with breaks of 20 minutes. Moving on to treatment
warming compresses with Vishnevsky ointment or butadiene ointment.
Considering the dominant role of Staphylococcus aureus in
initial forms of mastitis, semi-synthetic penicillins are prescribed:
oxacillin sodium salt, or ampicillin sodium salt, or
ampiox-sodium. With insufficient effectiveness of antibiotic therapy
sulfonamides are additionally prescribed. Along with this, the means
increasing the specific immunological reactivity of the body:
antistaphylococcal gamma globulin 5 ml (100 IU) intramuscularly every other day;
antistaphylococcal plasma, 100-200 ml intravenously;
adsorbed staphylococcal toxoid 1 ml subcutaneously with an interval of 3-4
days, for a course of 3 injections; transfusion of blood plasma in 150-300 ml. Enter
antihistamines.
POSTPARTUM THROMBOPHLEBITIS
What is the general characteristic of postpartum thrombophlebitis?
Postpartum thrombophlebitis is an inflammation of the vein wall with subsequent
the formation of a thrombus in this area, completely or partially covering
vessel lumen.
By localization, thrombophlebitis is divided into thrombophlebitis of the veins of the uterus, veins of the pelvis and veins
hips. Thrombophlebitis of the veins of the uterus occurs on the basis of endomyometritis.
What are the main symptoms of this complication?
The general condition of the patient worsens, the pulse becomes frequent, superficial.
The discharge is bloody and quite copious. Under adverse conditions
the process extends to the veins of the pelvis. As the process progresses
thrombophlebitis of the femoral veins occurs, which is clinically manifested on the 2nd-3rd
week after childbirth. Initially, chills, rapid pulse, high temperature,
pain in the legs, especially in the calf muscles. Locally determined smoothness
inguinal region, induration and soreness along the vein, swelling of the leg, sometimes sharply
expressed. Elevated temperature lasts 2-3 weeks, swelling - 1-2 months.
What are the possible complications of thrombophlebitis?
With an unfavorable course, thrombophlebitis can suppurate and be the main
source of septicopia. Dangerous pulmonary embolism on the soil
thrombophlebitis.
What treatment do patients receive?
Patients are shown absolute rest with a high position of the legs (with thrombophlebitis
hips). Do not use intravenous infusions. Placed on the lower abdomen
ice pack showing leeches along the affected leg vein. Antibiotics
combined with the use of antispasmodics (promedol, papaverine). In some cases
surgical operation - thrombectomy is shown.
After suffering thrombophlebitis, it is recommended to bandage the legs with an elastic
bandage or wearing elastic stockings.
THERAPEUTIC-PROTECTIVE AND SANITARY REGIME OF OBSTETRIC
HOSPITAL
What is a health care regimen?
Therapeutic-protective regime implies careful and preventive
attitude to the requests of patients, calm tone in conversation, cleanliness. it
all - the most important tasks of a nurse working in an obstetric hospital,
in the antenatal clinic and polyclinic. Positive emotions help
increase the reactivity of the body, faster recovery. pregnant,
especially in pathologically proceeding pregnancy, puerperas after
endured great physical and mental stress, which are childbirth,
need favorable conditions for rest and sleep. Need to support
appropriate room temperature. The mother should be provided with
during the day at least 8-9 hours of good sleep with mandatory continuous
night sleep for at least 6 hours. All manipulations, diagnostic and therapeutic
procedures should be carried out by a nurse painlessly.
It is necessary to try to ensure that every pregnant woman is prepared in a timely manner in
antenatal clinic, at the feldsher-obstetric station to a painless
the course of childbirth by conducting special classes - conversations according to the method
psychoprophylactic training.
What sanitary and hygienic and disinfection measures are carried out in
maternity ward?
The sanitary and hygienic maintenance of the maternity bed plays an important role in
prevention of postpartum infections. The couch in the examination room must be covered
oilcloth, which must be treated with a disinfectant solution after
examining every woman. Before the examination, each woman is laid a clean
lining diaper.
In the delivery room, an oilcloth mattress is wiped with warm water after each birth.
soapy water to remove the blood, then a solution of mercury dichloride (mercuric chloride) or
lysoform and cover with a clean lined oilcloth, and put under the woman in labor
sterile diaper. The lining oilcloth is washed in the washing room on the installed
inclined board under running warm water with soap and a brush, then washed
mercury dichloride solution (sublimate) and dried on a special rack.
Each puerperal must have an individual vessel with a number,
corresponding to the number of this bed, which is boiled once a day, and after each
use, wash with water and a disinfectant solution.
What sanitary-hygienic and disinfection measures are carried out
after discharge of puerperas from the hospital?
After discharge of the puerperal, the bed and oilcloth are washed with water and disinfectant.
solution, mattress, pillow and blanket are aired for at least a day. Disinfect
her. individual vessel, for which they first rinse with tap water, and then
steam sterilized or boiled. Linen removed from the patient should be
separately, before being sent to the laundry, it is soaked in a solution of lysol in
special tank with a lid.
In the obstetric department, as well as after feverish or dead puerperas
processing is carried out especially carefully: the beds are washed and treated with a solution
mercury dichloride, mattresses are ventilated for 2 days.
Folic acid (vitamin B9) is considered one of the main vitamins for a pregnant woman. Folic acid deficiency can cause early birth or mental underdevelopment of the fetus. On the other hand, B9 prevents anemia in the future mother and her child, is responsible for the normal condition of the skin and mucous membranes.
Therefore, in the diet of pregnant women, especially in the first half of pregnancy, fish, meat, raw vegetables and fruits, and dairy products must be present.
NB! Folic acid is destroyed during heat treatment, however, it is better preserved in meat products and milk.
It is very difficult to maintain a healthy diet when the body refuses to accept even the most ordinary foods - it is not up to it now, it is struggling with nausea and dizziness.
In these first weeks of pregnancy, the need for salty, spicy, etc. can be satisfied (of course, within reasonable limits) without damage to health.
In the fight against toxicosis, only natural, natural remedies are good. No drugs! Only the right products and diet. It is recommended to use the most easily digestible foods. In the morning, while still lying in bed, you can eat light yogurt or an apple.
A person is being formed at full speed. He is waiting for his mother to help him with building materials! Among the most important substances now are calcium and phosphorus. In the most optimal ratio, they are found in milk and dairy products.
7-8 weeks.
Pregnant women can’t go without milk, because milk in its pure form is calcium, phosphorus, folic acid and other B vitamins, vitamin E, fluorine, complete protein, animal fats.
Moreover, it is in milk that calcium and phosphorus are contained in that ideal proportion of 2: 1, in which both elements are best absorbed. Unfortunately, not all people can consume milk due to the fact that their body lacks the enzyme responsible for the absorption of milk and dairy products. Kefir and live yogurt combine all the best properties of milk, multiplied by the ease of absorption by the body.
10 week.
Iron is part of hemoglobin and ensures the normal process of hematopoiesis. Just what mom and baby need right now! The best absorbed iron is found in animal products. Especially a lot of iron in cottage cheese. Calcium and fluoride will help the development of the baby's teeth. Fluoride is found in meat, fish, milk, greens, fruits.
11 week.
Zinc is responsible for the development of the organs of smell and taste, the reproductive system and hematopoiesis. Most zinc in cheese, seafood, meat, legumes and nuts. Strengthens the immune system, helps the process of blood formation in the mother's body and the work of her heart muscle vitamin E. Vegetable oils, wheat germ, soybeans, broccoli, Brussels sprouts, leafy greens, spinach, whole grains, eggs.
12 week.
The risk of premature placental rupture is significantly reduced by increasing the dietary intake of vitamins C and E. Iodine is essential for the normal functioning of the thyroid gland. With hypofunction of the thyroid gland, growth retardation is observed due to inhibition of metabolism. The main source of iodine is seafood.
13 week.
During the first trimester, the expectant mother is unlikely to gain more than 1-3 kg in weight. But starting this week, you will have to closely monitor your weight and, of course, your diet. "Overdial" or "not enough" - is equally harmful. And this is the main problem of the next three trimesters.
If in the first trimester, when compiling her daily diet, the expectant mother constantly had to take into account the hormonal vagaries of her body and fight toxicosis with all her might, then starting from the second trimester, the situation will change somewhat.
The two main causes of poor digestion during pregnancy are dysbacteriosis and compression of the abdominal organs due to an increase in the volume of the uterus. In the event of constipation, in no case should laxatives be used. This problem should be solved only with the help of diet.
Fresh, stewed, baked vegetables and fruits, herbs will become especially relevant. Daily consumption of 30 grams (2 teaspoons) of bran will help the intestines get rid of all the excess.
Now you should start switching to a new diet. If in the first trimester it was possible to maintain four meals a day, then from the second trimester until the end of pregnancy, you need to eat more often, but in smaller portions.
Department of Public Health of the Kemerovo Region
State budgetary professional educational institution
"KEMEROVSK REGIONAL MEDICAL COLLEGE"
Prokopevsky branch
(PF GBPOU "KOMK")
Methodological development of a practical lesson
PM. 04. Participation in medical diagnostic and rehabilitation processes
MDK. 02.01. Nursing care for various diseases and conditions / Nursing care in obstetrics and gynecology
for specialty 34.02.01 nursing
Lesson #1
Topic: "Planning nursing care for pregnant women, childbirth and the postpartum period"
Compiled by the teacher: Prokhorenko M.V.
Learning goal: To form a system of knowledge about the normal course of pregnancy, physiological changes in organs and systems, hygiene of pregnant women.
Development goal: To develop interest in the subject, to promote the activation of students' thinking. To develop the cognitive activity of students, to master the program educational material.
educational goal: To form a conscious attitude to the learning process, the desire for independent work and comprehensive mastery of the specialty
The student must know:
methods for diagnosing pregnancy
signs of pregnancy
the role of the nurse in women's health and her responsibilities when working in the antenatal clinic;
anatomy of the pelvis and its main dimensions, the structure of the fetal head.
instruments for examination and examination of pregnant women.
a scheme for examining a pregnant woman in a antenatal clinic
paperwork for pregnancy
pregnancy hygiene.
pregnant diet.
psychoprophylactic preparation of a pregnant woman for childbirth .
The student must be able to:
Conduct an external examination of the genitals,
Measure the outer dimensions of the pelvis.
Use the simplest test to determine pregnancy.
Determine the gestational age and the term of childbirth by the date of the last menstruation and by the first movement of the fetus.
Be able to examine the cervix and vagina in the mirrors (on a phantom).
Take material for bacterioscopic examination (on a phantom)
Conduct an external obstetric examination (Leopold's maneuver)
Measure the circumference of the abdomen and the height, standing of the fundus of the uterus.
Listen to the fetal heartbeat.
Conduct a conversation on hygiene and nutrition of pregnant women.
Have practical experience:
Planning and implementation of nursing examination
communication with patients
history taking and examination of patients
documentation of nursing documentation
Formed competency elements:
PC 1. Present information in a form understandable to the patient, explain to him the essence of the interventions.
PC 2. To carry out medical and diagnostic interventions, interacting with participants in the treatment process.
PC 5. Comply with the rules for the use of equipment, equipment and medical products in the course of the treatment and diagnostic process.
PC 6. Maintain approved medical records.
PC 8. Provide palliative care.
OK 1. Understand the essence and social significance of your future profession, show a steady interest in it.
OK 2. Organize your own activities, choose typical methods and methods for performing professional tasks, evaluate their performance and quality.
OK 5. Use information and communication technologies in professional activities.
OK 7. Take responsibility for the work of team members (subordinates), for the result of completing tasks
Lesson type: development and consolidation of knowledge, skills
Class type: practical lesson
Interdisciplinary connections Keywords: clinical pharmacology, nursing in pediatrics, nursing in surgery, fundamentals of resuscitation, human anatomy and physiology, basics of pathology, psychology, a healthy person and his environment.
Lesson equipment:
obstetric phantoms
obstetric and gynecological instruments
gloves,
antiseptic solution
manipulation algorithms
projector
multimedia presentation
test forms, prescriptions, individual card of pregnant women
methodical development of a practical lesson
Literature:
main: Slavyanova, I.T. Nursing in obstetrics and gynecology [Text]: SPO textbook / I.T. Slavyanova - Rostov-on-Don, "Phoenix", 2014. - 395 p.: ill.
additional:
1 Androsova, E. N., Ovrutskaya, Z. L., Novitsky, S. N., Marchenko, A. M. Obstetrics and Gynecology. Methodological recommendations for performing manipulations. - M.: "ANMI", 1995 - 64s.; 39 ill.
2. Slavyanova, I. T. Nursing in obstetrics and gynecology
[Text]: Workshop. SPO / I.T. Slavyanova - Rostov-on-Don: Phoenix, 2002. - 352 p.
3 Krylova, E.P. Nursing in obstetrics and gynecology [Text]: SPO textbook / E.P. Krylova-Rostov-on-Don: "Phoenix", 2000. - 384 p.
Electronic sources:
Internet sites.
Electronic supplement to the “National Guide. Obstetrics" - M.: GEOTAR-Media. – 2007.
Electronic supplement to the textbook "Obstetrics. Textbook for obstetric departments of secondary specialized medical institutions. ed. V.E. Radzinsky - M.: GEOTAR-Media. - 2008.
Electronic supplement to the textbook "Women's consultation" ed. V.E. Radzinsky M.: GEOTAR - Media - 2009.
Electronic supplement to the practical guide "Infections in
Lesson structure
Organizing time
Setting goals and objectives for the lesson
Motivation
Updating basic knowledge
Instruction for independent work of students / demonstration of manipulations
Independent work of students
Summing up the lesson, checking diaries, marking (diagnostics)
Homework
| № p/p | Elements of the lesson, training questions | (min) | Teaching methods and techniques |
| Organizing time | |||
| 1.1. Greeting students, checking absentees | The teacher welcomes, notes the absent |
||
| 1.2. Lesson Plan Lighting | The teacher voices the topic, (written on the blackboard) |
||
| Setting goals and objectives for the lesson | The teacher sets the goals and objectives of the lesson |
||
| Motivation During pregnancy from the moment of conception to childbirth, a pregnant woman should be under the supervision of a antenatal clinic doctor. Early registration allows you to accurately determine the duration of pregnancy, timely resolve the issue of maintaining pregnancy in women suffering from any diseases, and most effectively prevent pregnancy complications. When examining women, problems arise: fear of manipulation, expectation of pain, anxiety. The nurse must learn how to conduct preventive examinations and conversations, observe ethical standards, reduce the feeling of fear, be able to calm the patient, explain the need for manipulation, prepare the pregnant woman for the study. | The teacher gives concepts and asks students about the role of a nurse in obstetrics, how they see it in their future profession |
||
| Updating basic knowledge | Situational tasks (presentation). Blackboard work. Pair work. Frontal survey |
||
| Instruction for independent practical work includes issues of labor protection and explanations to students of the course of the practical lesson. | Studying instructions - |
||
| Break (airing the audience, physical education) | Health saving |
||
| Doing practical work. | Work in pairs. Group work. Individual work. Performing manipulations according to the instructions of the teacher. |
||
| Summing up the lesson, marking (diagnostics) Reflection | The teacher evaluates each type of student's work (oral frontal and individual surveys, SIW, filling out a workbook and practice diary), based on the assessments of each type of activity, an overall grade for the practical session is given and informs the student about it. Marks the best and weak answers of students, gives recommendations for improving students' knowledge and reports the topic and homework of the next practical lesson |
||
| Homework : | Slavyanova I.T. Nursing in obstetrics and gynecology [Text]: SPO textbook. / I.T. Slavyanova - Rostov-on-Don, "Phoenix", 2014. – 395 p. : ill. |
Oral face-to-face interview
What does an obstetric and gynecological history include?
Rules for conducting pelvimetry?
Characteristics of the size of the pelvis.
4. Changes in a woman's body during pregnancy
5. Determination of the gestational age.
6.Methodology of the study of pregnant women
CPC: Preparation of abstract messages on the topic:
"Modern research methods in obstetrics"
"Birth Pain"
"Prevention of postpartum infectious and toxic diseases in an obstetric hospital"
"Modern diagnostic methods in gynecology"
Work of students in groups: "Diagnosis of pregnancy"
Exercise 1
There are three groups of signs and the signs themselves on your tables. Lay out the signs of pregnancy and list them.
probable: cessation of menstruation, enlargement of the mammary glands, cyanosis of the mucous membranes of the vagina and cervix, changes in the size, shape and consistency of the uterus.
reliable: palpation of small parts of the fetus, listening to the fetal heartbeat, fetal movement
hypothetical: nausea, vomiting, change in appetite, pigmentation on the face, white line of the abdomen, changes in the central nervous system - irritability, drowsiness, fatigue.
Task 2. Solution of situational problems
Situational tasks:
TASK 1. Patient J., 22 years old, first pregnancy. Last period August 22; first fetal movement on January 14th.
by menstruation;
by the first movement of the fetus.
Questions. Estimated due date:
by menstruation;
by the first movement of the fetus.
Patient I., 24 years old, second pregnancy, first delivery normal. Last period February 16; first fetal movement June 30th.
Questions. Estimated due date:
by menstruation;
by the first movement of the fetus.
TASK 4 Patient N., 21 years old, pregnancy 1. Last menstruation April 3; first fetal movement August 27
Questions. Estimated due date:
by menstruation;
by the first movement of the fetus.
or slide presentation
Blackboard work. Drag the cards to the right places on the picture.
anterior view, first position, cephalic presentation;
rear view, first position, cephalic presentation;
anterior view, second position, cephalic presentation;
rear view, second position, head presentation;
anterior view, first position, breech presentation;
rear view, first position, breech presentation,
anterior view, second position, breech presentation;
rear view, second position, breech presentation.
Business game "Admission to the antenatal clinic"
goal: to teach the correct sequence of examination of a pregnant woman, the manipulations carried out in the antenatal clinic
is selected from students: Senior Nurse, Nurse working with documentation, "Patient".
Equipment: Individual map of a pregnant woman, test forms, prescriptions.
task number 1 (the work of students in turn).
conduct (questionnaire, anamnesis, anthropometry, blood pressure measurement, pelvimetry.)
write down the results in the individual card of the pregnant woman.
task number 2 (second student)
Prepare the following tools for external examination: obstetric stethoscope, centimeter tape, tazomer, tonometer with phonendoscope, disinfectant solution, cotton balls.
obstetric and gynecological examination: vaginal examination, bimanual examination, examination in the mirrors.
task number 3
cover the table for examining the patient in the gynecological chair and for taking smears.
gloves, cortsang, tweezers, glasses, Cuzco mirrors, spoon-shaped mirrors, disinfectant solution, container with disinfectant solution, sterile balls, skin asepsis, Volkmann's spoons, Air's spatula.
task number 4
check in mirrors
take a smear for the degree of purity of the vagina, pronouncing the algorithm of action
choose from the directions and forms for tests that I have proposed for discharge of a pregnant woman.
Task number 6 (the whole subgroup)
Write a prescription for folic acid tablets No. 50 for oral administration
Reflection.

test control:
7 minutes to answer. One correct answer.
Menstrual cycle- this is
1. attachment of the egg to the wall of the uterus
2. cyclical changes in a woman's body
4. egg capture from the abdominal cavity
2. Menstruation is
1. the release of the egg from the follicle
3. rejection of the functional layer of the endometrium
3. Internal genitals
1. pubis
4. labia
4. Involved in the regulation of the menstrual cycle
1. parathyroid glands
2. hypothalamic-pituitary system
3. adrenal glands
4. pancreas
5.. In the ovaries are formed
1. estrogens
2. prolactin
3. blood cells
4. enzymes
6. A hormone is formed in the corpus luteum
1.estradiol
2. insulin
3.progesterone
4. oxytocin
7. Rupture of the follicle and release of the egg into the abdominal cavity
1. menstruation
2. ovulation
3. fertilization
4. implantation
8. Implantation of the ovum
1. accumulation of secretions in the uterine glands
2. attachment of the fetal egg to the wall of the uterus
3. the release of the egg from the follicle
4. fusion of nuclei of germ cells
9. The main component of the placenta
1. muscle tissue
2. epithelium
3. villi
4. uterine glands
10. Fetal membrane secreting amniotic fluid
1. chorion
3. decidua
4. myometrium
11. When vomiting, pregnant women are prescribed
1. papaverine
3. heparin
4. cerucal
12. Complication of reproductive function due to induced abortion
1. infertility
2. prolapse of the genitals
3. polyhydramnios
4. multiple pregnancy
Scheme of examination of a pregnant woman in a antenatal clinic:
STANDARDS OF ANSWERS
Clarification of basic passport data:
The number of the passport and insurance certificate are recorded. The surname, name, patronymic of the woman is found out (it is necessary to find out how the woman wants to be called, the midwife must introduce herself to the woman, and also introduce the doctor who will lead her, or the doctor will do it). Age (risk factors include young age up to 18 years, after 30 for nulliparous and more than 35 for multiparous). Home address and phone number (registration and residence, it is preferable that a woman be observed at the place of residence, this is convenient for patronage, however, in modern conditions, given the availability of convenient means of communication, the registration option is also possible).
the living conditions are specified, with whom the woman lives together, what are the amenities. Place of work and profession (working conditions, the presence of occupational hazards are immediately specified, in this case, exemption from hazardous work is provided).
Husband details:
(Full name, age, place of work and profession, the presence of occupational hazards). It is necessary to ask: which of the relatives can be contacted, whom the woman trusts most of all, if necessary. All of this information should be on the first page. Also, the most important information about risk factors is placed on the first page in natural or coded form.
Collection of complaints:
A healthy pregnant woman may not have complaints. Nevertheless, it is necessary to find out if she has any discomfort, pain. In the study of subsequent topics, those complaints that need to be identified will be studied.
Collection of anamnesis:
Information about the conditions of work and life. It is necessary to find out the nature of the work, what is the harmfulness of the workplace, and also to clarify what kind of work the woman does at home, to warn about the exclusion of excessive workload, household hazards, and also to find out if there are animals at home (probability of infection). Find out about the woman's education and interests, which will help improve contact with her.
Heredity:
To identify a hereditary predisposition in a pregnant woman: did the parents have diabetes, hypertension, other endocrine, genetic diseases. It is important to know the heredity of the husband. It is necessary to obtain information about the bad habits of the pregnant woman and her husband, to give recommendations.
And Information about past illnesses:
Children's infections, colds, diseases of the cardiovascular system, diseases of the urinary system, liver, initial blood pressure, etc. First of all, ask about tuberculosis, rubella and infectious hepatitis.
To find out whether the woman has recently come into contact with tuberculosis and infectious patients, whether she has such patients at home, to find out about her recent trips to epidemiologically disadvantaged areas.
Separately ask about surgical interventions, whether there was a blood transfusion. Ask about the features of the menstrual function (from what age menstruates, duration, regularity, frequency, painful menstruation, profusion of discharge). From what age did sexual life outside of marriage, in marriage, by what means was it protected from pregnancy. List the transferred gynecological diseases, sexually transmitted diseases (the health of her sexual partner - the father of the child).
In order of priority, list all pregnancies, their outcome and complications. Tell separately about the course of this pregnancy before registration.
The following is a general inspection in which attention is paid to height, weight, posture, physique, nutrition, condition of the skin, subcutaneous tissue, blood vessels, lymph nodes, and the presence of edema. Examine the pulse and blood pressure, heart sounds. They measure the temperature and conduct an examination of the nasopharynx, listen to the lungs. They palpate the abdomen, liver, check the symptom of tapping on the lower back, are interested in physiological functions.
Measurement of blood pressure in a pregnant woman
Purpose: to teach a student to measure blood pressure in a pregnant woman and record the obtained data in an individual card of a pregnant woman.
Equipment:
Tonometer;
Stethoscope;
Execution Method:
Explain to the woman the need for the procedure;
To acquaint the woman with the course of the procedure and the need for its implementation;
Seat the pregnant woman to the table, putting her forearm in a horizontal position on the table (clothes should not squeeze the arm above the forearm); you can measure blood pressure in the "lying" position;
Fasten the cuff tightly so that only a finger passes between it and the shoulder;
Put your hand with your palm up in an unbent position, asking the pregnant woman to relax;
Connect the pressure gauge to the cuff;
In the region of the cubital fossa, feel for a pulse and put a phonendoscope in this place;
Close the valve on the pear and pump air with it until the pressure in the cuff exceeds 20 mm Hg. Art. (or units) the level on the scale at which the pulse ceases to be determined;
Open the valve and slowly release the air from the cuff, listening with the help of a phonendoscope tones on the brachial artery, simultaneously following the scale readings;
When a sound appears on the brachial artery, note the level of systolic pressure;
The moment of disappearance of tones on the brachial artery corresponds to the level of diastolic pressure;
Release the air from the cuff completely and repeat the procedure on the second arm;
Record the data obtained when measuring blood pressure on both arms in an individual card of a pregnant woman;
Wash and dry your hands.
Pulse study
Equipment:
Stopwatch;
Execution Method:
Explain to the woman the purpose, necessity and course of the procedure;
It can be carried out in the position of "sitting" and "lying";
Put the second, third and fourth fingers of the right crayfish on the region of the radial artery: the first finger - from the rear of the hand, the second and third - on the radial artery;
Press the artery against the bone, feeling its pulsation;
Mark and characterize the rhythm of beats and their clarity (pulse tension);
Record the data obtained in the individual card of the pregnant woman;
Wash, dry your hands.
MEASURING THE EXTERNAL DIMENSIONS OF THE PELVIS
Purpose: to teach the student to measure the main dimensions of the pelvis using a pelvis meter and fix it in the individual card of the pregnant woman.
Equipment:
Couch;
Tazomer;
Cotton or gauze balls;
70% ethyl alcohol;
Individual card of a pregnant woman;
Oilcloth.
Execution Method:
Explain to the woman the purpose, necessity and course of the procedure;
Lay the pregnant woman on the couch, spreading an oilcloth under it (under the buttocks and under the legs), in the “on the back” position with straightened legs;
Sit or stand to the right of the couch facing the woman;
Pick up the tazomer so that the scale is turned upwards, and the first and second fingers lie on the buttons of the tazomer;
Wipe the buttons of the tazomer with a ball of alcohol;
Palpate the anterior-superior iliac spines with the index fingers, attach the buttons of the tazomer to them - the spinarum distance (normally, the size corresponds to 25-26 cm);
Move the buttons of the tazomer to the most distant points of the iliac crests (the normal distance of the cristarum is 28-29 cm);
Find with your index fingers the large trochanters of the femur;
Press the buttons of the tazomer to the large skewers of the femurs;
Determine the distance between the large trochanters of the femurs on the scale of the tazomer (the distance of the trachanteric normally corresponds to 30-31 cm);
Invite the woman to lie on her side with her back to the midwife, the lower leg is bent, the upper leg is straight;
Put one button of the tazomer on the upper edge of the pubic joint, and the second - in the upper corner of the Michaelis rhombus, determine the distance on the scale of the tazomer (outer conjugate is normally 20-21 cm);
To obtain the value of the true conjugate, you need to subtract 8-9 cm from this figure, which will correspond to 12-13 cm;
Enter the obtained data in the individual card of the pregnant woman in the columns:
a) dist. spinarum:
b) dist. cristarum
c) dist. trachanterika
d) con. externa
Treat the tazomer with a ball of alcohol;
Wash and dry your hands.
All subsequent studies are carried out in the second half of pregnancy.
Measuring the circumference of the abdomen
Purpose: to teach the student to measure the circumference of the abdomen of a pregnant woman using a centimeter tape and record the result in an individual chart of the pregnant woman.
Equipment:
Couch;
Tape measure;
Oilcloth;
70% ethyl alcohol;
Pregnant individual card.
Execution Method:
If it is difficult for a woman to stand, lay her on a couch with straightened legs, placing an oilcloth under her buttocks;
Stand or sit to the right of the pregnant woman, facing her;
Wipe the measuring tape with a ball moistened with alcohol;
Bring the measuring tape under the back so that it is at the level of the navel in front, and at the back - at the level of the lumbar region;
Mark on the scale of the centimeter tape the volume of the abdomen at the level under study;
Help the pregnant woman get up from the couch, first turning on her side, and then sitting on the couch;
Throw the oilcloth into a basin;
Wash and dry hands;
Enter the result obtained during the measurement in the individual card of the pregnant woman.
Leopold's first reception: Determining the height of the uterine fundus
Purpose: To teach a student to measure the height of the uterine fundus using a centimeter tape and record the data in an individual card of a pregnant woman.
Equipment:
Couch;
Cotton balls;
70% ethyl alcohol;
Oilcloth;
Tape measure;
Pregnant individual card.
Execution Method:
Explain to the woman the purpose, necessity and progress of the procedure;
Warn about the need to empty the bladder;
Lay the pregnant woman on the couch with straightened legs, spreading an oilcloth under the buttocks;
Sit to the right of the woman, facing her;
Wipe the measuring tape with a ball of alcohol;
Apply a centimeter tape vertically along the midline of the abdomen; from below, the centimeter tape should touch the upper edge of the symphysis, from above - the highest point of the fundus of the uterus;
Mark the result on the scale of a centimeter tape;
Help the pregnant woman get up from the couch by turning on her side, and then sitting on the couch;
Throw the oilcloth into a basin;
Evaluation of the received data
Second Leopold maneuver: Determining the position, presentation, position, type of fetus using four methods of external obstetric examination of a pregnant woman.
Purpose: to teach a student to conduct an external obstetric examination of a pregnant woman using four obstetric appointments and record the result in an individual card of a pregnant woman.
Equipment:
Couch;
Oilcloth;
Pregnant individual card.
Execution Method:
Explain to the woman the need, purpose and progress of the procedure;
Lay the pregnant woman on the couch in the “on the back” position with straightened legs, spreading an oilcloth under the buttocks;
Sit to the right of the pregnant woman, facing her;
I Reception - the definition of VSDMS by palpation. The palms of both hands are located on the bottom of the uterus and determine the level of standing of the bottom of the uterus in relation to the upper edge of the pubic joint, the navel and the xiphoid process.
II Reception - determination of the position, position and type of fetus.
Hands are transferred to the side walls of the uterus, palpation of parts of the fetus is performed alternately with the right and left hands. With the longitudinal position of the fetus, on the one hand, the back is determined, on the other, small parts.
The position of the fetus is the ratio of the longitudinal axis of the fetus to the longitudinal axis of the uterus.
The position of the fetus is longitudinal, transverse and oblique.
Longitudinal position - the longitudinal axis of the fetus coincides with the longitudinal axis of the uterus.
The transverse position of the fetus - the longitudinal axis of the fetus is at right angles to the longitudinal axis of the uterus.
Oblique position - the longitudinal axis of the fetus is at an acute angle to the longitudinal axis of the uterus.
The position of the fetus is the ratio of the back of the fetus to the side wall of the uterus.
I position - the back is turned to the left,
II position - the back is turned to the right.
View - the ratio of the back of the fetus to the anterior or posterior wall of the uterus. The back is turned more anteriorly - front view, more backwards - rear view.
III Leopold's maneuver
Defines the presenting part of the fetus, which is closest to the entrance to the small pelvis (head, pelvic end)
The nurse stands on the right, facing the patient, takes the thumb of the right hand as far as possible and carefully plunges the fingers deep over the pubic joint and covers the presenting part. If this is the head, then it is dense, round and ballots, and if the pelvic end, then it is soft, not rounded and does not ballot.
IV Leopold reception
determination of the ratio of the presenting part of the fetus to the entrance to the small pelvis (mobile, pressed, in the small pelvis).
Listening and assessing the fetal heartbeat
Purpose: to teach the student to find the best place to listen to the fetal heartbeat using an obstetric stethoscope, to listen, count and evaluate the fetal heartbeat.
The fetal heartbeat with an obstetric stethoscope can be heard after 20 weeks (preferably 24 weeks) of pregnancy.
Equipment:
Couch;
Oilcloth;
obstetric stethoscope;
Stopwatch;
70% ethyl alcohol;
Pregnant individual card.
Execution Method:
Explain to the woman the purpose, necessity and progress of the procedure;
Lay the pregnant woman on the couch in the “on the back” position with straightened legs, spreading an oilcloth under the buttocks;
Sit to the right of the pregnant woman;
Wipe the obstetric stethoscope with a ball of alcohol and take it in your right hand;
Take a stopwatch in your left hand;
using an obstetric stethoscope, moving it across the abdomen, find a place to clearly listen to the fetal heartbeat (with head presentation below the navel, and with gluteal presentation above the navel);
Using a stopwatch, set off the time and count the number of beats per minute (to avoid errors with the pregnant woman's pulse, which should not coincide in rhythm with the fetal heartbeat);
Note the rhythm and clarity of beats;
Help the pregnant woman get up from the couch, turning first on her side, and then sitting on the couch;
Wipe the stethoscope again with a ball of alcohol;
Throw the oilcloth into the basin;
Wash and dry hands;
Record the data obtained in the individual card of the pregnant woman.
With twins, the fetal heartbeat is heard at two points distinctly, independently of each other, while between these points there is a “zone of silence”.
Normal fetal heartbeat is 120-140 beats per minute, rhythmic, clear.
Deviations in the frequency, rhythm and clarity of strokes may indicate threatening intrauterine fetal asphyxia.
Blackboard work. Match
The method of taking a smear for the degree of purity of the vagina and preparation for a doctor's examination
Purpose: to teach a student to properly lay a woman on a gynecological chair and take a swab from the vagina to determine the degree of purity.
Equipment:
Gynecological chair;
The table is sterile with tools (mirrors, tweezers) and soft inventory (balls, napkins);
Lighting lamp-crane;
glass slides;
Volkmann's spoon;
Rubber gloves;
Referral to the laboratory;
disinfectant solution.
Execution Method:
Explain to the woman the need and progress of the procedure;
Inform about the need to empty the bladder;
Lay an oilcloth and lining on the chair;
Help the woman to lie down on the gynecological chair in the “on the back” position, the legs are bent at the hip joints, divorced, the popliteal fossae rest against the supports;
Explain that breathing should be free during the examination;
Prepare the external genitalia for examination by lubricating them on the outside and the inner surface of the thighs with a disinfectant solution using a forceps and a ball;
Wash your hands and put on gloves;
With the first and second fingers of the left hand, separate the large and small labia;
With the right hand, carefully insert the Cusco mirror into the vagina: first in a longitudinal position, then transfer it to a transverse position and open it into the vagina without reaching the cervix;
Fix the mirror in the open state with a screw;
Insert Volkmann's spoon into the vagina (you can use tweezers) and carefully take a smear, touching slightly the upper lateral wall of the vagina;
Apply a smear on a glass slide in a thin layer, without crushing the cells;
If there is abundant discharge in the vagina, then before taking a smear, it is recommended to gently blot the vagina with a cotton swab on tweezers (for better visibility);
Open the screw on the mirror;
Carefully remove the speculum from the vagina, gradually closing it;
Place the mirror in a 3% chloramine solution for one hour;
Remove gloves and wash hands;
Make a referral to the laboratory:
answers to tasks :
1. Patient Zh., 22 years old, first pregnancy. Last period August 22; first fetal movement on January 14th.
Patient A., 28 years old, pregnancy 3, childbirth 2. Last menstruation on December 25; first fetal movement on May 19.
Patient I., 24 years old, second pregnancy, first delivery normal. Last period February 16; first fetal movement June 30
Patient N., 21 years old, pregnancy 1. Last menstruation April 3; first fetal movement on August 27.
Blackboard work.
1 - front view, first position, head presentation;
2 - rear view, first position, head presentation;
3 - front view, second position, head presentation;
4 - rear view, second position, head presentation;
5 - front view, first position, breech presentation;
6 - rear view, first position, breech presentation,
7 - front view, second position, breech presentation;
8 - rear view, second position, breech presentation.
test survey: (answers)
1.2 ; 2.3; 3.2; 4.2; 5.1; 6.3; 7.2; 8.2; 9.3; 10.2; 11.4; 12.1.
Fizminutka
| DIRECTION ANALYSIS OF THE SMEAR FOR THE DEGREE OF PURITY OF THE VAGINA FULL NAME……………………………………………………………….. G.R……………………………………………………………….. |
 What should be the diet during pregnancy?
What should be the diet during pregnancy? Medical Robotics
Medical Robotics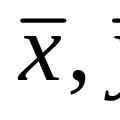 Analysis and interpretation of the results of the study Checking the significance of the correlation
Analysis and interpretation of the results of the study Checking the significance of the correlation